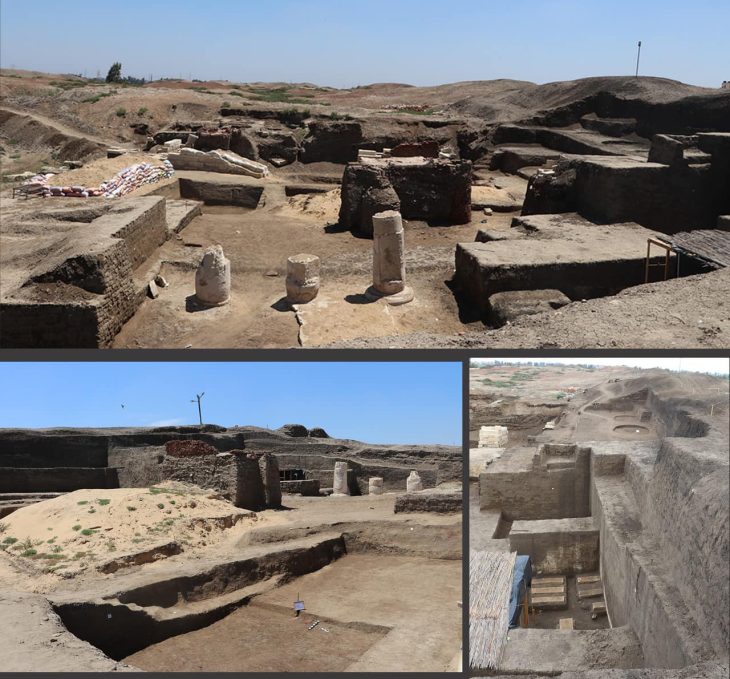
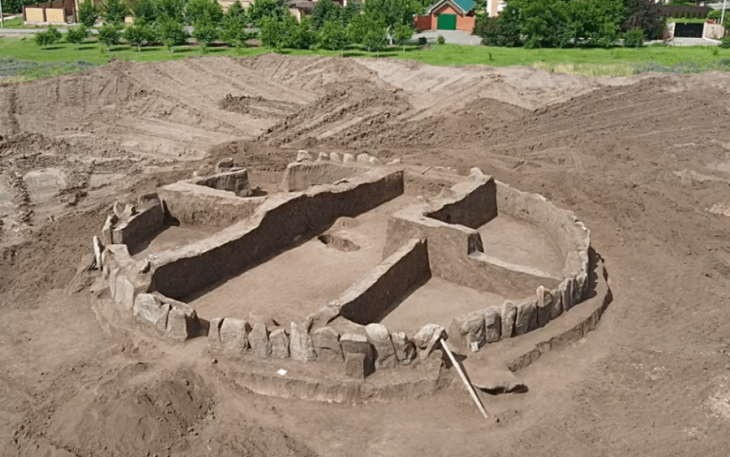
Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Culture and Tourism reported that an in-situ floor mosaic was found at the St Constantine and Helena Monastery Church in Ordu.
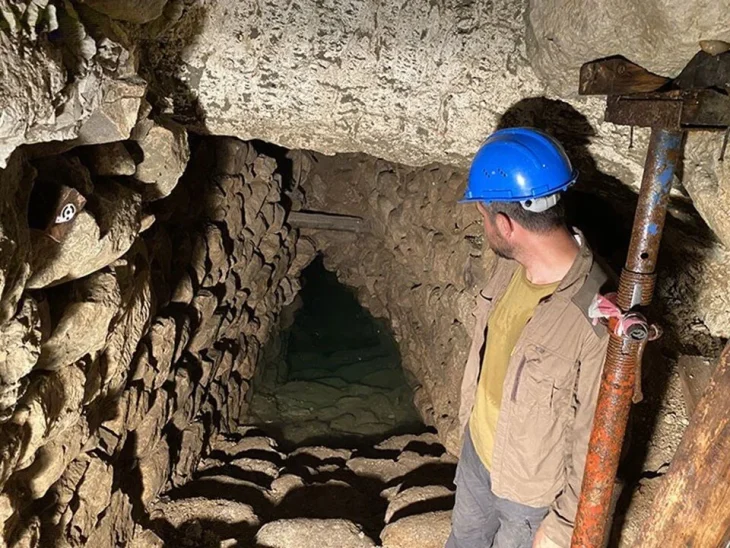
During the excavations in the region known for its ancient Roman tombs in the north of Ordu, archaeologists found the St Constantine and Helena Monastery Church in 2021.
In the Fatsa district of Ordu, it was determined that the monastery church uncovered in the area where 8 Roman-era tombs were found. The church from the Byzantine period was dedicated to Saint Constantine and Saint Helena. The church and the tombs are an important part of the Ancient Polemonion City.
During the Pontus Kingdom era, Fatsa was originally named Polemonium, after King Polemon I, a Roman client king chosen by Mark Antony. In AD 62, the kingdom was turned into a Roman province under Nero.
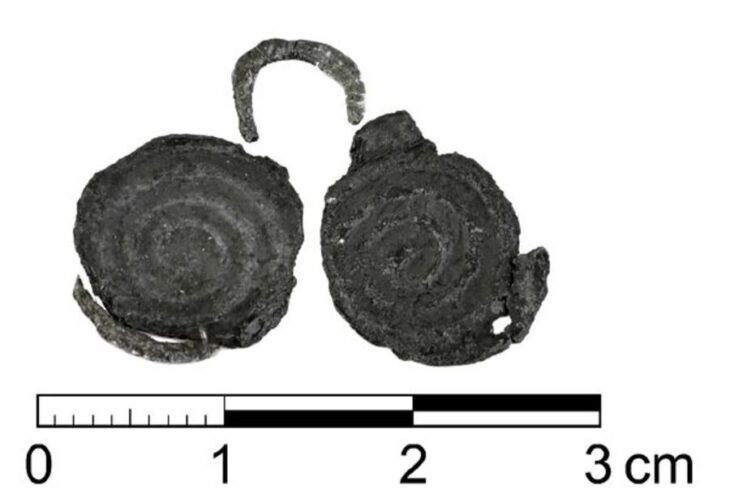
The artifact found during the excavations carried out under the scientific responsibility of Associate Professor Seçkin Evcim and the Directorate of Ordu Museum is the first in-situ floor mosaic unearthed in Ordu province.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
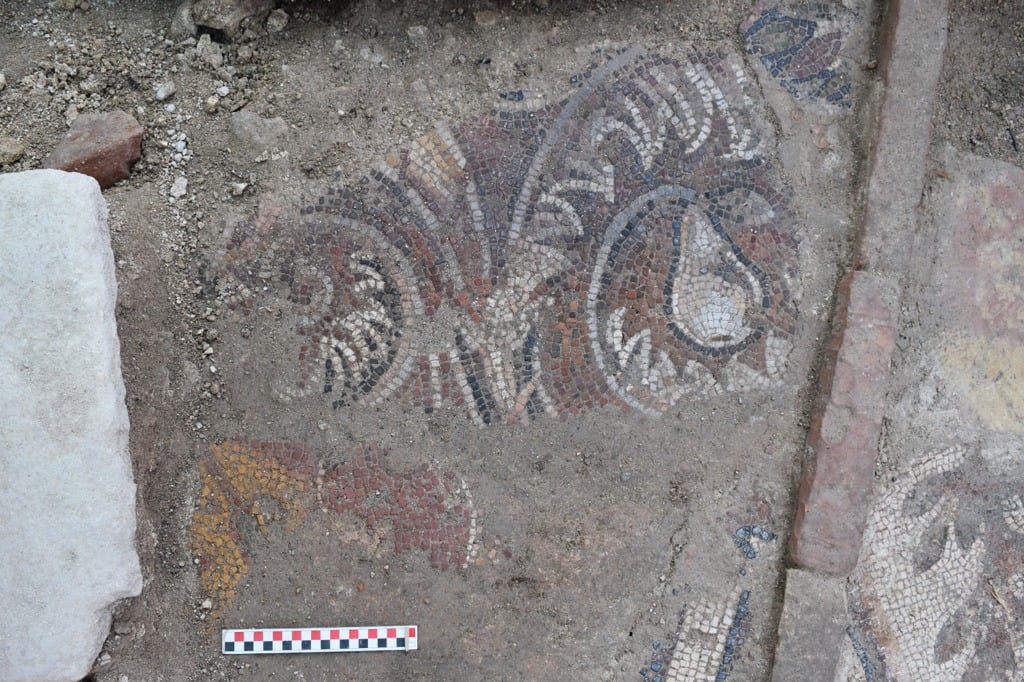

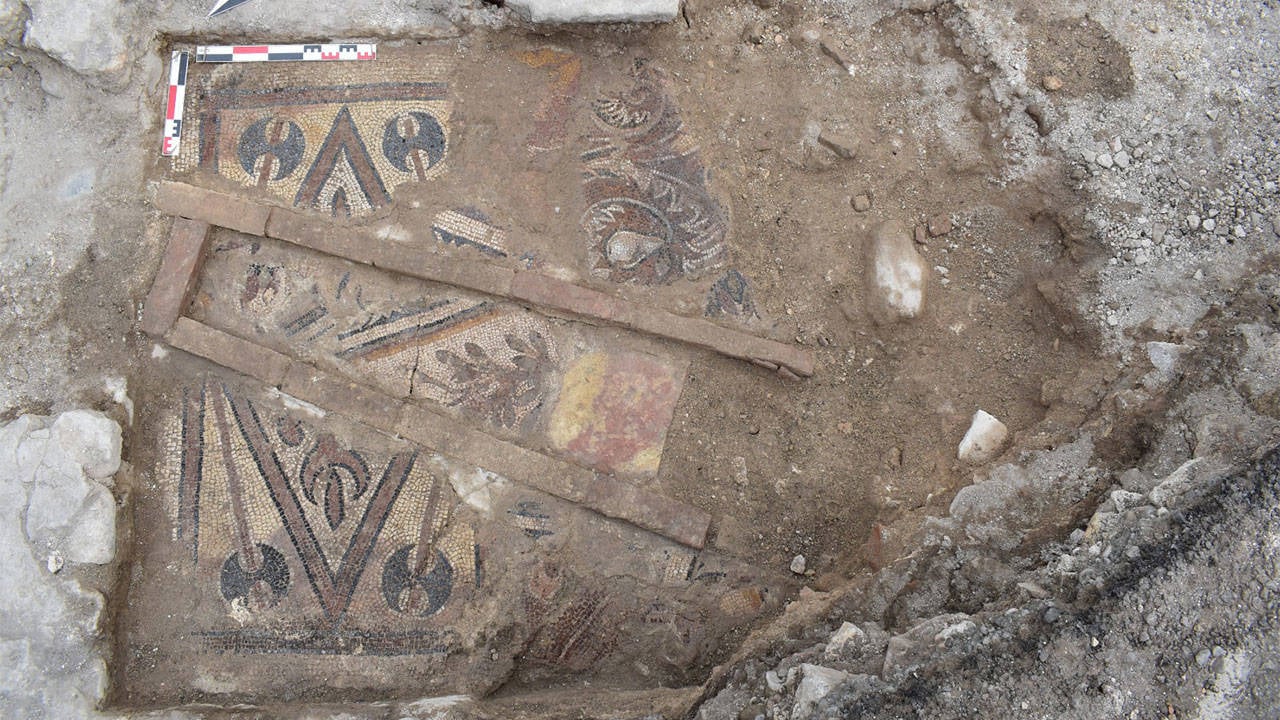
The in-situ floor mosaic unearthed in the Church of the Monastery of Saints Constantine and Helena can be dated between the 5th and 6th centuries in terms of style and form.
When the in-situ floor mosaic is analyzed in terms of style and form, it is known that geometric and floral motifs were widely used in the Early Byzantine period.
It is seen that the rhombus, which is mostly encountered in the borders, forms a panel here. It is possible to see similar panels formed with rhombus and labrys around it in Anatolia. It is known that the curved acanthus design was also used in the Early Byzantine period.
It is also seen that the curved acanthus, which is generally preferred for borders, is embroidered with fruit motifs and animal figures reflecting nature.
Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy announced on his social media account that an in-situ floor mosaic was found in the Monastery of Saints Constantine and Helena in Ordu.
Stating that the work found during the excavations carried out under the direction of the Ordu Museum Directorate is the first in-situ floor mosaic unearthed in Ordu province, Ersoy said, “I would like to wholeheartedly thank the Excavations Research Department and our excavation team who worked on the project.” he said.
Cover Photo: Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Culture and Tourism