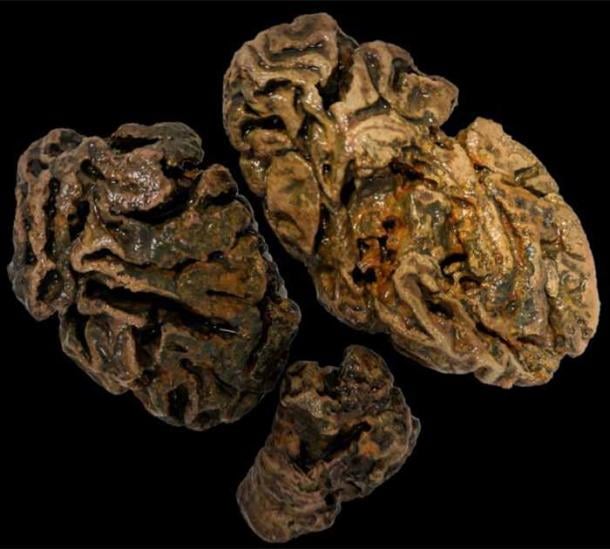
A study by forensic anthropologist Alexandra Morton-Hayward and her team from the University of Oxford has shown that the human brain can survive the test of time far better than previously believed. This finding shows that human brains are surprisingly resistant to disintegration, which is a sharp contrast to previous theories.
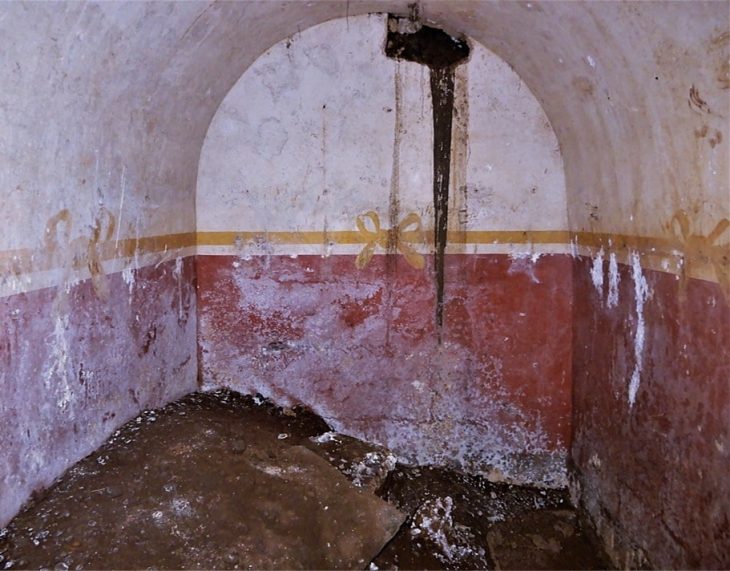
Researchers, canvassed archaeologists around the world for this research project, resulting in a global archive collating records—and some specimens—of more than 4,400 preserved human brains. These brains, found across diverse environments—from the icy terrains of the North Pole to the dry deserts of Ancient Egypt—challenge the notion that brains are among the first organs to decompose.
The brain is usually one of the first organs to decompose following death. Thus, the perception persists that naturally preserved brains are “unique” or “extremely rare” discoveries, particularly in the absence of other soft tissues. However, recent research challenges these perceptions, demonstrating that preserved brains exist in far greater abundance than previously thought, thanks to conditions that prevent decay.
Morton-Hayward says these ancient brains might be an untapped source of information about the past.
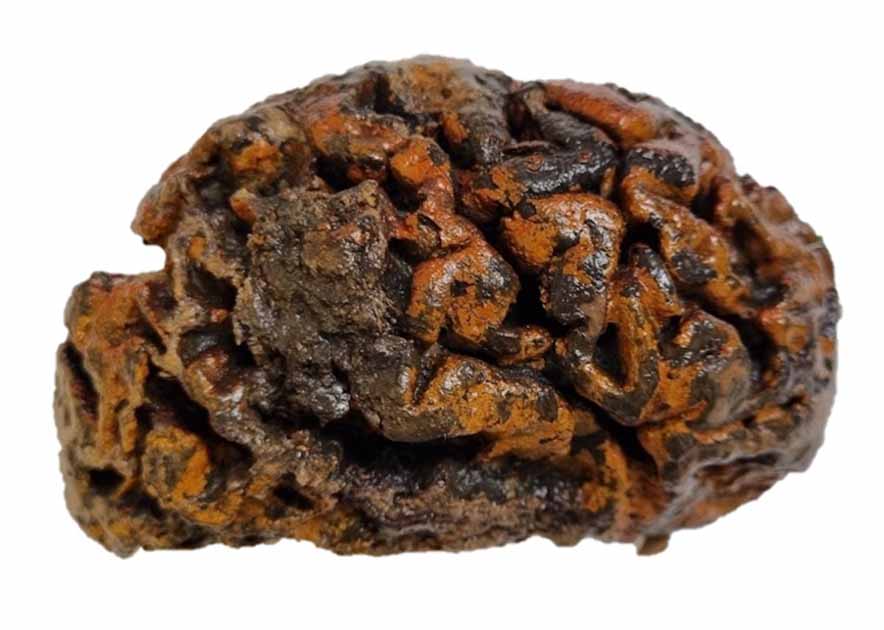
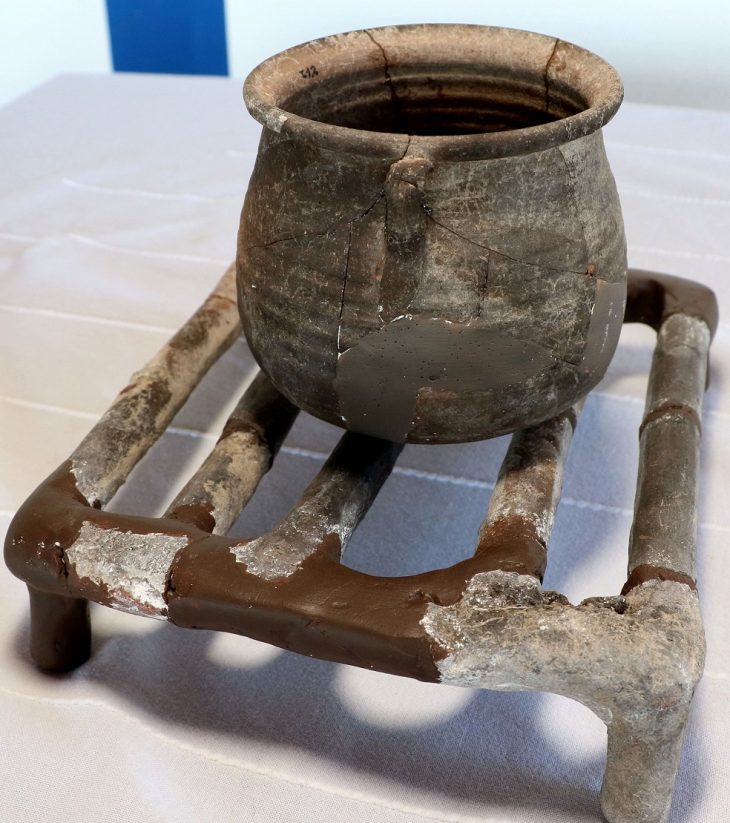
The preserved brains displayed a variety of conditions, with textures ranging from brittle and dry to soft and spongy. Surprisingly, a significant portion of these brains were discovered in bodies where no other soft tissues survived, presenting an unusual phenomenon in the realm of archaeological discoveries.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
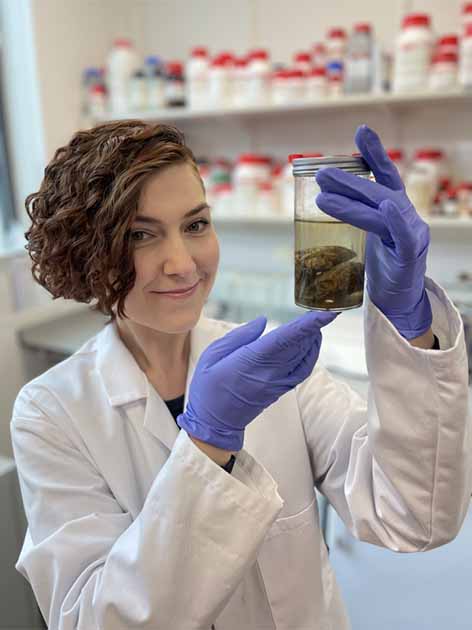

Morton-Hayward, in an interview with Science: The brain usually just liquefies almost immediately. But I sometimes had autopsy cases where the body had been opened up but the brain was still perfect, like a jelly in the skull. When I went looking in the literature, I was surprised to find a lot of examples of preserved brains. I eventually found thousands, going back 12,000 years, and from every continent except Antarctica. “Yet no one is investigating this material,” said.
“I think what’s intriguing about this research is that although we know the brain can liquefy quickly, clearly, in some circumstances, it also preserves and on incredibly long timescales,” Morton-Hayward told Science. “So, I would argue that we need to start thinking in greater depth about soft tissue preservation.”
Though less than 1 percent of the archive is currently being studied, the sheer volume of preserved brains has opened up new research opportunities. The factors like freezing, tanning, and dehydration that help preserve them are being closely examined. Yet, what makes brains endure when other organs do not remains a mystery. This mystery could lie in the brain’s unique brain’s distinct chemical composition, particularly its balanced ratio of proteins to lipids, which may interact with environmental factors such as metals, resulting in preservation.
Therefore, Morton-Hayward’s ongoing research represents an “untapped archive” that could shed light on human evolution, as well as help us to better understand ancient health and disease. The research could even provide insights into neurodegenerative conditions that affect people today, such as Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
As Morton-Hayward notes, “Ancient brains may provide new and unique paleobiological insights.” This research could revolutionize our understanding of neurological development and disorders, offering a window into the health and lifestyle of our ancestors.
This new study was published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2023.2606
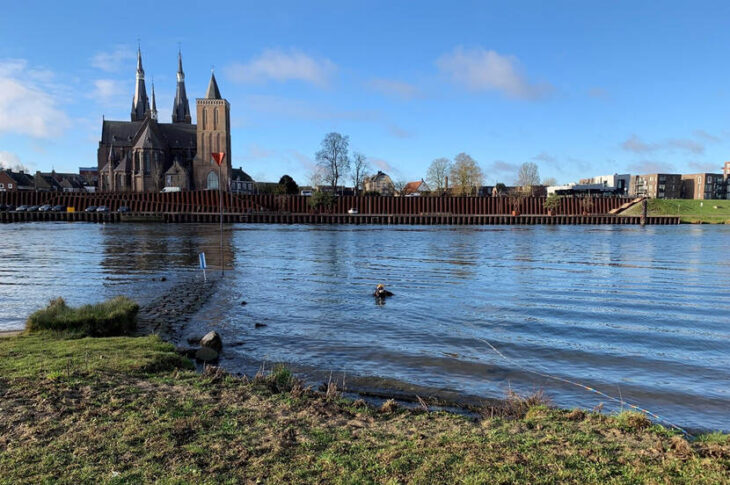
Cover Photo: The thousand-year-old preserved human brain of an individual excavated from the c. 10th-century churchyard of Sint-Maartenskerk in Ypres, Belgium. This specimen is among more than 4,000 recorded in a newly compiled archive. Source: Alexandra L. Morton-Hayward/Royal Society Publishing