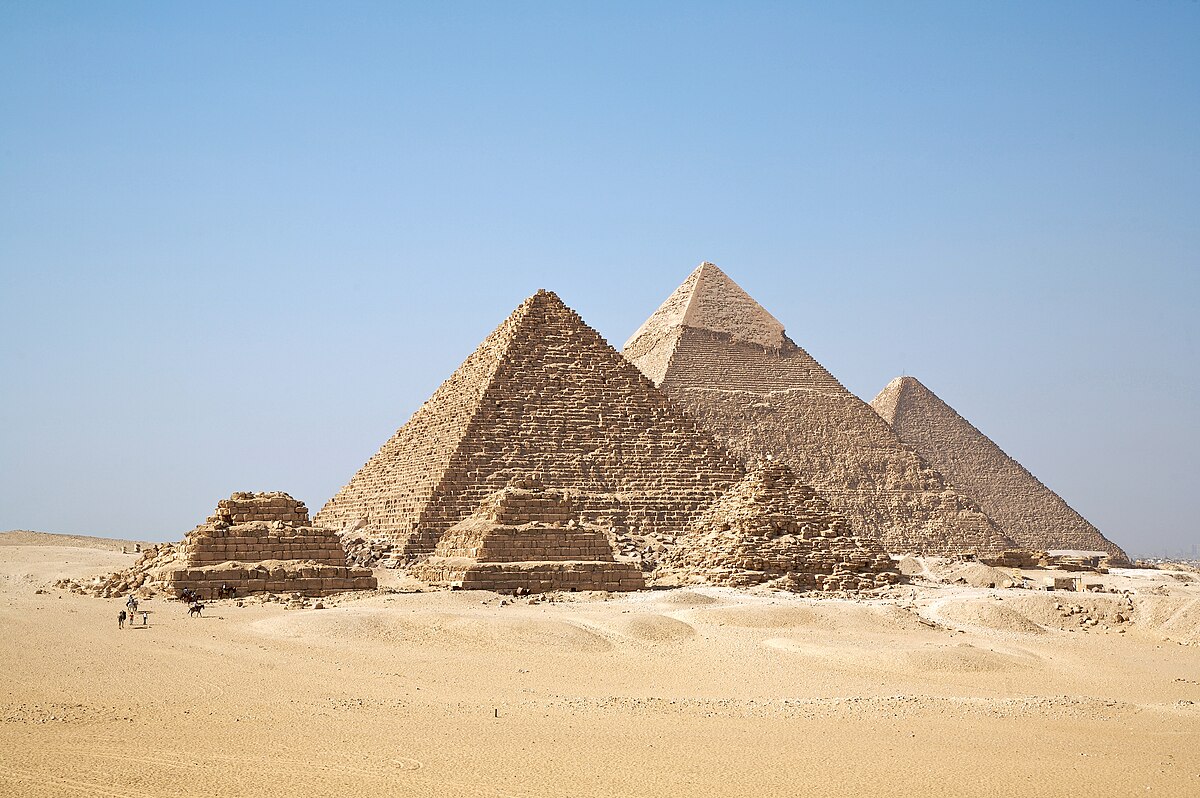
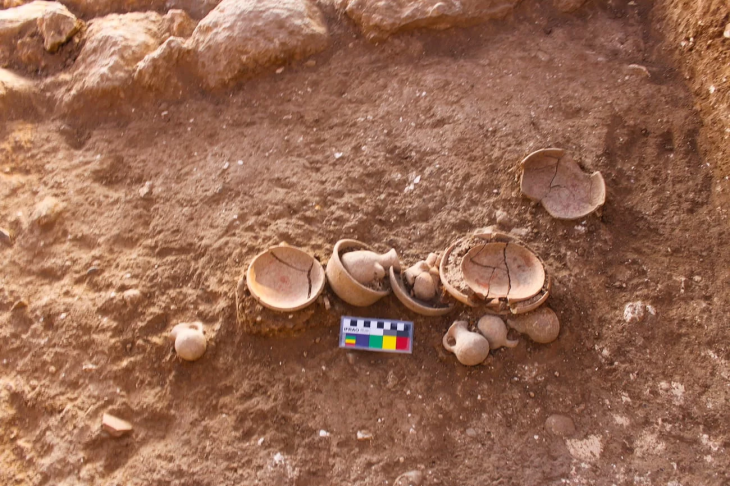
More than 30 pyramids in Egypt are located in an unremarkable strip of barren desert far from the shores of the modern Nile River, and now scientists may have found the reason for this. The extinct branch of the Nile River could explain the pyramids’ location and how they were built, according to recent research.
The discovery of this extinct waterway, according to the University of North Carolina Wilmington team, explains the high concentration of pyramids in the region and provides an answer to the question of how materials were transported to build the Giza complex and other pyramids that dot the Western Desert Plateau.
The strip near the ancient Egyptian capital of Memphis includes the Great Pyramid of Giza — the only surviving structure of the seven wonders of the ancient world — as well as the Khafre, Cheops and Mykerinos pyramids.
The pyramid field is a fair distance from the Nile River we see today. Archaeologists had long thought that ancient Egyptians must have used a nearby waterway to move the giant materials used to build the pyramids.
In a recent study, researchers searched for the potential location of a former river branch that may have run alongside the pyramid fields, close to the Western Desert Plateau’s foothills, using satellite imagery. They went to the region to gather sediment samples and conduct geophysical surveys after discovering a viable candidate.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
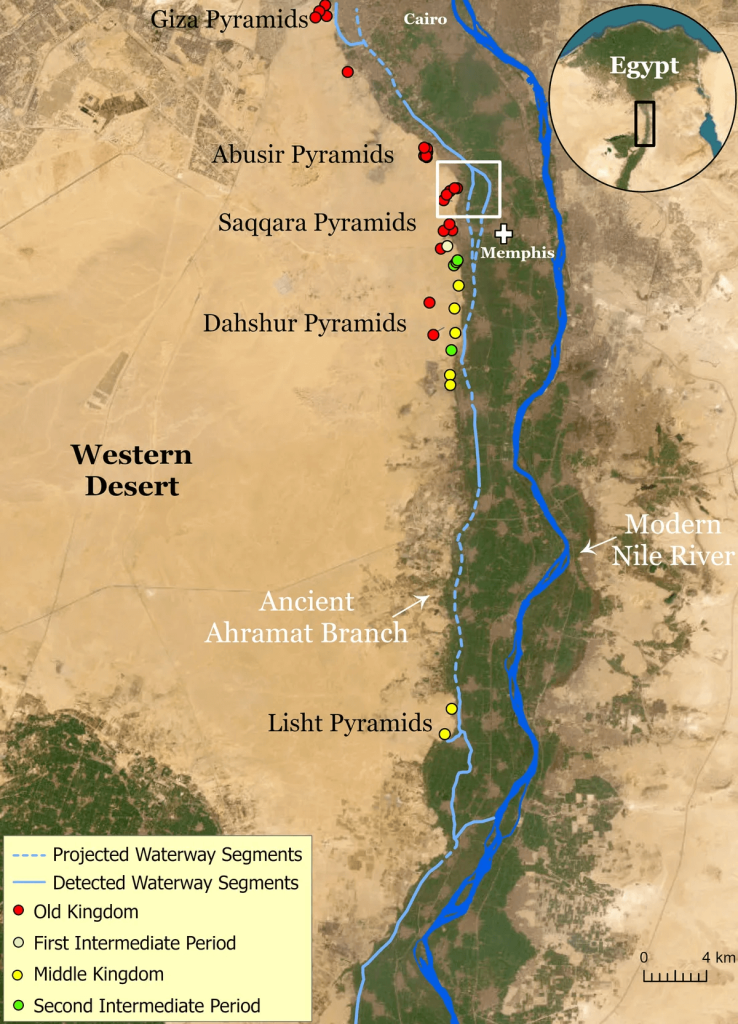
Researchers claim this revealed evidence of a 64-kilometer (40-mile) ancient branch of the River Nile that has since disappeared. They propose naming the long river “Ahramat,” which means “pyramids” in Arabic.
In a report published in the journal Communications Earth and Environment, the researchers stated: “Many of the pyramids, dating to the Old and Middle Kingdoms, have causeways that lead to the branch and terminate with Valley Temples which may have acted as river harbors along it in the past. We suggest that the Ahramat Branch played a role in the monuments’ construction and that it was simultaneously active and used as a transportation waterway for workmen and building materials to the pyramids’ sites.”
It seems the river branch was approximately 39 miles long and over 2,000 feet wide, however following an intense drought, the strip became caked in windblown sand and was gradually lost to the desert and farmland.
Surveys in the field and cores of sediment from the site confirmed the presence of the river, according to the study in the journal Communications Earth & Environment. Unlike the arid and inhospitable landscape known today, up to 6,000 years ago, the valley was a network of freshwater marshes and floodplains, with inhabitants moving to natural levees of the river and jeziras (islands) by the beginning of the Old Kingdom period (around 2686 B.C.E.).
The Ahramat Branch moved steadily eastward, with abandoned channels visible in 1911 historical maps of the area. The Dahshur Lake is probably the last existing trace of the tributary.
“As branches disappeared, Ancient Egyptian cities and towns also silted up and disappeared, and we have no clue actually where to find them,” said Dr Eman Ghoneim.
















