Archaeologists discovered two brick tombs at an old cemetery with 14 crypts in north China‘s Shanxi Province. The findings offer insight into affluent families’ funeral customs during the Jin Dynasty (1115-1234).
The 14 tombs were found in July 2016 by employees of the Shanxi Provincial Institute of Archaeology in Dongzhuang Village, Houma City. Two tombs with wood-like constructions and brick chambers numbered M12 and M14, were found completely, artistically painted, and elegantly adorned.
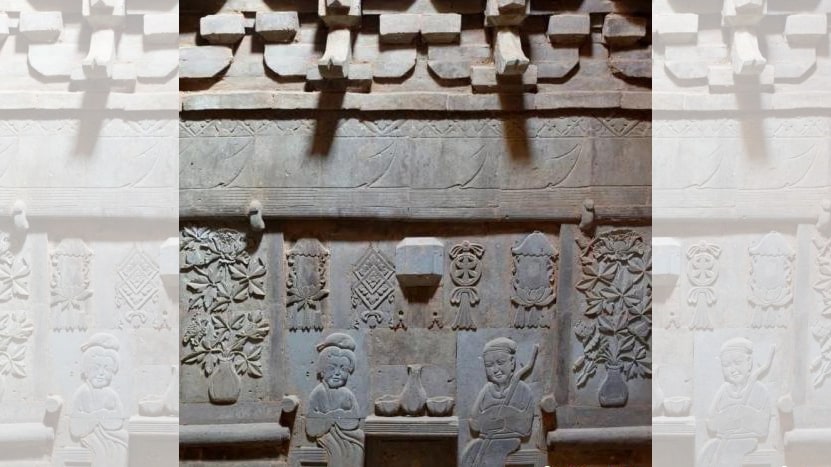
A door, two corridors, and a room make up M12. The bricks above the entryway are engraved with three Chinese characters that translate to “great luck.” Brick sculptures and colorful murals adorn the walls of the chamber. The brick carvings were mostly discovered on the tomb’s walls and door, while the colored paintings were found everywhere around the chamber, with the exception of the corridor.
The north wall was engraved with images of the tomb’s owners. They were seen seated on seats with a square table on either side, each holding a dish of peach fruits or pastries.
The female tomb owner held a scroll, while her male counterpart had a rosary around his neck. There is a round bun on the head of the female tomb owner, while the male tomb owner has a black scarf and a long-sleeved shirt on his head.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The sculptures of the owners of tombs M12 and M14 chanting sutras and reciting the Buddha facing each other are similar to those of Jin Dynasty tombs in other areas of China in terms of decorative content and precise portrayal.
Although it is thought that the M12 and M14 tombs are from the same family, there were no artifacts discovered that might confirm the tomb owners’ identities. But it is believed that they were members of the Han people, who were controlled by the Jin people, and belonged to a rather rich society.
According to the items found, the porcelain pillows are similar to those found at the Jin Tomb of Haojiazhuang in Changzhi, Shanxi, the Shanghai Museum’s second year of Dading (1162), and the Hebei Museum’s fifth year of Taihe (1205).
The two brick tombs are thought to have been built in the middle of the Jin Dynasty, roughly between the reigns of King Hailing and Zhangzong.
Cover Photo: Carvings on the wall of the tomb. /Chinanews