A team of archaeologists has discovered a Pictish symbol stone close to the site of what is thought to have been one of the most important battles in Scotland’s history.
The stone was discovered in a field near Forfar’s Aberlemno, an area already well known for its Pictish origins and a spectacular array of distinctive standing stones.
Researchers from the University of Aberdeen were conducting geophysical surveys to try and build a greater understanding of the important Pictish landscape of Aberlemno, near Forfar.
The team found the 1.7metre-long stone in a farmer’s field while investigating the areas around one of the most significant carved stone monument sites ever uncovered in Scotland.
The Battle of Nechtansmere is thought to have been one of the most important battles in Scotland’s history.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The most renowned Aberlemno stone is thought to show events from the 7th Century Battle of Nechtansmere, which concluded with Pictish ruler King Bridei Mac Bili beating Anglo Saxon King Ecgfrith in a victory that halted the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms’ northward progress.
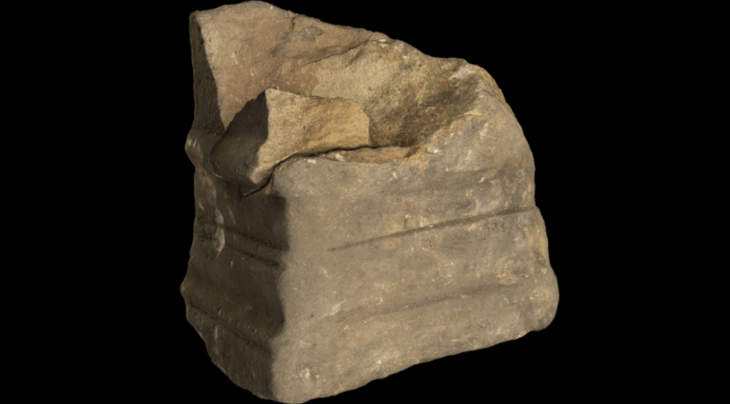
Now, further evidence of the area’s importance during the Pictish period has been found with the discovery of a symbol stone in a farmer’s field, a few miles away from the likely battle site.
The stone was discovered as archaeologists examined anomalies in the ground which looked like evidence of a settlement.
Research fellow Dr. James O’Driscoll, of the University of Aberdeen, who initially discovered the stone, said: “We thought we’d just uncover a little bit more before we headed off for the day. We suddenly saw a symbol. There was lots of screaming.
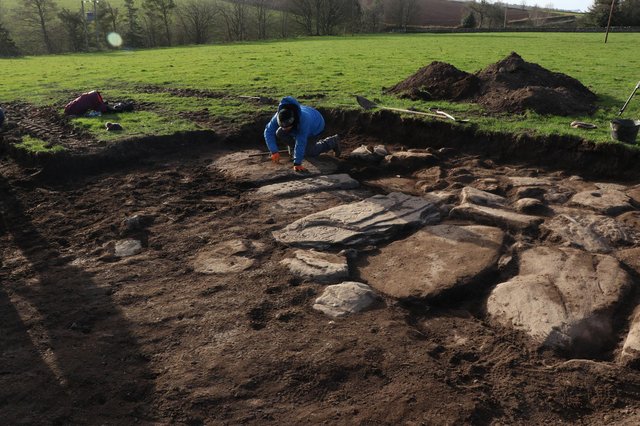

“It’s a feeling that I’ll probably never have again on an archaeological site. It’s a find of that scale.”
Researchers have analyzed the stone and think it dates to around the fifth or sixth century.
Professor Gordon Noble, head of archaeology at Aberdeen University, said: “Here at the University of Aberdeen we’ve been leading Pictish research for the last decade but none of us have ever found a symbol stone before.
“There are only around 200 of these monuments known. They are occasionally dug up by farmers ploughing fields or during the course of road building but by the time we get to analyse them, much of what surrounds them has already been disturbed.
Professor Noble hopes that it could make a significant contribution to understanding the significance of Aberlemno to the Picts.
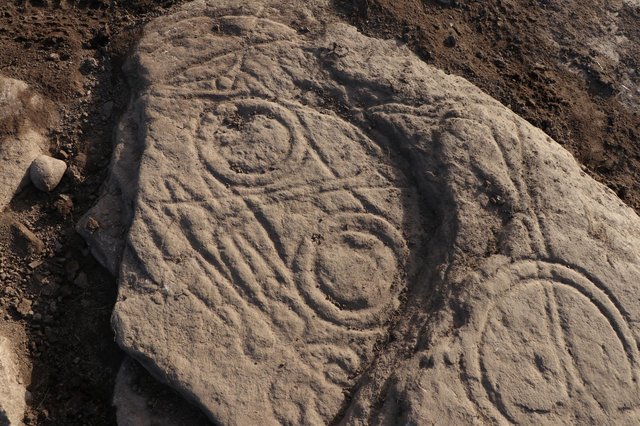
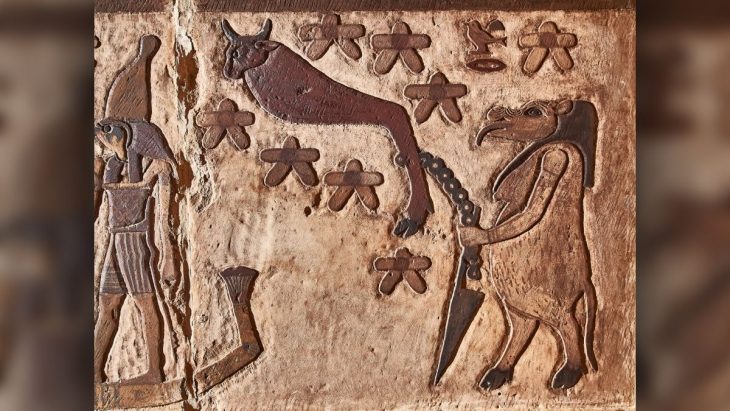
Like the other stones at Aberlemno, the new discovery appears to be intricately carved with evidence of classic abstract Pictish symbols including triple ovals, a comb and mirror, a crescent and V rod and double discs. Unusually the stone appears to show different periods of carving with symbols overlying one another.
The stone has now been moved to Graciela Ainsworth conservation lab in Edinburgh where more detailed analysis will take place.
Cover Photo: A close up of the rare Pictish symbol stone, which has been found in a field close to Aberlemno in Angus. PIC: Aberdeen University.