A Roman military watchtower the first of its kind was discovered by a team of Polish and Moroccan archaeologists in the ancient city of Volubilis, northern Morocco.
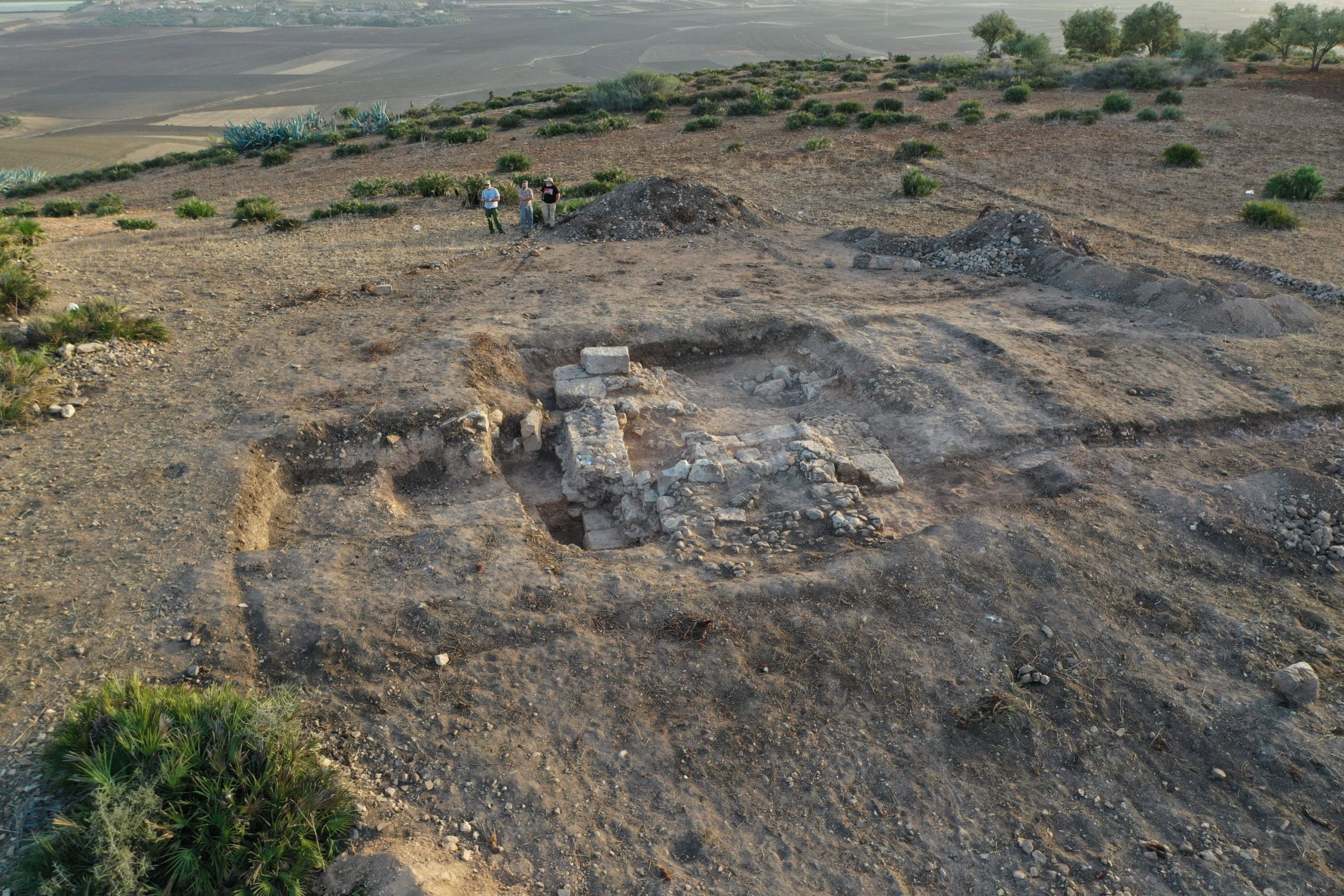
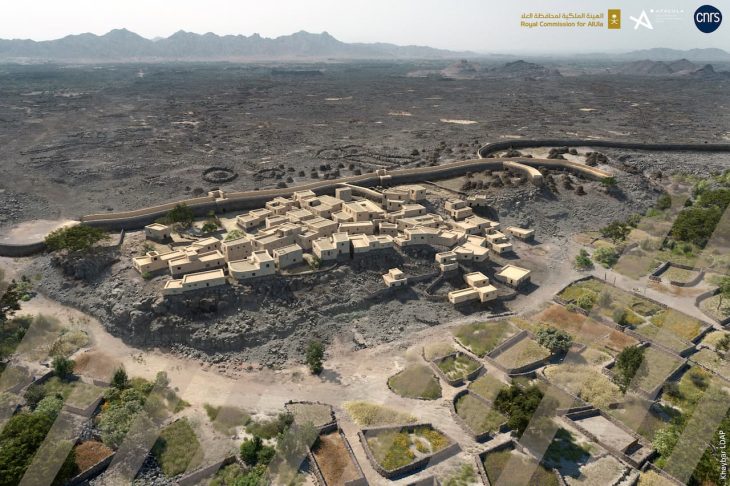
The tower was discovered at the site of El Mellali near the ancient city of Volubilis, on the ancient Roman province’s southern border. Until this discovery, it was unclear whether towers of this kind existed in this area.
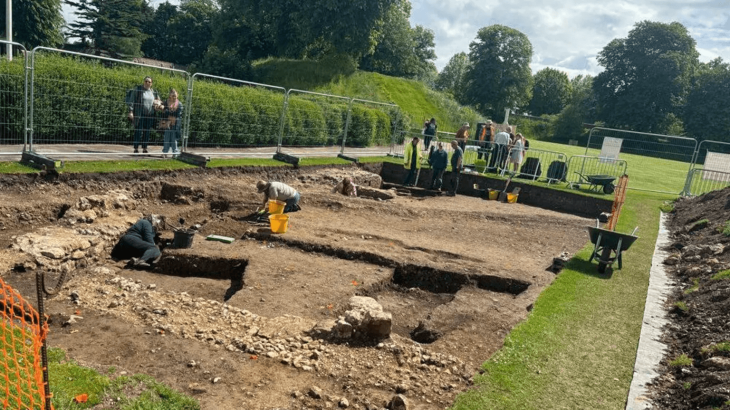
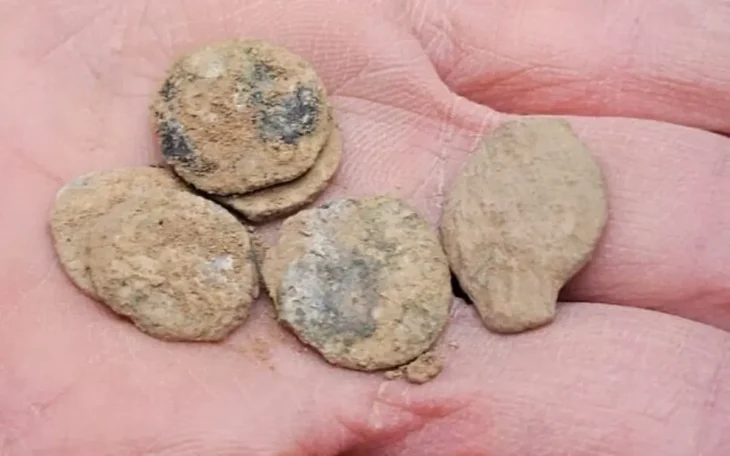
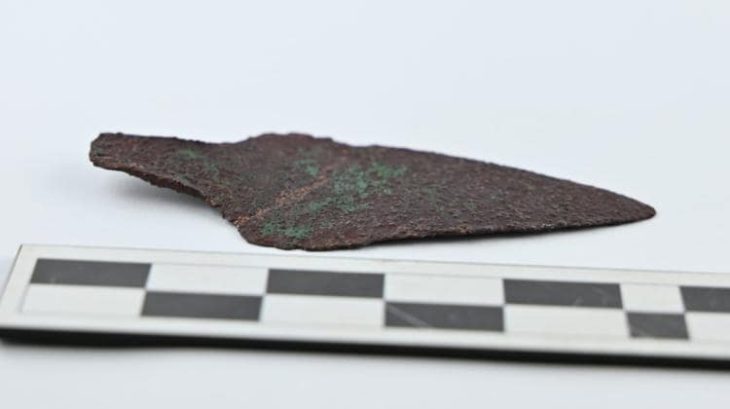
The foundations and walls up to 80 cm (2’8′′) high, as well as a section of an internal staircase and some of the cobblestone pavers around the structure, are still standing. The team also discovered pilia (Roman spearhead) fragments, nails from caligae (military hobnailed sandals), and Roman military belt fittings. Roman observation towers have previously been discovered in Scotland, Germany, and Romania, but this is the first one discovered in Morocco.
Morocco was a part of the Roman Empire beginning in the fifth century CE, but due to its geographical isolation, little is known about this region and archaeologists treat it as a niche.
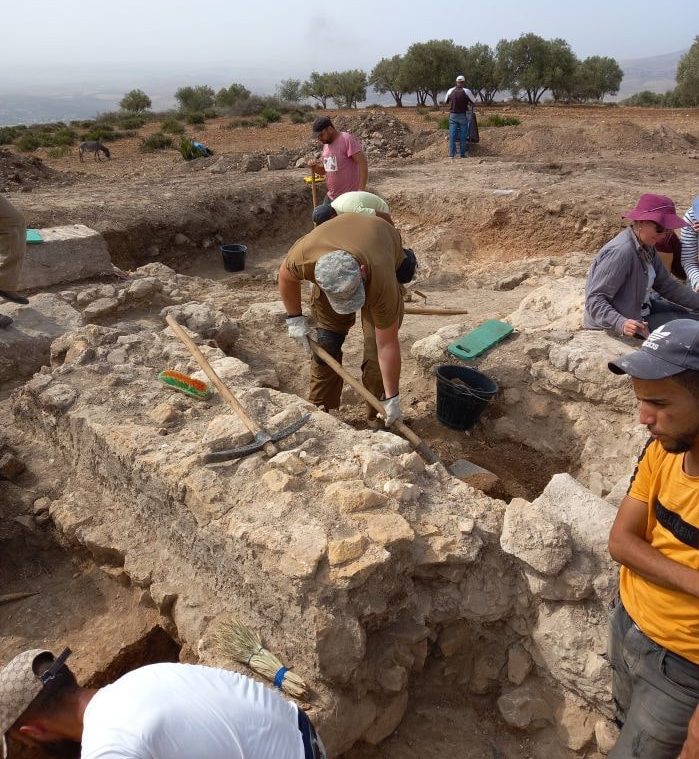

‘Based on satellite images, we have selected several sites that have a common feature: an oval plan with an inscribed rectangle or square. We have chosen this particular site because it is located farthest to the south. There are a few brief descriptions of this site in French publications indicating that the place could have been associated with the Roman army’, says Maciej Czapski, an archaeologist from the University of Warsaw.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researcher also mentions that spending numerous hours in libraries in London and Rimini helped with the preparations for the excavation work. He was cautious, though, noting that the time spent reading previously published materials and analyzing satellite images did not ensure success.
“We were lucky to have started digging in the right place. Just a 500-600 m shift of the starting point would have resulted in finding nothing. Our discovery is a significant contribution to the general state of research on the Roman limes – the system of Roman border fortifications, erected on the outskirts of the empire, especially vulnerable to raids’, says Czapski.
The main focus of the Polish-Moroccan team is determining how the Romans maintained the acquired territories and what were their contacts with the local population.

The watchtower has yet to be definitively dated. Archaeologists believe Antoninus Pius, Marcus Aurelius’ predecessor who ruled from 138 to 161 A.D., may have built and maintained defenses at the location between the first and third centuries A.D. At this time, epigraphic evidence points to increasingly tense relations between the Berber population and the Roman administration, bad blood that would boil over during Marcus Aurelius’ reign.
Volubilis was founded in the third century B.C. by Carthaginian colonists at the foot of Zerhoun mountain. It was part of the kingdom of Mauretania (at one point the capital), which was ruled by a dynasty of Berber kings who were allies of Carthage. Volubilis was annexed by Rome along with the other North African colonies following the fall of Carthage at the end of the Third Punic War in 146 B.C.
Under Roman rule, the city thrived by exporting agricultural products like grains and olive oil as well as providing wild animals for gladiatorial fights. However, it was on the outskirts of the empire’s borders, and tensions with the Berber tribes around the Romanized city grew so quickly that Marcus Aurelius (r. 161-180 A.D.) had a massive circuit of defensive walls built around it. Around 280 A.D., amid the political and military turbulence of the Third Century Crisis, Roman rule finally came to an end. In the late fourth century, an earthquake caused Volubilis itself to collapse.
Cover Photo: El Mellali site with visible remains of the tower. Photo: Karol Bartczak