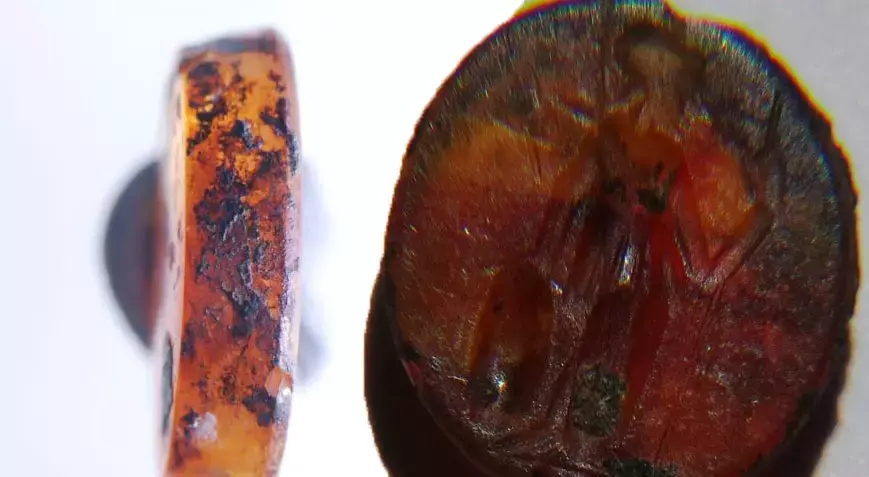
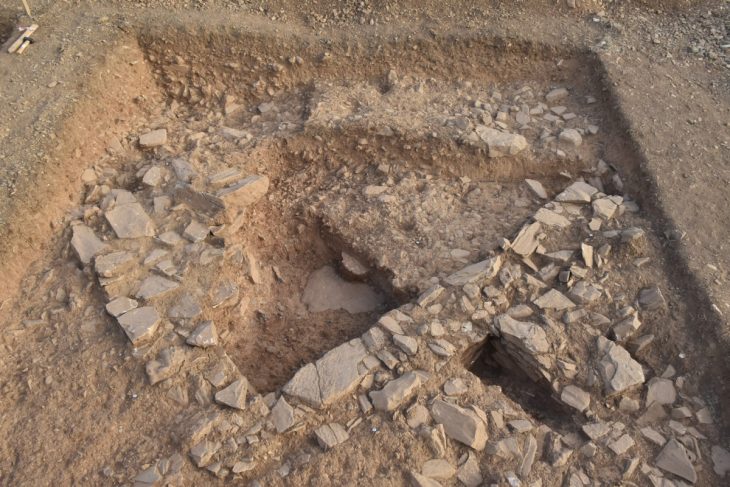
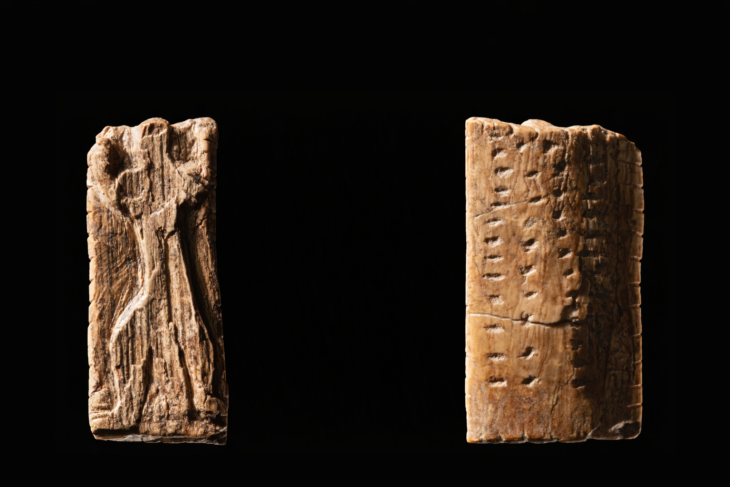
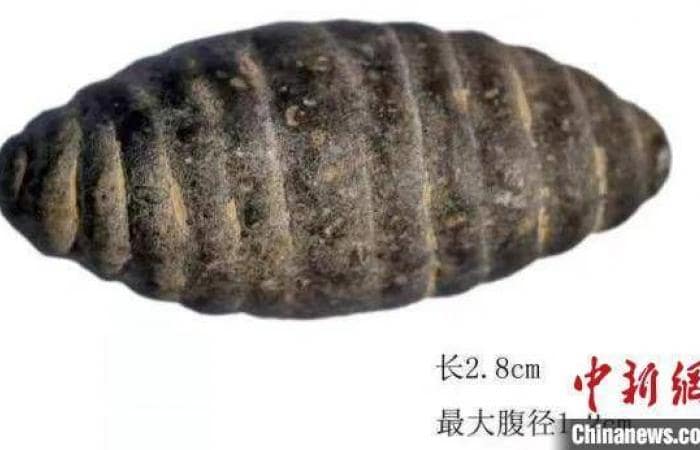
A Roman Imperial Period ringstone depicting Athena, the mother goddess of the Assos ancient city, has been discovered in the Ksenedochion structure (hostelry buildings) in the Assos Ruins in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale.
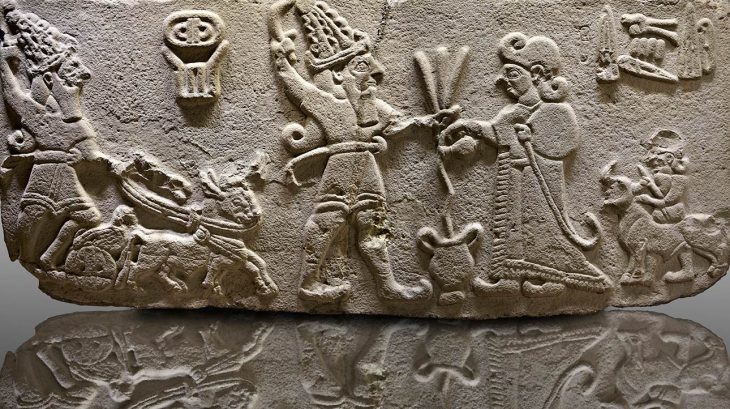
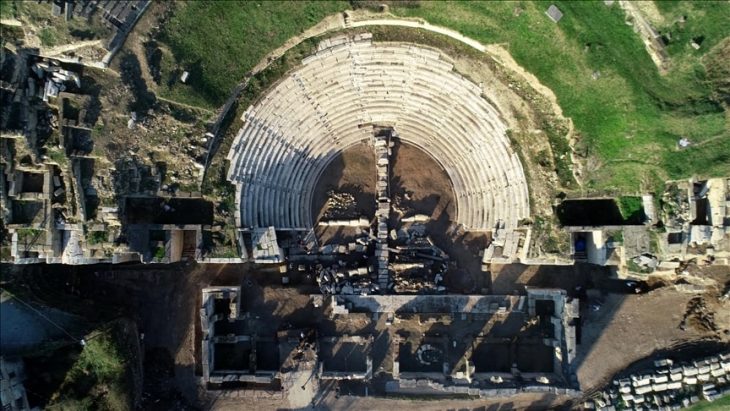
The Assos is located in the southwestern part of the Biga Peninsula (Troad), within the borders of the Village of Behramkale, south of the district of Ayvacık in the province of Çanakkale. It was once an important regional center but had few chances to control its fate. First settled during the Bronze Age. The Bronze Age cities Assuwa, mentioned in the Hittite texts, and Pedasos, mentioned in Homer’s Iliad, are both set to be equal to Assos. According to antique sources, Methymnians from the island of Lesbos founded the Greek city of Assos in the 7th century BC. Athena, who is the daughter of Zeus and one of the 12 Gods of Olympus, was the protector of the city.
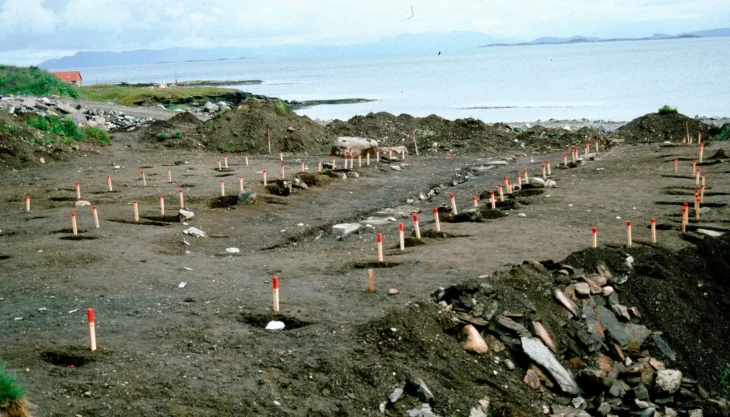
Turkish scientists have been carrying out excavations in the ancient city for nearly 40 years. Under the direction of Professor Nurettin Arslan of the Department of Archeology at Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University’s Faculty of Science and Letters, a team of twenty individuals is conducting archaeological excavations in the ancient city of Assos. The excavations continue under the main sponsorship of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and İÇDAŞ.
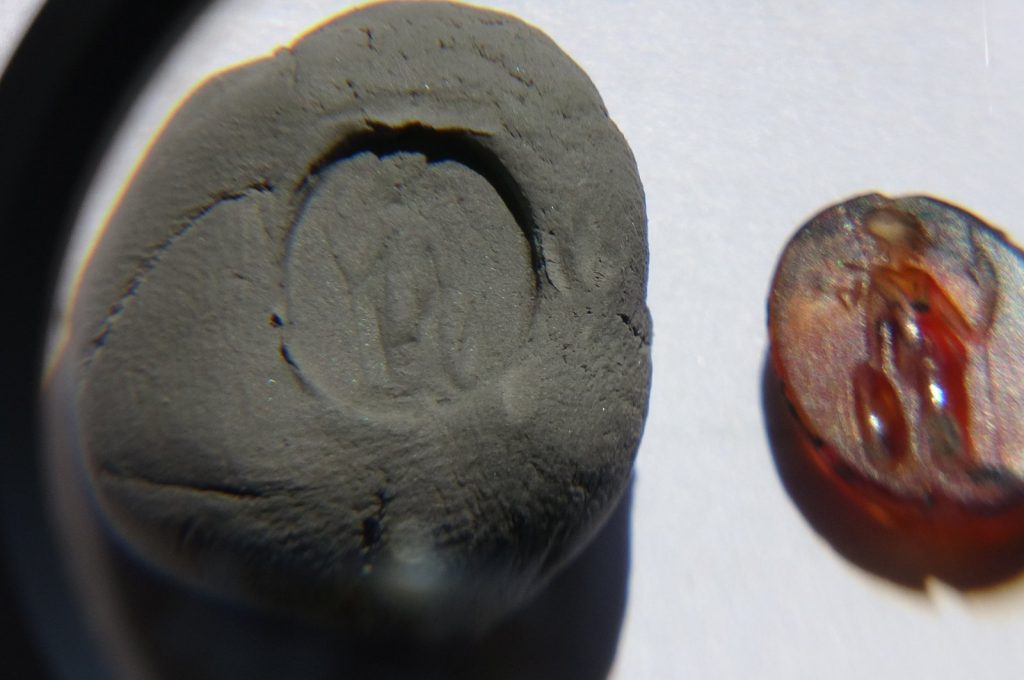

Professor Arslan stated: “During our work this year, we found a valuable ringstone made of stone in the Ksenedochion structure. This ringstone depicts Athena, who was the main goddess of the city, standing. As far as we know, such stones were quite common during the Roman period, but they were also used before and after that era. We can say that this belonged to a prominent person in the city and was used as a seal. We estimate it to date to the 2nd or 3rd century A.D., suggesting a history of 1,600 to 1,700 years. This, of course, helps to identify individuals. In the ancient period, such seals were used as a substitute for signatures, similar to how signatures are used today.”
In the 6th century BC, Assos was among the western Greek states that became subject to Lydia. After the destruction of the Lydian Kingdom by the Persian King Cyrus II, it was incorporated into the Persian Empire. In the 5th century BC, it became a member of the Athenian Confederacy. Later, Assos came once again under Persian control “until the advent of Alexander the Great in 334. After the conqueror’s death, the city passed from one of his successors to the next, finally coming under the dominion of the Kingdom of Pergamon, which was eventually absorbed into the Roman Empire. Assos prospered during the first and second centuries A.D. but later dwindled as it came at times under the Byzantines, Seljuk Turks, Frankish Crusaders, and finally the Ottoman Turks in 1330.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!