Experts analyzing the symbols on a 2,500-year-old tablet recently discovered in Spain have uncovered a mysterious ancient alphabet.
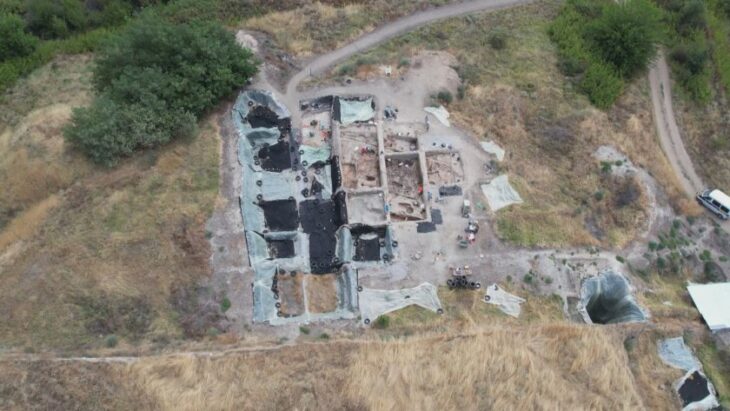
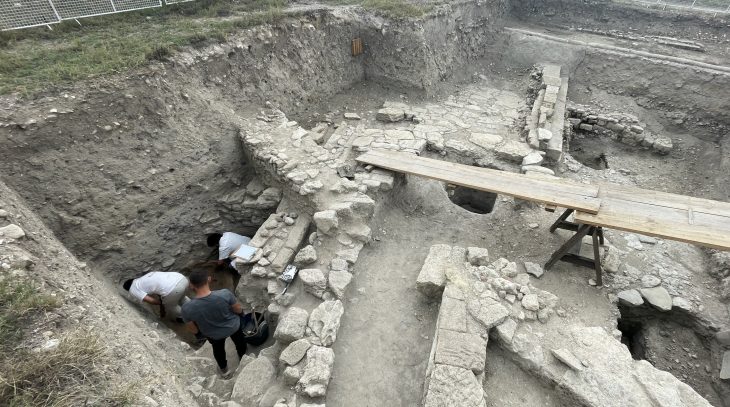
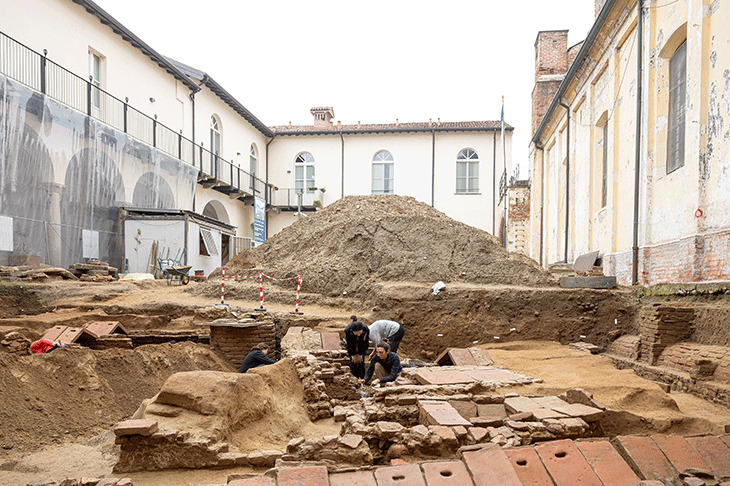
According to a translated statement, the slate tablet was found during excavations at Casas del Turuñuelo, an ancient Tartessian site in southwestern Spain. If their interpretation of the tablet is correct, the slab is the third-ever “southern Paleo-Hispanic alphabet of which there is evidence,” according to the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC).
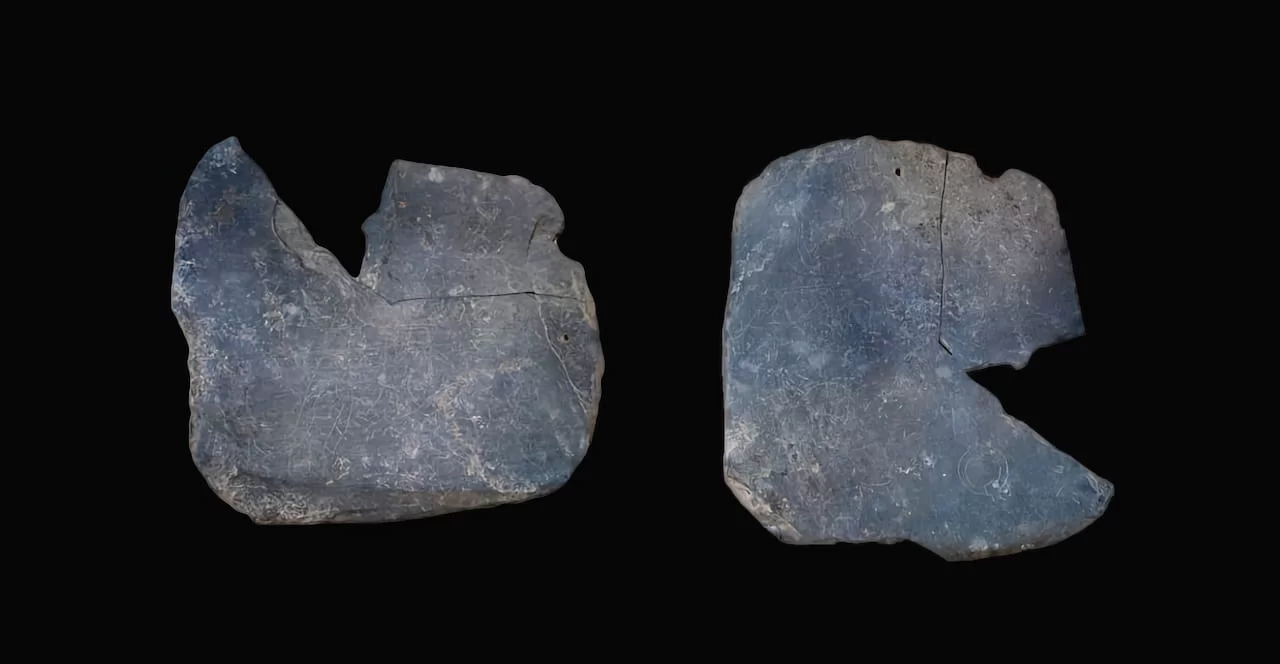
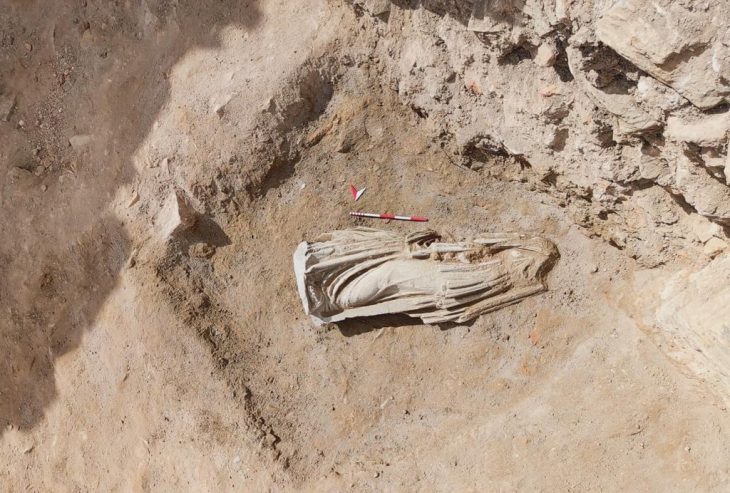
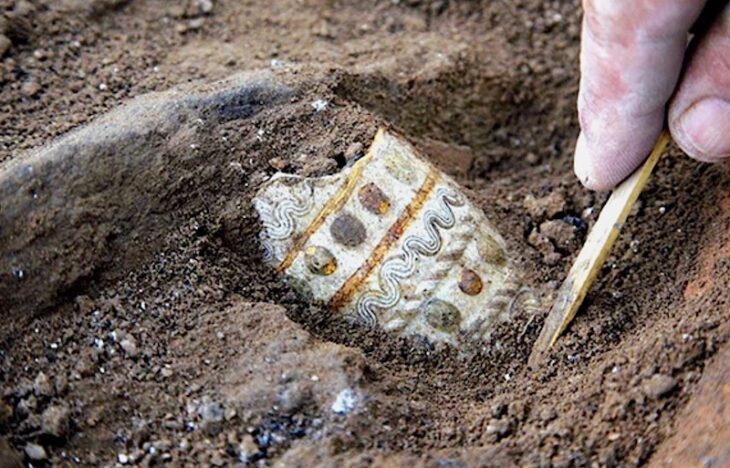
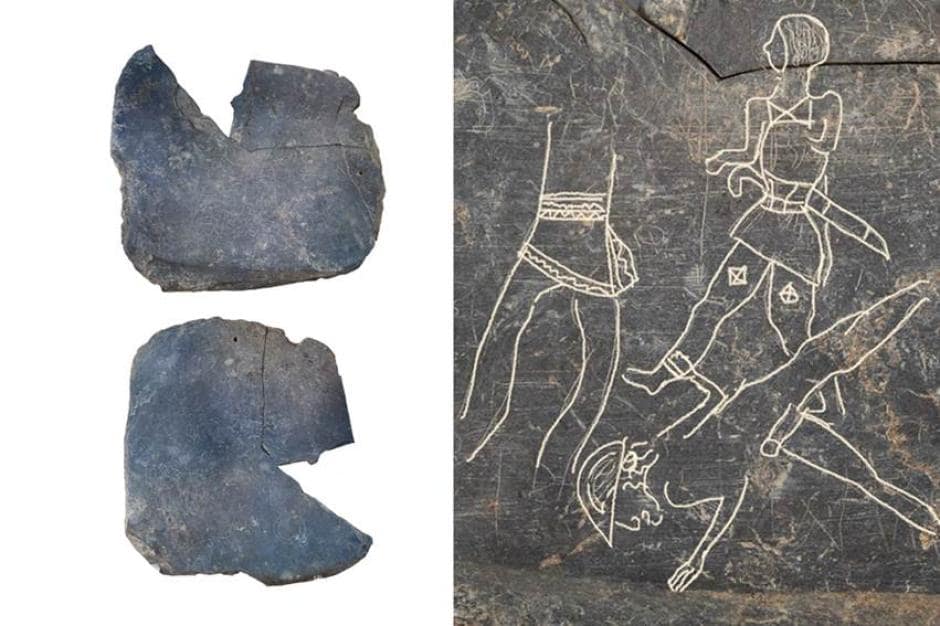
Archaeologists first recognized the adorned tablet as a tool used by artists for practice drawings. The tablet was carved on both sides with geometric shapes, recurring faces, and three warriors engaged in combat. The slate is around 8 inches long and dates back as early as 600 B.C.
Joan Ferrer i Jané, a researcher associated with the LITTERA group at the University of Barcelona, learned about the discovery of a slate plaque with the silhouettes of three warriors at the Badajoz site through the media.
Beyond the figures, when I observed the plaque, I saw that on one side there seemed to be a Paleo-Hispanic sign, a sign that cannot be mistaken for any other. Other traces compatible with known sequence signs were also noticeable, he explains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
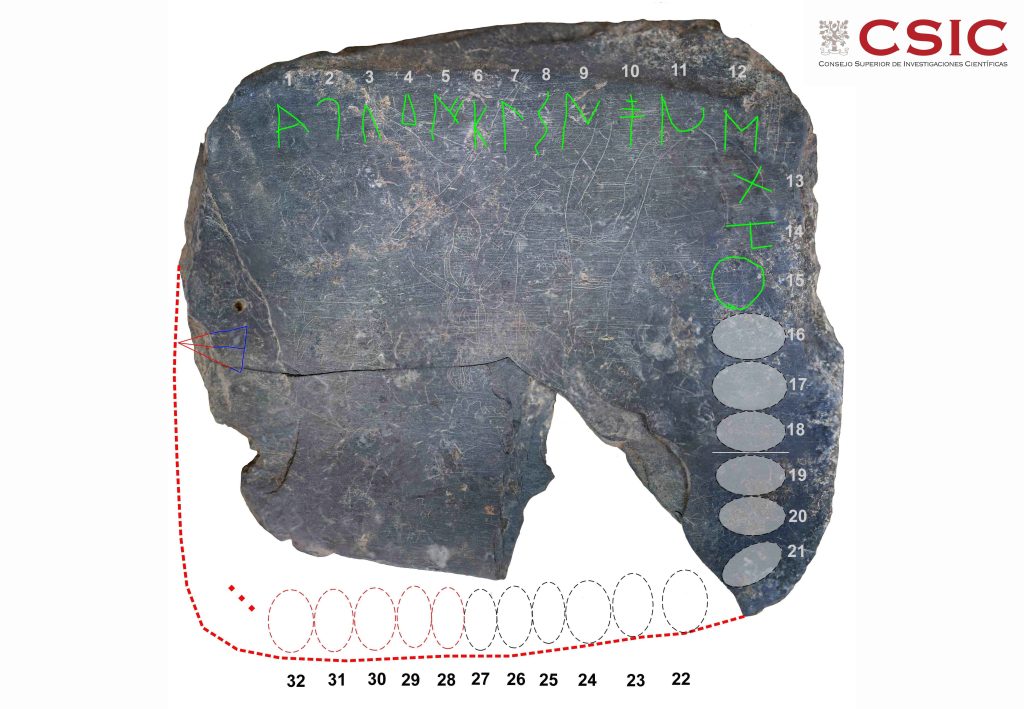
Ferrer contacted the team at the Institute of Archaeology of Mérida, responsible for these archaeological excavations, and requested partial macro photographs of the area to confirm his suspicions. After studying the images, everything points to an alphabet of southern script with the initial sequence ABeKaTuIKeLBaNS?ŚTaUE, which is almost the same as documented in the Espanca alphabet, except for the eleventh sign, which has a special form, indicates Ferrer i Jané.

“This alphabet has 27 signs and is the only complete one we know to date,” he added. “Another was found in the excavation of Villasviejas del Tamuja (Cáceres) but it is very fragmented, it only has some central signs… [this one] would be the third and would provide a lot of information.”
According to CSIC, there are 21 signs, or letters, drawn on the tablet. It is considered incomplete, and experts believe it once held as many as 32 symbols.
“At least 6 signs would have been lost in the split area of the piece, but if it were completely symmetrical and the signs completely occupied three of the four sides of the plate it could reach 32 signs, so the lost signs could become eleven or perhaps more if a possible sign, ‘Tu’, isolated in the lateral quarter, were part of the alphabet,” Ferrer explained.
Esther Rodríguez González, a CSIC researcher and one of the leaders of the archaeological excavations at Casas del Turuñuelo, highlights that from the moment the slate tablet was found, she was aware that the volume of information it contained was even greater than that of the warriors’ faces.
Experts are not sure if this is another copy of a known alphabet or a completely independent script.
The northeastern family and the southern family are the two groups of Paleo-Hispanic scripts. The boundary between them is roughly south of Valencia. All of them originate from Phoenician writing, which was first adapted into an original Paleo-Hispanic signary. This was followed by two distinct adaptations, one in the north and one in the south. The latter gave rise to the alphabet and the family of Southern scripts.
There are only two other southern script alphabets known to exist as of yet. Based on preliminary investigations, the alphabet of Turuñuelo appears to repeat the first ten signs of the Espanca site alphabet in Castro Verde (Portugal). There are 27 signs in this alphabet, which up until now was the only one we were aware of. In the Villasviejas del Tamuja (Cáceres) excavation, another was discovered, although it is extremely fragmented and only has a few central signs. Researchers point out that the Guareña one would be the third and provide a lot of information.
Cover Photo: Carved slate plate from the 6th-5th century BC found in the Tartessian site Casas del Turuñuelo. E. Rodríguez / M. Luque / CSIC
















