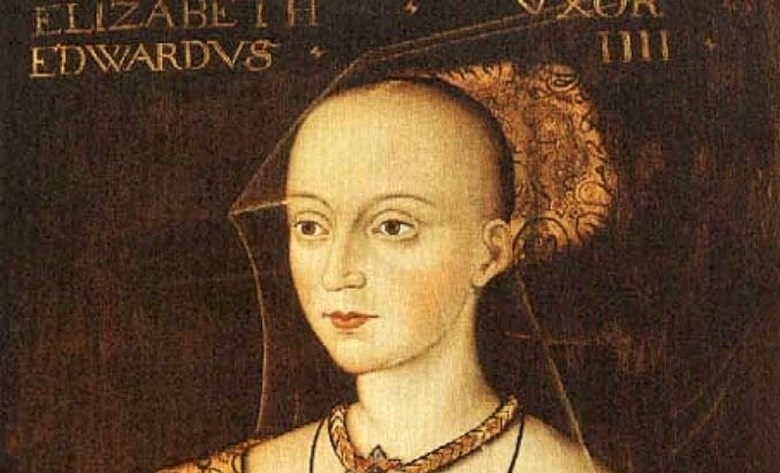
A new study reveals the story of how England’s “White Queen”, Elizabeth Woodville, wife of Edward IV, once worshipped at the chapel of St. Erasmus.
Erasmus of Formia, also known as Saint Elmo, was a bishop who lived in the 3rd century CE and fell afoul of Western Roman Emperor Maximian. He was reportedly variously tortured, imprisoned, burned alive (which, according to the legends, he survived), imprisoned, and ultimately killed by having his entrails wound slowly around a windlass.
In addition to being one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers—saintly figures revered specifically as intercessors in Christian tradition—he is also known as the patron saint of sailors, children’s health, and abdominal pain.
And new research suggests, a sacred space dedicated to the royal cult of Saint Erasmus of Formia.
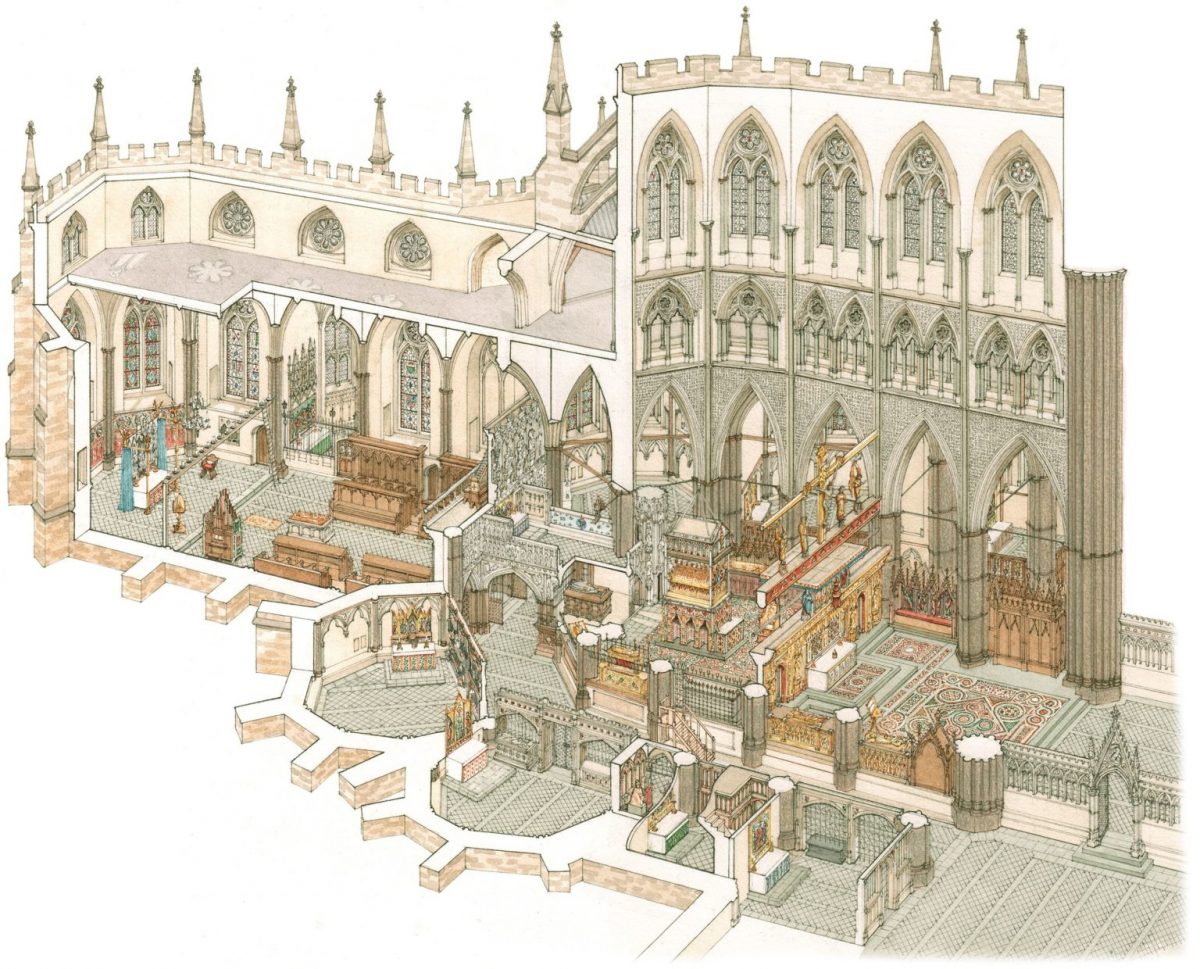
The Chapel of St Erasmus was built at a section of Westminster Abbey in the late 1470s under order of Elizabeth Woodville, wife of King Edward IV and Queen consort, also known as the ‘White Queen’.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

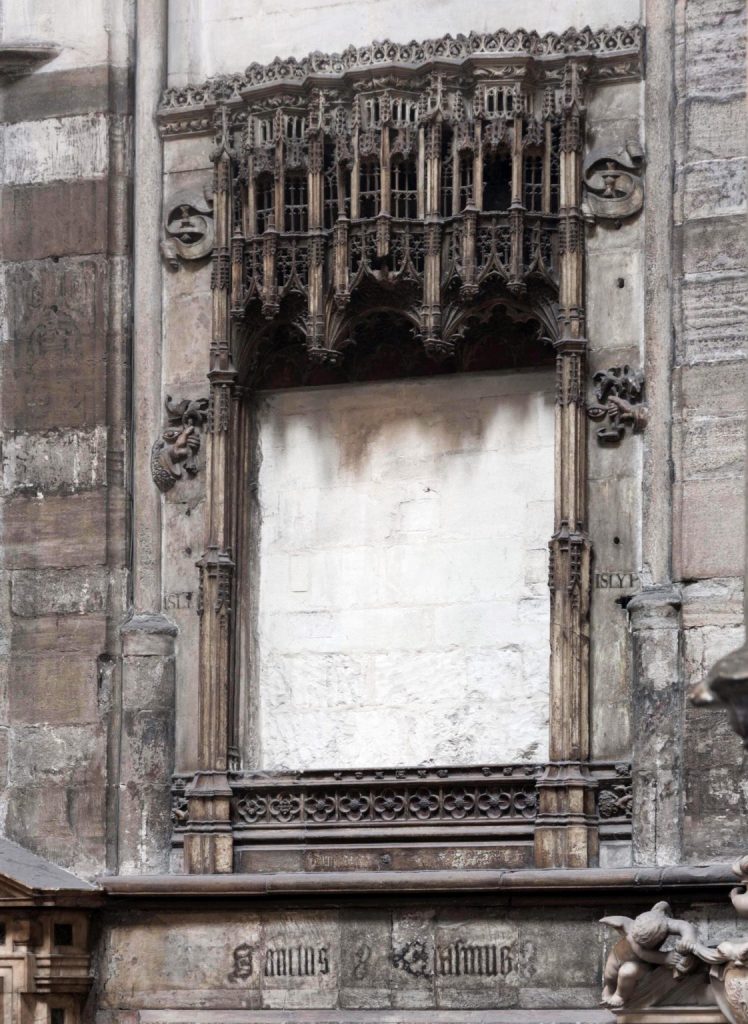
Little was known about the chapel until recently; all that was left of it after it was destroyed in 1502 was an intricate stone frame. The chapel, which was at the east end of the Abbey church, can now be reconstructed thanks to a thorough study.
The chapel likely contained gruesome images of the saint’s death, as well as one of his teeth, among other relics that were stored there.
According to Abbey archivist Matthew Payne, and John Goodall, a member of the Westminster Abbey Fabric Advisory Commission, it may have been a site of worship used by England’s ‘White Queen’ Elizabeth Woodville, wife of Edward IV.
According to Goodall and study co-author Westminster Abbey archivist Matthew Payne, the Chapel of St Erasmus was a place of devotion to the ‘cult’ of the disembowelled saint, but also a royal burial site.
Commenting on the prominence of the chapel, Matthew Payne, said: “The White Queen wished to worship there and it appears, also, to be buried there as the grant declares prayers should be sung ‘around the tomb of our consort (Elizabeth Woodville).

“The construction, purpose and fate of the St Erasmus chapel therefore deserves more recognition.”
Although its precise location is unknown, the chapel was almost certainly built on space formerly allotted to a garden and near stalls where English merchant William Caxton sold his wares, according to the authors.
Henry VII ultimately gave the order to demolish the chapel so that his and his wife’s chantry and burial place could be built. The authors speculate that a statue of St. Erasmus in the Lady Chapel, which took its place, maybe a nod to the now-forgotten chapel.
Despite her connections to Westminster, the White Queen was buried with her husband, King Edward IV, at St George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle, after her death in 1492.
The presented evidence, the researchers say, suggests that further investigation into this lost piece of English history is warranted.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00681288.2022.2101237
Cover Photo: A reconstruction of the chapel. (Stephen Conlin/Payne & Goodall, J. Br. Archeol. Assoc., 2022)