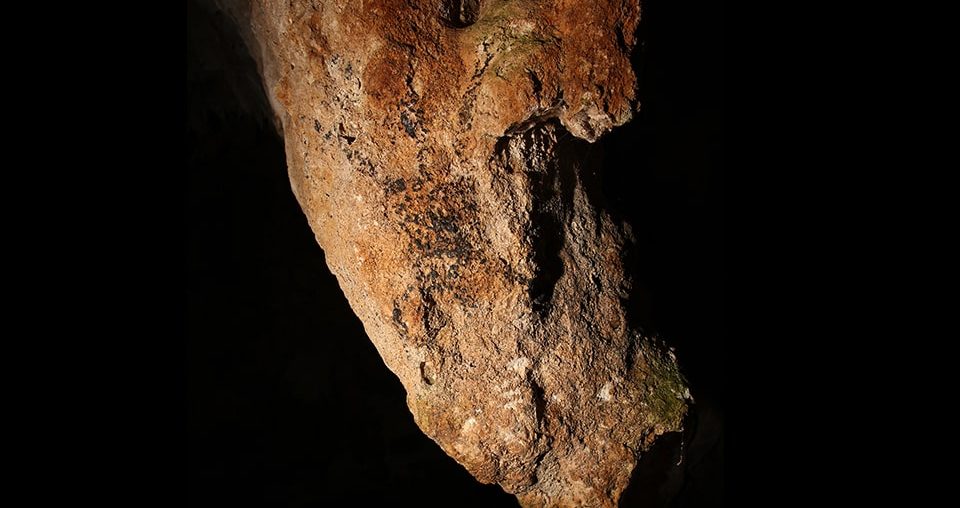
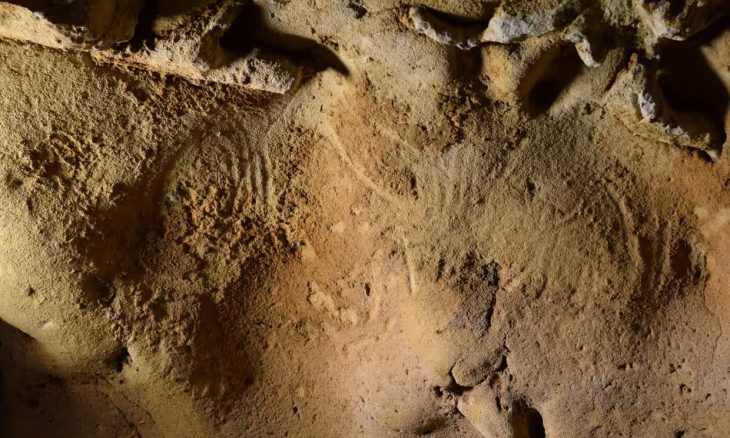
A depiction depicting a human-like figure on a cave wall in Penablanca town, Cagayan province, is Southeast Asia’s first directly dated rock art.
It was learned that the pigment samples taken from the cave drawing were approximately 3,500 years old using the radiocarbon dating method.
The results of the research were published in the Radiocarbon journal under the title “First Directly Dated Rock Art in Southeast Asia and The Archaeological Implications”.
Dr. Andrea Jalandoni, lead author of the paper entitled “First Directly Dated Rock Art in Southeast Asia and The Archaeological Implications,” said samples of pigment from the cave drawing have been dated to be around 3,500 years old using the radiocarbon dating method.
“This date is older than anyone expected, and it marks the beginning of the direct rock art dating revolution in Southeast Asia. Hopefully, this will lead to better appreciation and more protection for this significant cultural heritage in the Philippines,” Dr. Jalandoni said at Monday’s virtual media conference.
She said that direct dating rock art entails dating the paint material from the artwork itself rather than dating the materials around or on top of the artwork.

Jalandoni, an Associate at the National Museum of the Philippines Research and Research Fellow at Griffith University in Australia, also stated that the directly dated rock art whose dated samples were taken from a black pigment human figure was discovered in Hermoso Tuliao cave in Peablanca, a region where the Philippines’ oldest human remains were discovered.
“The black pigment human figure forms part of a gallery of paintings with two other human figures, and a few leaf and circle motifs. Similar motifs have been found in other places in Southeast Asia,” she added.
Noel Hidalgo Tan, Senior Specialist in Archaeology at the Southeast Asian Regional Centre for Archaeology and Fine Arts in Bangkok, stated that they previously considered black rock art was more contemporary because black art was placed atop red art or because the things depicted were relatively modern.
“This new finding forces us to be more cautious about attributing black rock art as ‘recent’ and also encourages us to embark on direct dating for more rock art sites in the region,” Tan said.
During the virtual media conference, it was also revealed that the data acquired by Jalandoni’s study team indicates that the rock art is either early Austronesian or Agta, the local Negritos.
Jalandoni further mentioned that Negritos are thought to have come earlier, before the end of the Pleistocene, a geological period that lasted up to 10,000 years ago, via land bridges in the south or brief inter-island sea crossings.
“There is a need for more research to be done to determine which among these two groups specifically made the drawings,” she said.
The age supports prior research findings on other early human occupation activities in Peablanca, such as archaeological evidence of foraging in Eme and Arku Caves and pottery in Callao Cave, all inside the same limestone formation, according to the research team.
The study stated that Peablanca has been a hotbed for notable archaeological findings since the early 2000s, with fossils of the newly identified early human species Homo luzonensis unearthed in Callao Cave 67,000 years ago.
“The rock art in some of the caves in Peñablanca provides us with a glimpse into the lives of the people who occupied the area long before the beginning of the Spanish colonization of the Philippines 500 years ago. From archaeological evidence and research, we now know these people obtained food by foraging, were using pottery and were creating rock art on cave walls,” the research team added.
Cover Photo: Anthropomorph from Hermoso Tuliao cave in the Philippines. Photo by Mark D. Willis.