A new study resolves the complex relations between geography, ancestry, and gene flow in Scandinavia – encompassing the Roman Age, the Viking Age, and later periods.
Researchers investigated a 2,000-year genetic transect through Scandinavia spanning the Iron Age to the present, based on 48 new and 249 published ancient genomes and genotypes from 16,638 modern individuals.
A surprising increase of variation during the Viking period indicates that gene flow into Scandinavia was especially intense during this period.
An international study coordinated from Stockholm and Reykjavik investigates the development of the Scandinavian gene pool over the latest 2000 years. In this effort the scientists relied on historic and prehistoric genomes, and from material excavated in Scandinavia. These ancient genomes were compared with genomic data from 16,638 contemporary Scandinavians. As the geographical origin and the datings were known for all these individuals, it was possible to resolve the development of the gene pool to a level never realised previously.

Dr Ricardo Rodríguez Varela at the Centre for Palaeogenetics*, who analyzed all the data and extracted some of the ancient DNA used in the study, explains: “With this level of resolution we not only confirm the Viking Age migration. We are also able to trace it to the east Baltic region, the British-Irish Isles and southern Europe. But not all parts of Scandinavia received the same amounts of gene flow from these areas. For example, while British-Irish ancestry became widespread in Scandinavia the eastern-Baltic ancestry mainly reached Gotland and central Sweden.”
The gene pool bounced back after the Viking period
Another new discovery in this study was what happened to the gene pool after the Viking period. The scientists were surprised to find that it bounced back in the direction of what it looked like before the Viking period migration.
Professor Anders Götherström at the Centre for Palaeogenetics, who is a senior scientist on the study, is intrigued: “Interestingly, the non-local ancestry peaks during the Viking period while being lower before and after. The drop in current levels of external ancestry suggests that the Viking-period migrants got less children, or somehow contributed proportionally less to the gene pool than the people who were already in Scandinavia.”
Yet a new discovery was the history of the northern Scandinavian gene pool. There is a genetic component in northern Scandinavia that is rare in central and western Europe, and the scientists were able to track this component in northern Scandinavia through the latest 1000 years.

Dr Ricardo Rodríguez Varela comments, “We suspected that there was a chronology to the northern Scandinavian gene pool, and it did indeed prove that a more recent influx of Uralic ancestry into Scandinavia define much of the northern gene pool. But if it is recent, it is comparatively so. For example, we know that this Uralic ancestry was present in northern Scandinavia as early as during the late Viking period”.
Based on well-known Swedish archaeological sites
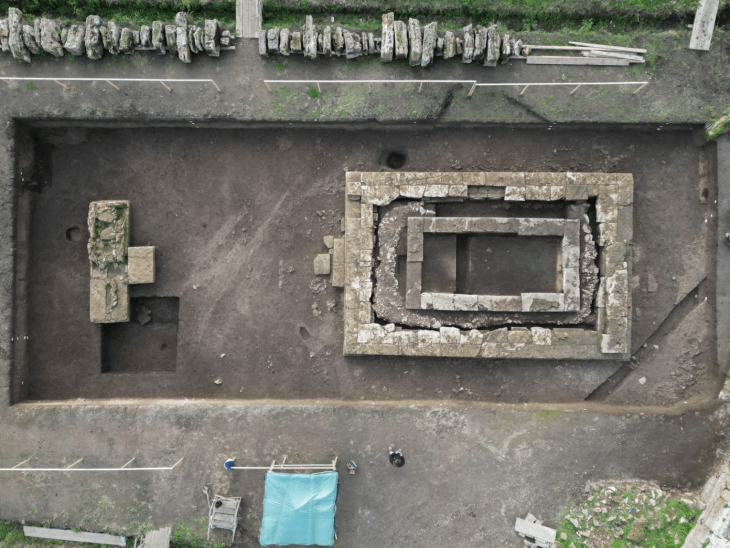
The study is based on a number of well-known Swedish archaeological sites. For example, there are genomes from the 17th century warship Kronan, from the Viking and Vendel period boat burials in the lake Mälaren Valley, and from the migration period ring fortress Sandby borg on Öland.
Anders Götherström conclude: “We were working on a number of smaller studies on different archaeological sites. And at some point it just made sense to combine them into a larger study on the development of the Scandinavian gene pool.
The study, published today in Cell, is an international effort with several collaborators, but it was led by Dr Ricardo Rodríguez Varela and Professor Anders Götherstörm at Stockholm University, and Professor Agnar Helgason, and Kristjáan Moore at deCODE in Reykavijk.
The article “The genetic history of Scandinavia from the Roman Iron Age to the present” is published in Cell.
Cover Photo: Sandby borg archaeological excavations. DANIEL LINDSKOG