Archaeologists have uncovered a rich trove of 209 Roman-era coins in northwestern Spain, due to the apparent efforts of a hungry badger seeking food.
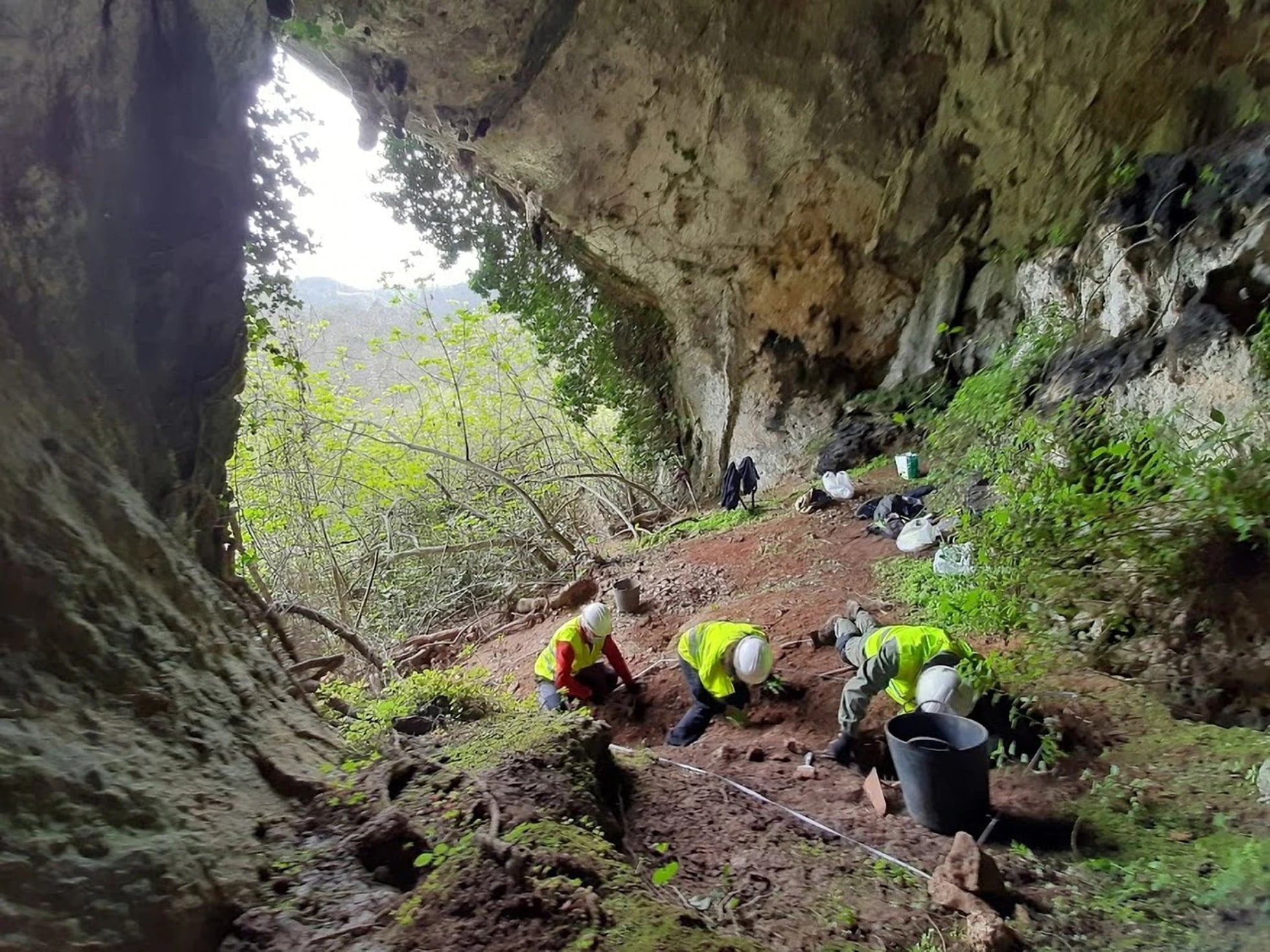
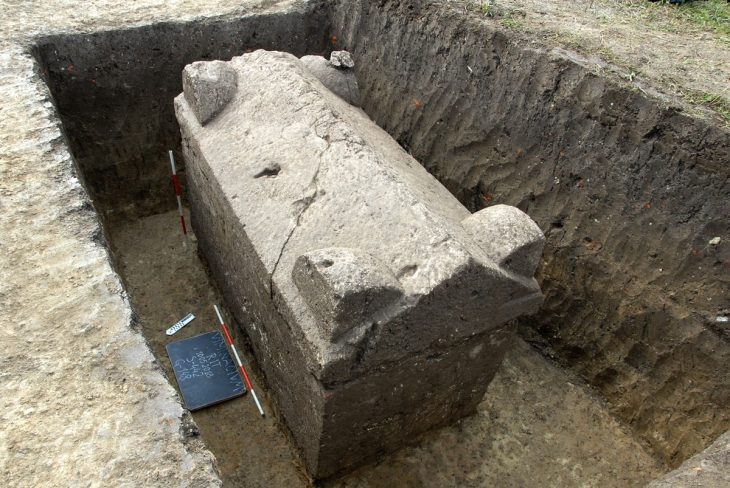
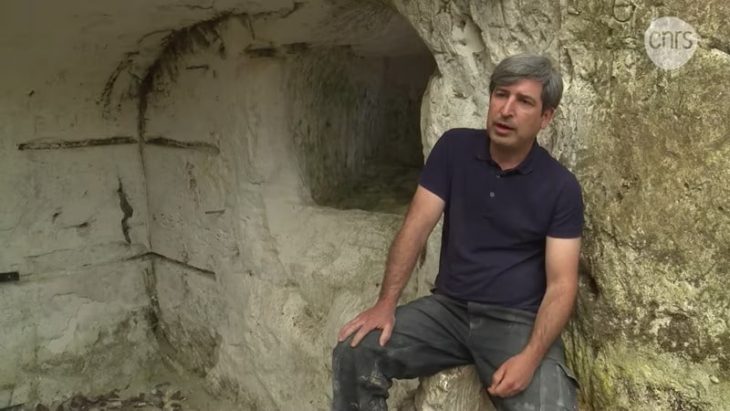
The coins were discovered in April 2021 in La Cuesta cave near Berció, Asturias, and were described as “an exceptional find” in the Journal of Prehistory and Archaeology published last month by Madrid’s Autonomous University.
The coins were most likely dug up by a badger looking for food during an unusual snowfall that immobilized Spain in January 2021, dubbed “the most violent storm in the past 50 years” by officials.
After fully excavating the cave, researchers collected 209 coins dating to between the third and fifth centuries A.D., according to Spanish news site El Pais. The find is the largest collection of such coins ever discovered in northern Spain.
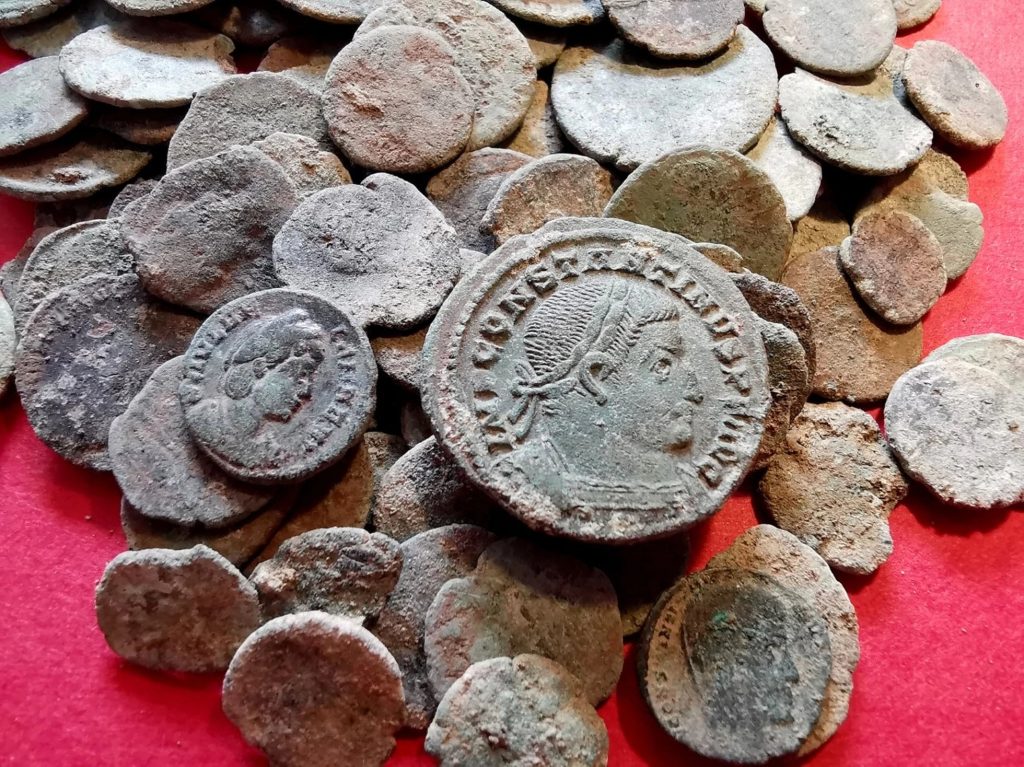

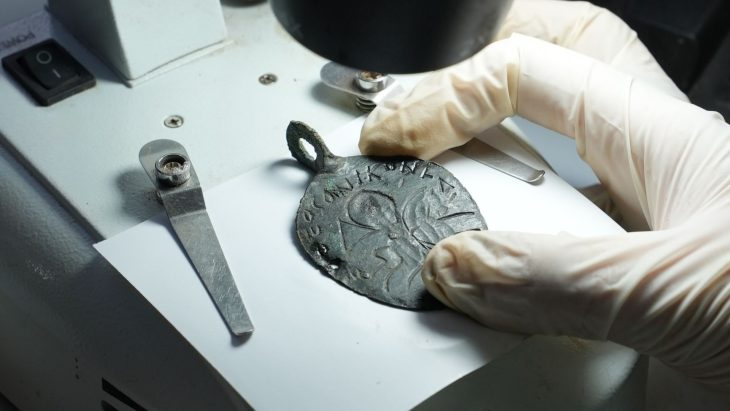
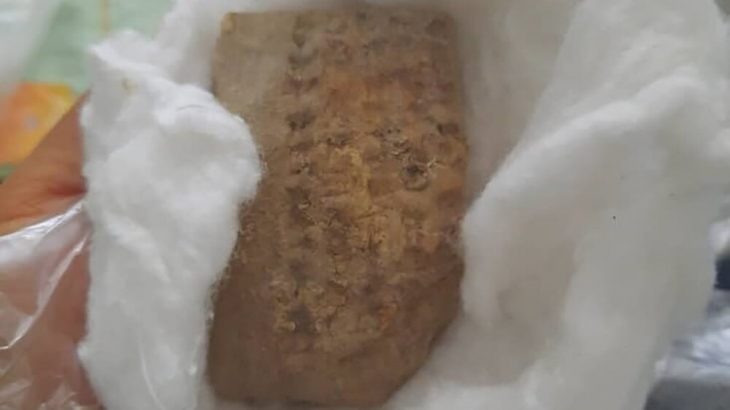
The coins themselves are “mainly from the north and the eastern Mediterranean, forming a line from Antioch, Constantinople [modern day Istanbul, Turkey], Thessaloniki”. However, one coin appears to have originated in London. The authors believe these 209 coins to be part of a larger set, which has now disappeared.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researchers told El Pais the one minted in London was one of the most well-preserved coins and is “bronze, weighing between eight and 10 grams, with an approximate 4% silver.”
“The quantity of coins recovered, as well as the undoubted archaeological interest of the transition to the early medieval period, make the hoard discovered at Berció an exceptional find,” they wrote.
The researchers said the coins had likely been moved there in the “context of political instability” linked in particular to the invasion of the Suebians, a Germanic people, who pushed into the northwestern part of the Iberian peninsula in the 5th century.
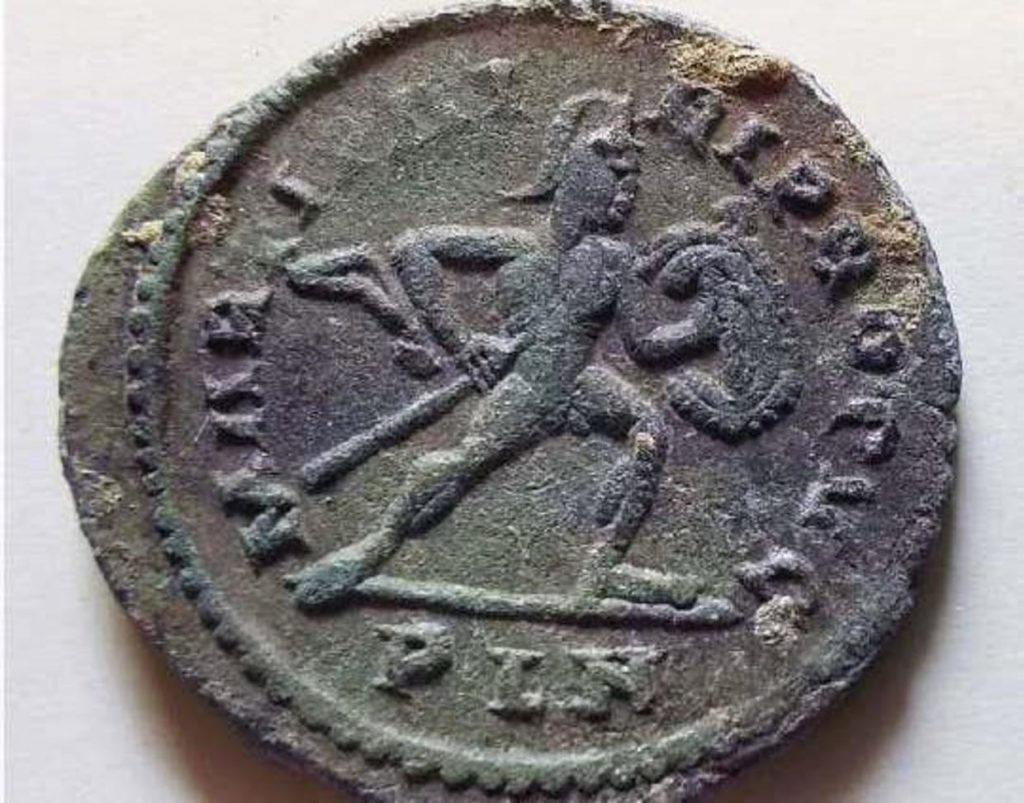

The coins themselves are “mainly from the north and the eastern Mediterranean, forming a line from Antioch, Constantinople [modern day Istanbul, Turkey], Thessaloniki”. However, one coin appears to have originated in London. The authors believe these 209 coins to be part of a larger set, which has now disappeared.
As to how they came to be in a cave in northern Spain, the authors speculate they were moved – perhaps even hidden – there, “in times of instability for fear of theft or attacks”. They also suggest that such caves could have served as a sort of ancient bank account, into which people could deposit money and make withdrawals.
In the 5th century, the western part of the Asturias was invaded by the Suebians – Germanic people originating from what is now Germany and the Czech Republic – which could perhaps explain the “political instability” that would lead someone to hide their fortune in a cave.