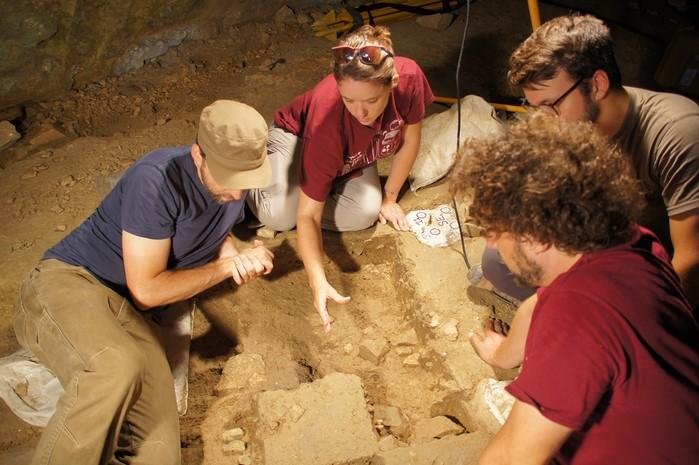
Archaeologists from Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have discovered a fascinating panel containing an extensive Maya hieroglyphic text, engraved into the rock of a lagoon near the majestic pyramid structure Nohoch Mul, located in the emblematic Archaeological Zone of Cobá in Quintana Roo.
The discovery sheds light on the intricate and rich past of an area continuously inhabited for more than 1,300 years, from 100 B.C. to 1200 A.D.
Coba is a large and important Mayan archaeological zone located in the eastern portion of the Yucatan Peninsula. It is one of the few sites to retain its original Maya name, Ko’ba a, which translates to ruffled/uneven water. Its early settlement dates to the Preclassic (350 BCE – 250 CE), and it reached its height in economic and political power as a regional capital in the Late/Post Classic (600-1000 CE).
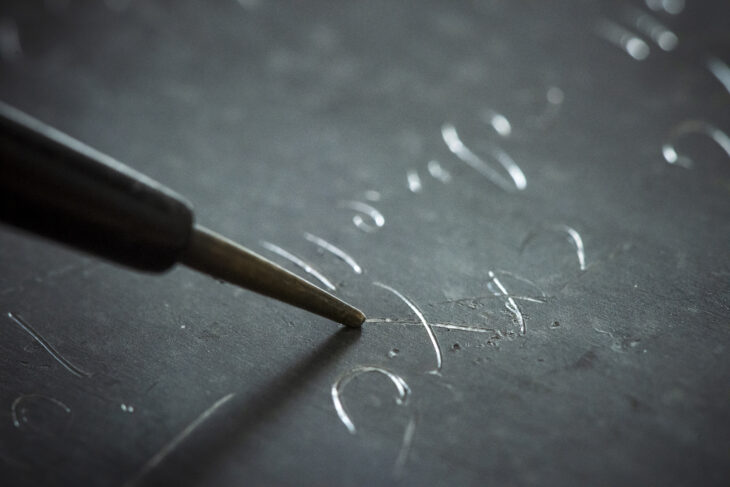
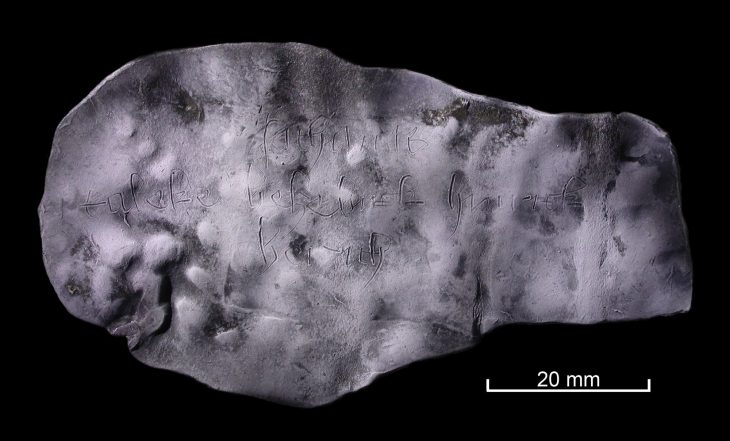
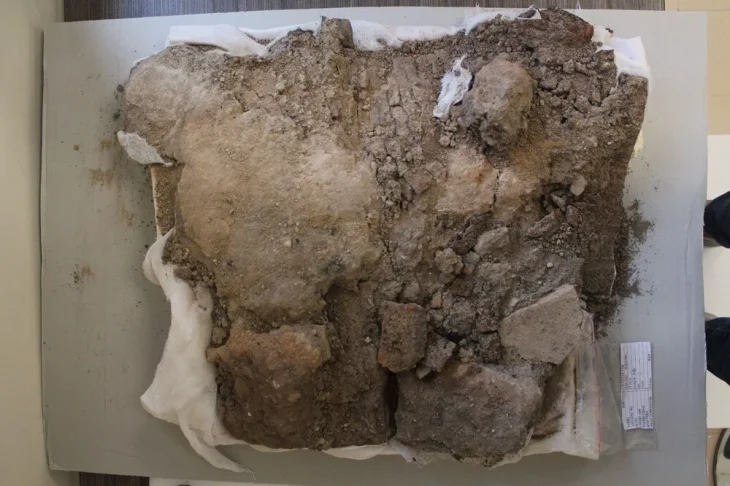
Thorough archaeological work has led to the discovery of a panel made up of 123 hieroglyphic cartouches that form an extensive L-shaped inscription. The panel is carved directly into the rock, just 160 meters from the majestic Nohoch Mul, and covers an impressive surface area of over 11 square meters. This inscription’s size and intricacy highlight Cobá’s significance as a Maya cultural and political hub in antiquity.
Important details have been uncovered thanks to a preliminary epigraphic analysis, such as the establishment date of Keh Witz Nal, also known as “Mountain of the Deer,” which was established on May 12, 569 A.D.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Furthermore, the inscription supplied crucial information to complete the Cobá dynastic sequence by identifying K’awiil Ch’ak Chéen, a sovereign who was previously unknown. This information fills an important gap in our knowledge about the rulers of the ancient city-state.
Until today 14 rulers of Cobá have been identified, including three women, one of whom ruled for four decades, suggesting a dynamic power structure and possibly more egalitarian than previously thought.
The hieroglyphic text also reveals that many of Cobá’s rulers adopted the name of the god K’awil, a practice believed to confer divine attributes as protectors of the place.
The inscription impressively links historical events with a mythical past. The text refers to a group of tutelary gods who founded Cobá, including Bolón Tz’akab Ajaw, known as the Lord of countless generations, who was believed responsible for establishing the maize and cacao dynasties.
The researchers took additional measures to preserve the glyphic text while using state-of-the-art technology to create three-dimensional models and a high-precision recording of the glyphic text. These models will facilitate the full deciphering of the text, thereby promoting a more thorough understanding of its meaning and content and enabling deeper epigraphic studies.
As part of the advancements of the ambitious Archaeological Zones Improvement Program (Promeza) in sites adjacent to Segment 5 of the Maya Train, Diego Prieto Hernández, General Director of INAH, presented this discovery during President Andrés Manuel López Obrador’s morning conference.
Cover Image: INAH