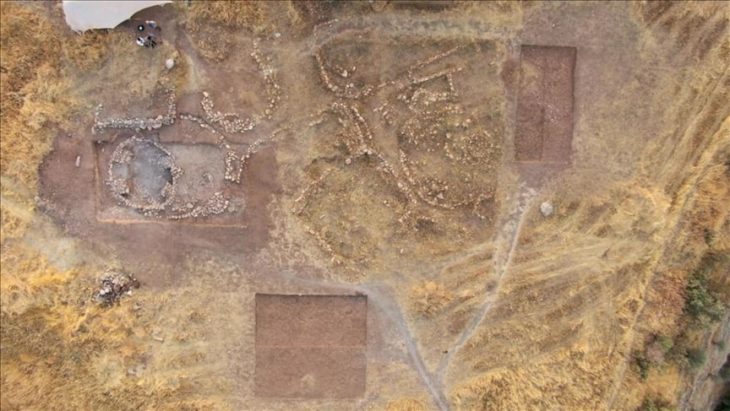
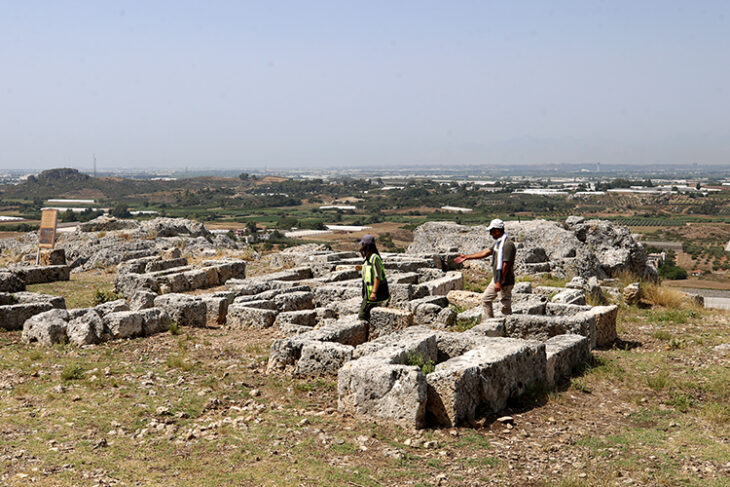
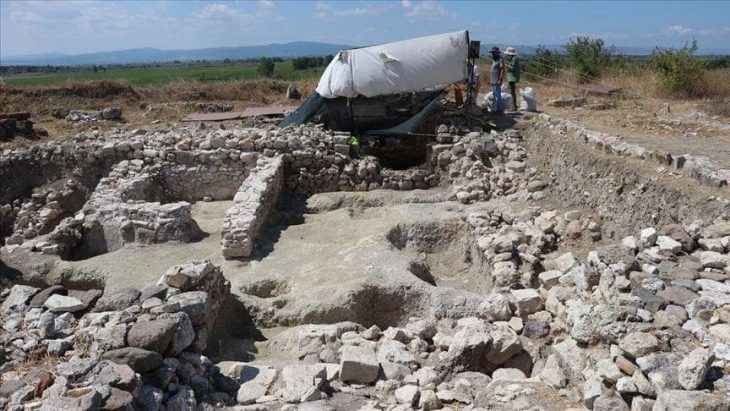
During the restoration of the ancient Sheikh Suleiman Mosque, which was restored as part of the Med-Art Education Project by the Turkish General Directorate of Foundations and the Italian Association for Architecture, Art and City Restoration, a pagan cemetery that preserved its originality was unearthed.
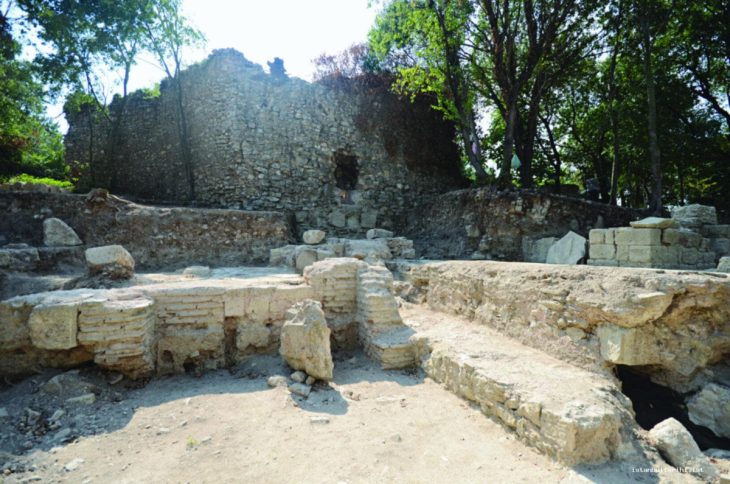
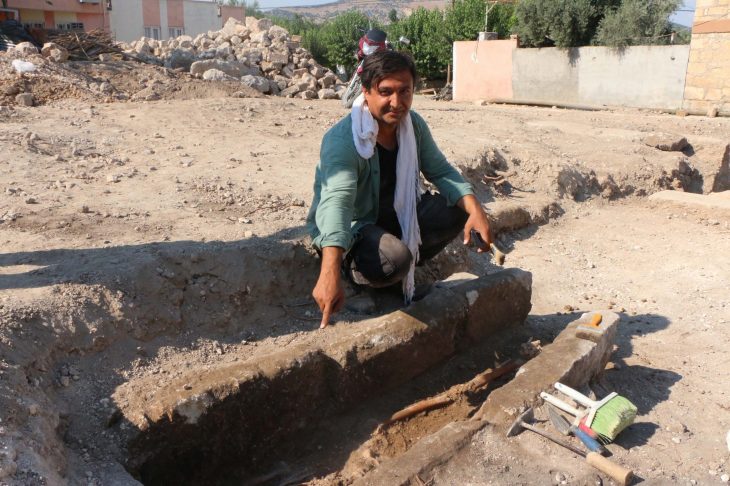
The “pagan cemetery”, which is estimated to be 1700 years old, was found in 2018 in the basement of the historical Sheikh Suleiman Mosque in the Zeyrek District of the Fatih district of Istanbul.
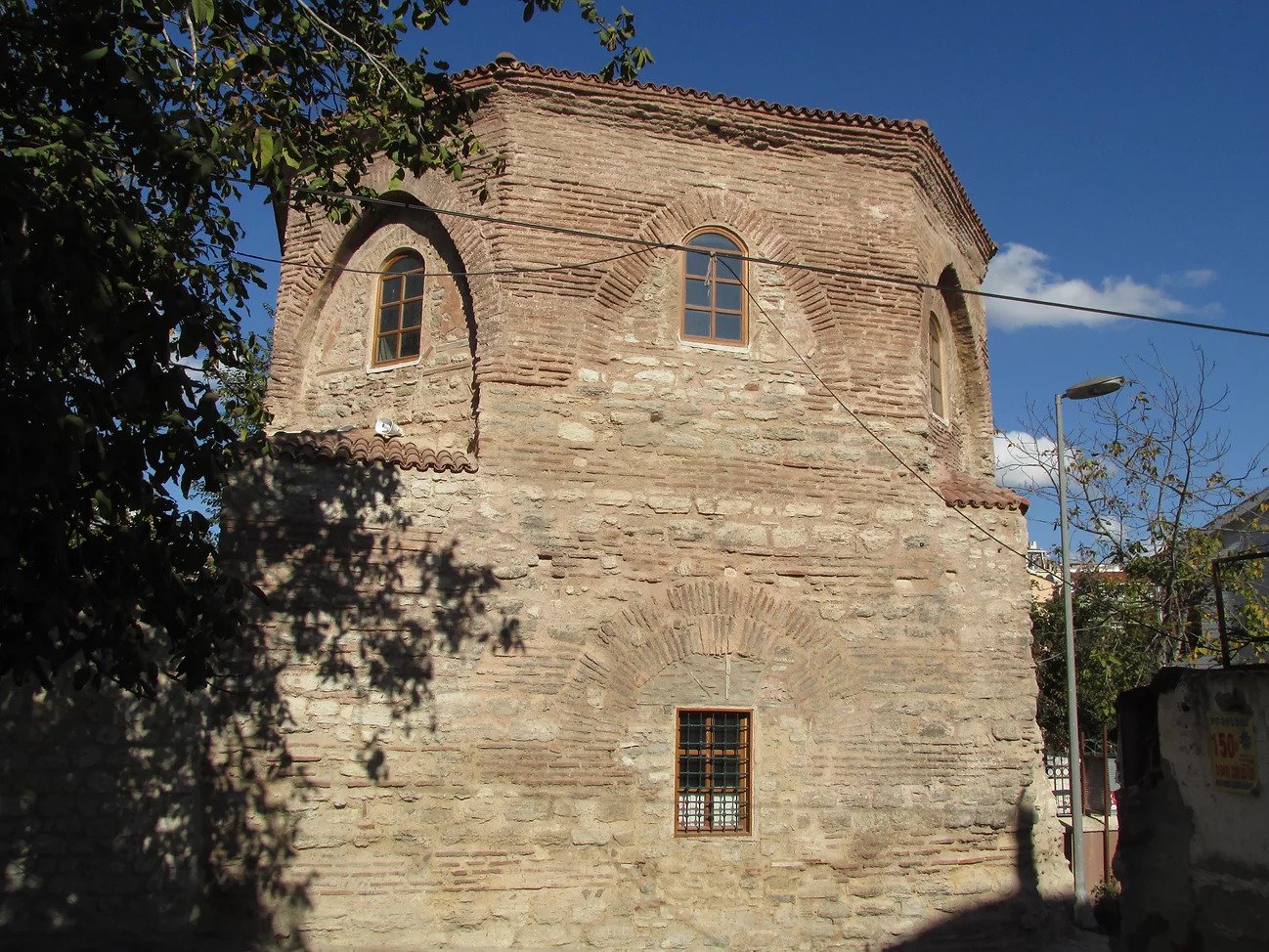
The Sheikh Suleiman Mosque (Turkish Şeyh Süleyman Mescidi) originally was a Byzantine structure near the Pantocrator Monastery in Constantinople (Istanbul). Neither its identity nor its function was known until now.
The restoration was part of a project that included archaeological excavations, seismological tests, and scans near the site of the mosque, and research has shown that the masjid was originally built as a burial structure.
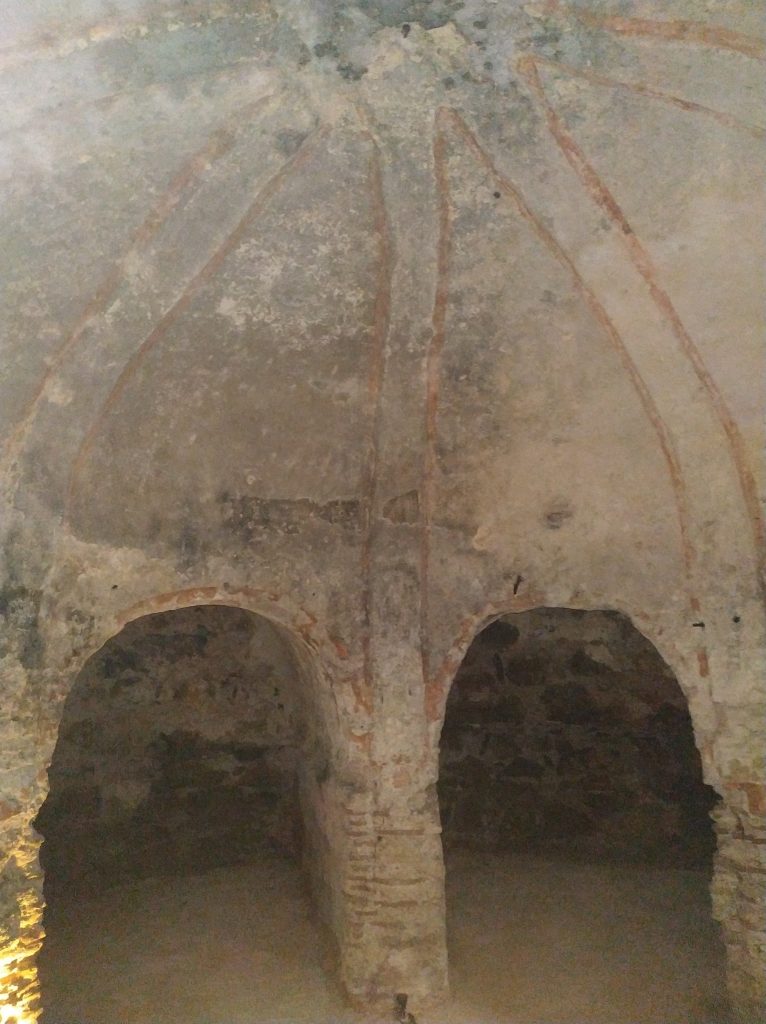

The grave was found on the ground floor of the mosque and belongs to the late Roman Empire period. Paganism continued and it was seemingly ended until Christianity became widespread in Istanbul, that is, until the 7th century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Although the building is thought to be a Palaiologan structure, it is still controversial. Most of the Palaiologan buildings of Constantinople are dated to the era of Andronikos (12th century), but relative and absolute chronologies, especially for some neglected cases, are not always clear.
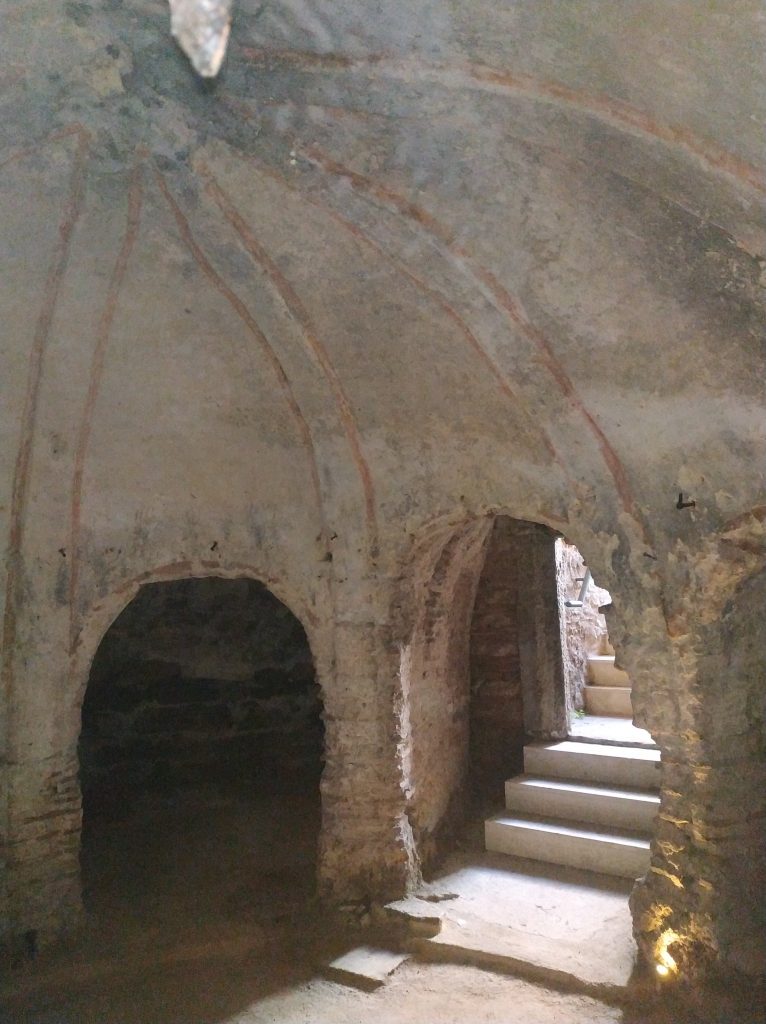

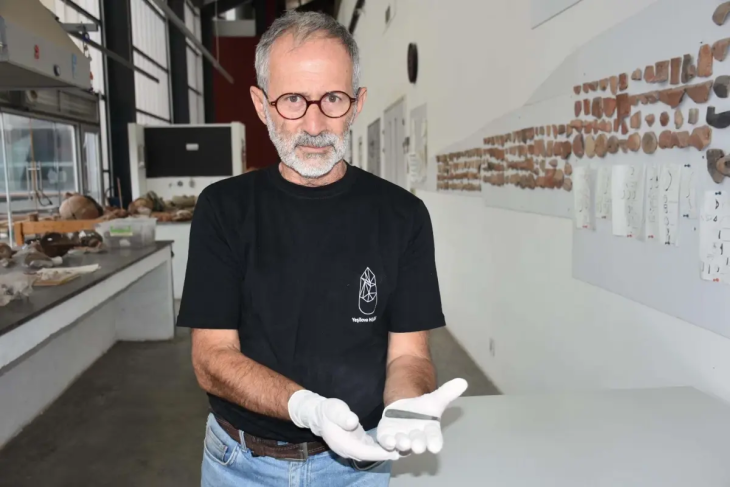
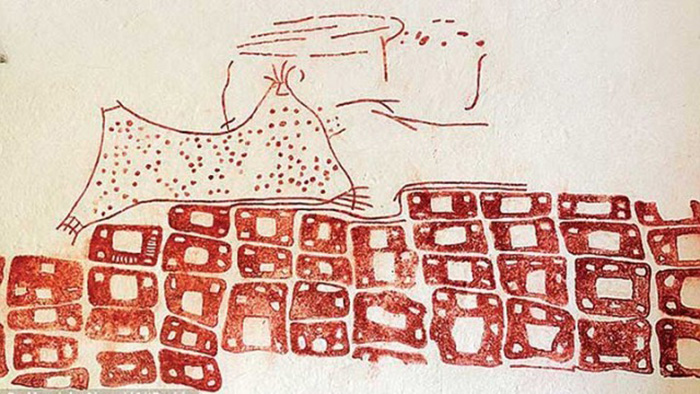
Archaeologist Murat Sav told: “In the basement of the structure on which a mosque has been built, there are two more floors [underneath] from the Roman period. The first floor underneath is an eight-section burial chamber. It is called an arcosolium,”.
The term arcosolium applies to one form of tombs that exist in ancient Roman catacombs. “Arcosoliums are an important burial structure from the pagan period. It is very important that they are found in Istanbul. In one of its sections, we have found a part that belongs to the altar used for pouring blood during an oath. It was plundered during the Byzantium period,”.

In addition, amphorae belonging to the Byzantine period were found on the roof of the mosque and were taken under protection.
It consists of a central hexagonal superstructure with pendentives rising on a square substructure. There are four semicircular niches on the corners of the square and is surmounted by a shallow dome. Each of the walls that constitute the octagon have pointed arches on the outside, pointing to a later Ottoman renovation. The southern niche was walled up and transformed into a mihrab when it was converted into a mosque.
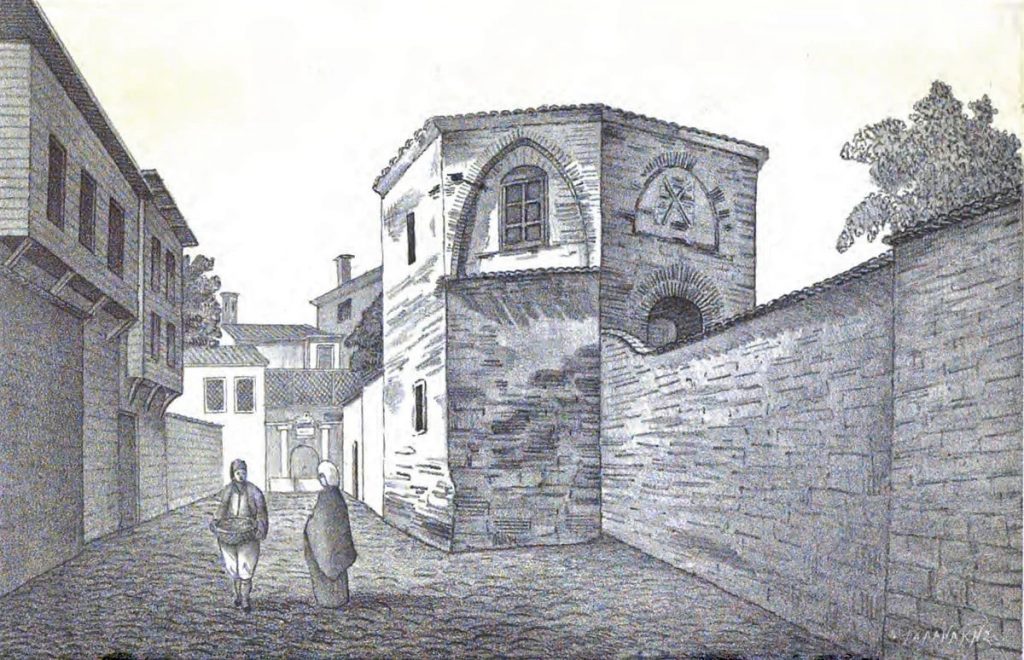

The building was converted into a mosque by Sheikh Suleiman in the reign of Mehmed II. It was damaged by a fire in 1756 and later restored.
This beautiful mosque, which has an original architecture, is currently open and still in use.