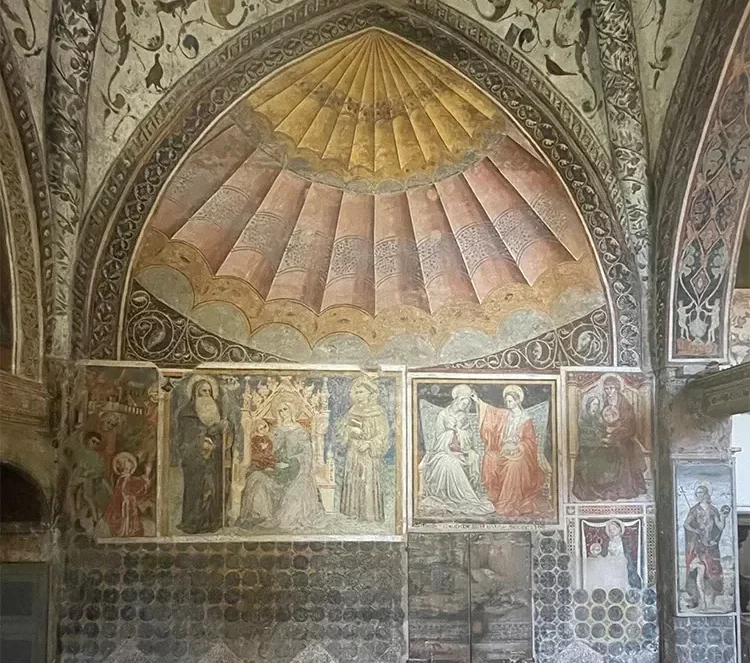
A recently rediscovered 13th-century fresco in Ferrara, Italy, offers significant insights into the medieval practice of utilizing Islamic tents to conceal high altars in Christian churches. This fresco, believed to be the only surviving representation of its kind, provides valuable evidence of a lesser-known Christian tradition.
The fresco, which is only partially visible, was identified by Dr. Federica Gigante, a historian from Cambridge University. It is thought to depict a real tent, now lost, that the artist may have encountered within the same church. The original tent, characterized by its vibrant colors and adorned with jewels, could have been a diplomatic gift from a Muslim leader or a trophy acquired from a battlefield.
Dr. Gigante’s research, published in The Burlington Magazine, posits that a prominent figure, such as Pope Innocent IV—who donated several valuable textiles to the Benedictine convent church of S. Antonio in Polesine, Ferrara—may have been responsible for providing such a tent. “Initially, it seemed implausible and overly exciting to consider that this could be an Islamic tent,” Dr. Gigante remarked. “I dismissed the idea at first but returned to it years later with more experience and a bolder research approach. It is unlikely that we will find another image like this; my belief is that it is quite unique.”
The fresco serves as crucial evidence of the integration of Islamic elements into key Christian practices, including the celebration of Mass. Dr. Gigante noted, “Islamic textiles were associated with the Holy Land, from which pilgrims and crusaders brought back the most precious examples. The existence of artistic continuity from the time of Christ justified their use in a Christian context. Medieval Christians admired Islamic art, often without fully recognizing its origins.”
While it is well-documented that Islamic textiles were present in late medieval European churches, surviving fragments are typically found wrapped around relics or within the burials of notable individuals. Some traces of Islamic textiles can be seen on church walls in Italy and in late medieval Italian paintings. However, depictions of Islamic tents from the Western Islamic world, such as those from Spain, are exceedingly rare, making this fresco potentially the only detailed, full-size representation identified to date.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
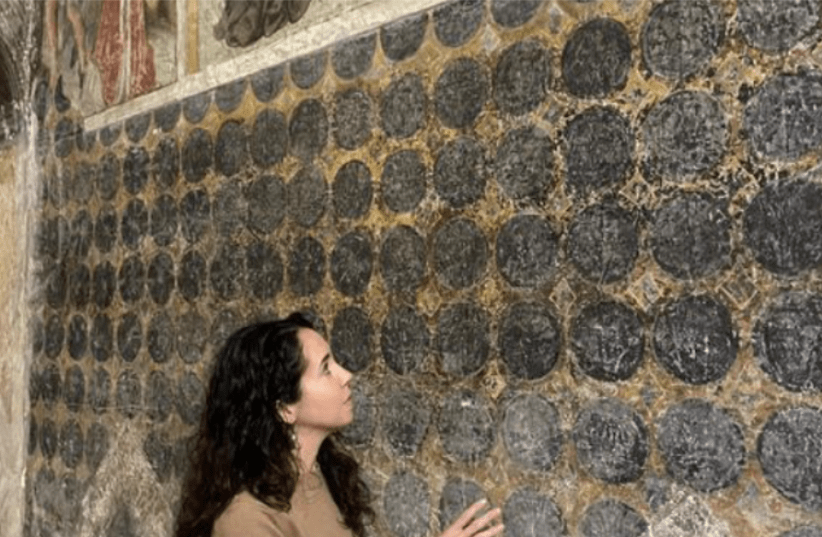

Painted between the late 13th and early 14th centuries, the fresco illustrates a canopy over the high altar, transforming the apse into a tent with blue and gold drapery enveloping three walls, topped by a double-tiered, bejeweled conical canopy typical of Islamic design. “The artist invested considerable effort into rendering the textile lifelike,” Dr. Gigante stated.
The background features a blue sky dotted with stars and birds, creating the illusion of an outdoor tent. In the early 15th century, portions of the fresco were painted over with scenes depicting the lives of the Virgin Mary and Jesus Christ, which has drawn the attention of art historians who have overlooked the earlier sections. Dr. Gigante first identified the depiction of Islamic textiles during a visit to the church a decade ago, but it required extensive research to confirm that the fresco represents an Islamic tent.
Dr. Gigante argues that the fresco depicts a real tent that may have been physically present in the convent church during the 13th century, serving as a direct reference for the artist. It is already established that medieval churches employed precious textile hangings to obscure the altar, either permanently or during specific liturgical periods. Upon examining the fresco, Dr. Gigante observed that it illustrates the corner of a veil, painted as if drawn in front of the altar. She posits that the actual tent may have been adapted to function as a ‘tetravela’ or altar-curtains.
“If the real tent was only erected in the church on certain occasions, the fresco could have served as a visual reminder of its splendor when it was not present,” Dr. Gigante explained. “The interplay between painted and actual textiles is evident throughout Europe and the Islamic world during the late medieval period.”
Dr. Gigante’s study highlights the walls of the apse, which are adorned with nails and brackets that could have supported a hanging textile. She points to the fresco’s “extraordinarily precise details” as further evidence of its depiction of a real tent. The fabric illustrated features blue eight-pointed star motifs within roundels, originally highlighted in gold leaf, mirroring the golden fabrics used in precious Islamic tents. Additionally, a band with pseudo-Arabic inscriptions runs along the top and bottom borders, while white contours emphasize contrasting colors, reflecting a trend in 13th-century Andalusi silk design.
The structure, design, and color scheme of the tent closely resemble the few surviving depictions of Andalusi tents, including those found in the 13th-century manuscript, the Cantigas de Santa Maria, as well as one of the rare surviving Andalusi tent fragments, the ‘Fermo chasuble,’ attributed to St. Thomas Becket, Archbishop of Canterbury.
Cover Image Credit: Federica Gigante