A recent British Museum video reveals that the “oldest map of the world in the world” on a clay tablet from Babylon was deciphered to reveal a surprisingly familiar story.
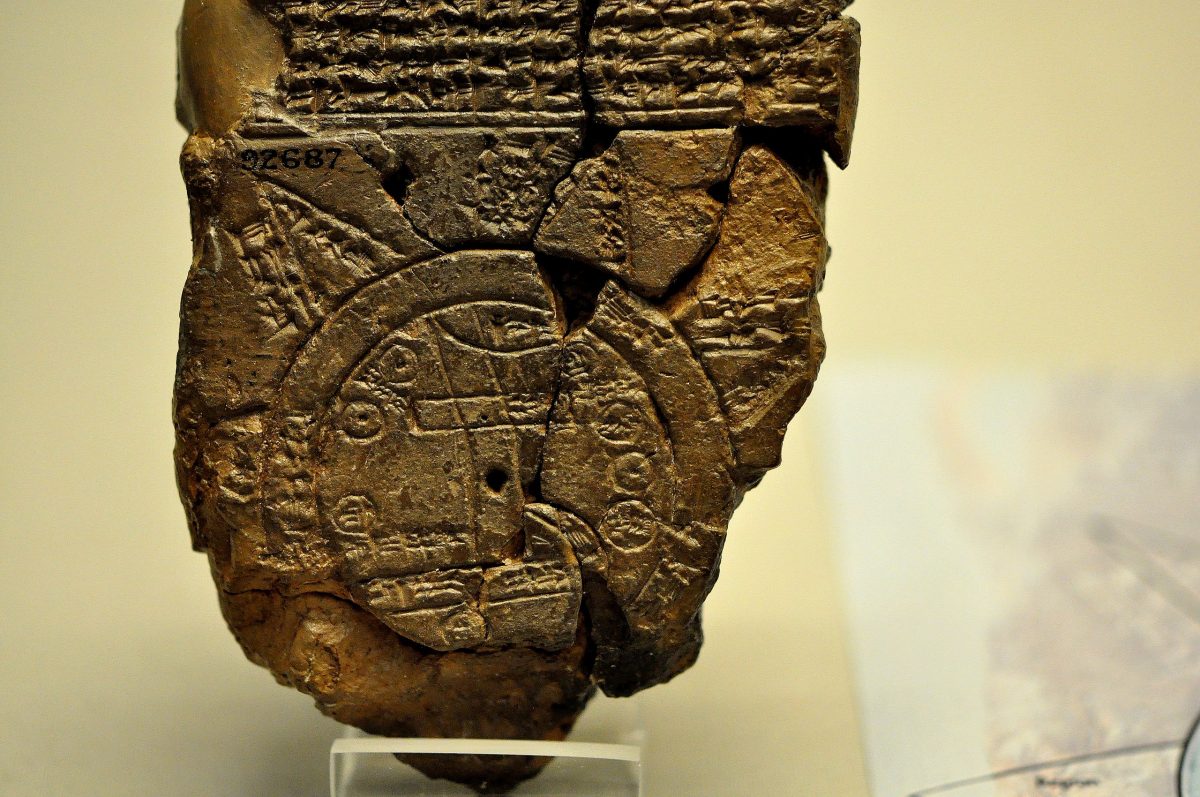
The oldest globe ever found is the Imago Mundi, a Babylonian map of the world. This map is a Babylonian clay tablet with a schematic world map and two inscriptions written in the Akkadian language. The probably seventh century BC is when this map was created. It shows a small part of the world as the ancient Babylonians knew it, and it was found in the southern Iraqi city of Abu Habba (Sippar).
The ancient artifact was acquired by the British Museum in 1882 but remained a mystery for centuries until curators found a missing part and transcribed its cuneiform.
The cuneiform tablet from the 6th century BC shows an aerial view map of Mesopotamia — the land “between the rivers” in modern-day Iraq— and what the Babylonians believed lay beyond the known world at the time.
After centuries of deciphering, the ancient tablet provides insight into the Babylonians’ beliefs about the known world at the time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The tablet has several paragraphs of the cuneiform on its backside and above the map diagram describing the creation of the Earth and what its writer believed existed beyond it.
Researchers confirm the circle around Mesopotamia suggests that Babylonians believed the area was the center of the world. There also shows the river Euphrates cutting through ancient Mesopotamia.
The map depicts a double ring encircling Mesopotamia, which the ancient scribe called the “bitter river.” This river formed the boundaries of the Babylonians‘ known world. Small circles and rectangles inside the Bitter River stand in for various Mesopotamian cities and tribes, such as Babylon, while another rectangle symbolizes the Euphrates River.
“You have encapsulated in this circular diagram the whole of the known world in which people lived, flourished, and died,” British Museum curator and cuneiform expert Dr. Irving Finkel said in the video. “However, there’s more to this map than that.”
“When it comes to operating beyond the limits of the known world into the world of imagination, [the tablet] is indispensable,” Finkel added.
Aside from mapping out what they thought existed outside of their world, the Babylonian scribe also included references to a well-known story (basically the Babylonian version of the biblical story of Noah’s Ark) and mythical animals and lands.
The ancient Babylonians thought that the remains of the enormous ark that their version of Noah, named Utnapishtim, had constructed in 1800 BC at God’s command were located on the backside of a mountain, the same mountain that the Bible says Noah’s Ark crashed on, beyond the bitter river.
“That’s quite a meaty thing, quite an interesting thing to think about because it shows that the story was the same, and of course, that one led to the other,” Finkel concluded.
The tablet also confirms the Babylonian’s belief in the God of creation Marduk and other mythical monsters such as scorpion-man and a lion-headed bird called Anzu.
Cover Image Credit: Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin