Experts have recovered around 50,000-year-old turtle shell fragments from the Barleben-Adamsee gravel pit near Magdeburg. The turtles could have been easily transportable food reserves.
The numerous gravel pits in the middle Elbe valley near Magdeburg have already yielded many special archaeological finds from the period between the Middle Pleistocene (Ice Age) and modern times.
In the Adamsee lake area near Barleben (Börde district), gravel accumulation occurred over a period of several tens of thousands of years. Since gravel extraction is conducted with bucket dredgers below the water table, observing the find layers is not possible.
Dating is therefore only possible using the shape of tools or, especially in the case of organic finds, scientific dating, e.g. the radiocarbon method. The finds are usually recovered from the excavator’s conveyor belts. Here, the contribution of voluntary archaeologists, who invest great amounts of time in surveying the material for finds, is of paramount importance. In the case of the Barleben-Adamsee gravel quarry, the finds from recent years are especially attributed to Uwe Beye.
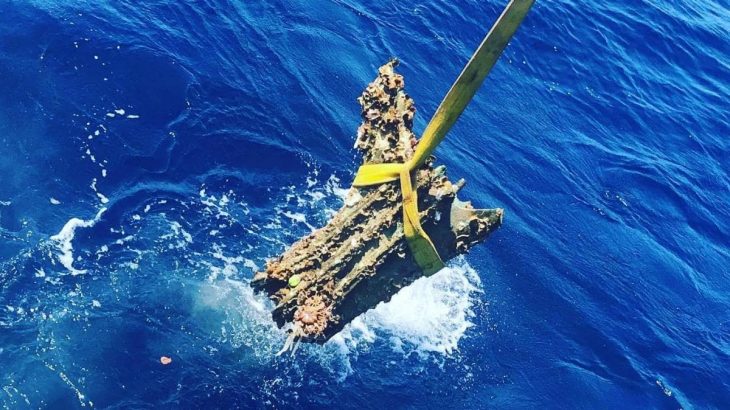
Not only around 180 flint artifacts have been recovered from the Adamsee (including hand axes, other tools, cores and flakes), but a very special find also came from the gravel pit. As early as 1998/99, a 41.8 centimeter long tip made from the rib of a bovid (aurochs or bison) was discovered. One end of the bone has been very carefully prepared in the form of a long, slender point approximately twelve centimeters long.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Radiocarbon dating places the animal’s time of death with 95 percent probability between 32,992 and 32,406 BC, in the late Middle or early Upper Paleolithic period. This makes the find one of the oldest ground bone tools in Central Germany. The stone implements belong to the same period. Among them is, for example, the fragment of a bifacial leaf point, which can be compared with finds from the Ilsenhöhle near Ranis in Thuringia.

A team of researchers with the participation of the Saxony-Anhalt State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology recently identified early modern humans as manufacturers of these devices 45,000 years ago. Previously, the leaf points had often been associated with Neanderthals.
Turtles – living tins?
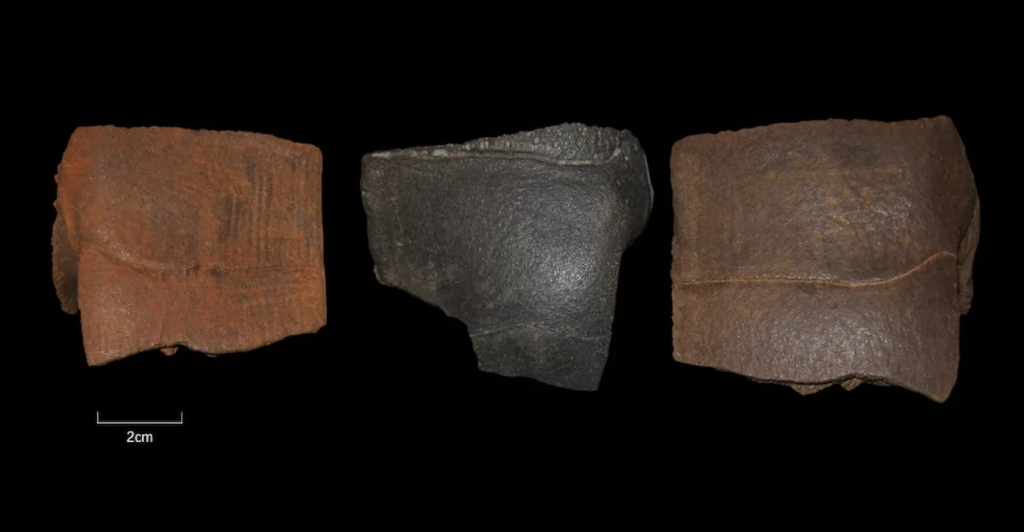
Among the more recent finds from Adamsee, five fragments of turtle shells that can be assigned to the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) stand out. All fragments were dated twice using the radiocarbon method. The age is between around 50,000 and 42,000 years BP. The turtles therefore lived during the Weichselian Glacial, a date that was unexpected for Central Europe.
The eggs of the European pond turtle, which are laid in the ground, require a temperature of more than 18 to 20 degrees Celsius for embryonic growth. The Barleben-Adamsee finds are therefore likely to be outside of the natural range of the European pond turtle at that time, which raises the question of their origin.
Ethnographic and historical comparisons show that people often took turtles with them when traveling as provisions, as “living tins” so to speak. The animals are easily transportable and provide a supply of fresh meat even if the hunt is unsuccessful.
It is possible that Ice Age hunters – Neanderthals or modern humans – brought the turtles with them to northern, cool regions. Future research will have to prove whether this is actually the case.
Cover Photo: Uwe Beye / Archäologie in Sachsen-Anhalt