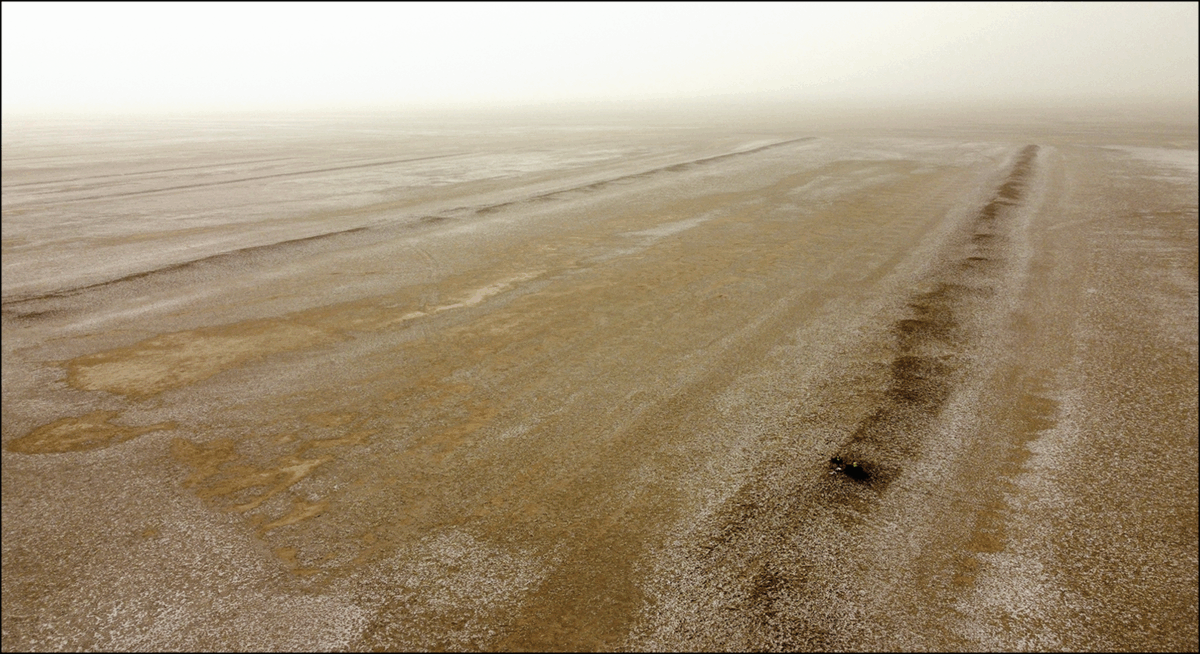
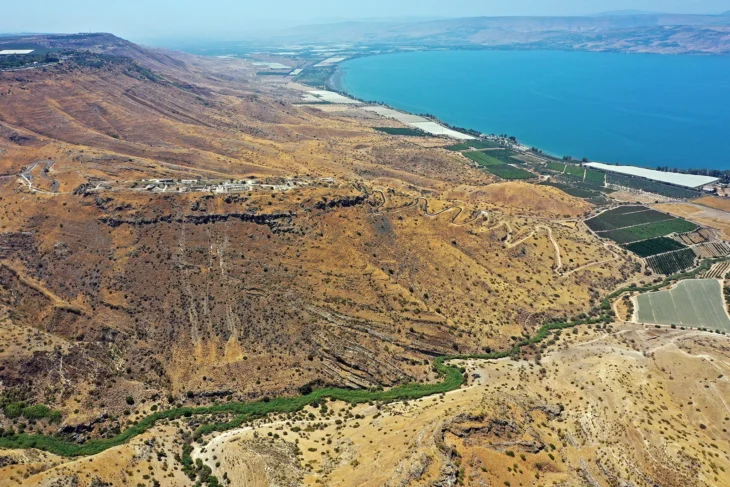
A recent archaeological study has unveiled compelling evidence of a vast agricultural infrastructure in southern Iraq, believed to have been constructed and maintained by enslaved laborers during and after the Zanj Rebellion in the 9th century CE. This discovery sheds new light on the historical significance of the Zanj people and their enduring impact on the region’s landscape.
Published in the journal Antiquity, the research offers the first scientific dating of an extensive network of canals and ridges across the Shatt al-Arab floodplain, illuminating the long-overlooked legacy of enslaved laborers in early Islamic history.
Rediscovering the Zanj Legacy
The Zanj Rebellion (869–883 CE) was a major uprising against the Abbasid Caliphate, led by Ali ibn Muhammad, involving enslaved Africans and other marginalized groups. The rebellion, which began near Basra, highlighted the oppressive conditions faced by laborers in the salt marshes of southern Iraq. Despite its eventual suppression, the revolt underscored the significant role of enslaved populations in the region’s socio-economic fabric.
Unveiling the Ancient Agricultural Network
Using high-resolution satellite imagery, radiocarbon dating, and optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) analysis, researchers have mapped more than 7,000 agricultural ridges and irrigation channels. These features span over 500 square kilometers, dating between the late 9th and mid-13th centuries CE.
What makes this discovery extraordinary is its timing: the system was established during or shortly after the Zanj Rebellion—a major uprising led by East African enslaved workers against the Abbasid Caliphate. The archaeological evidence strongly suggests that enslaved or coerced labor was used to construct and maintain this immense infrastructure.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
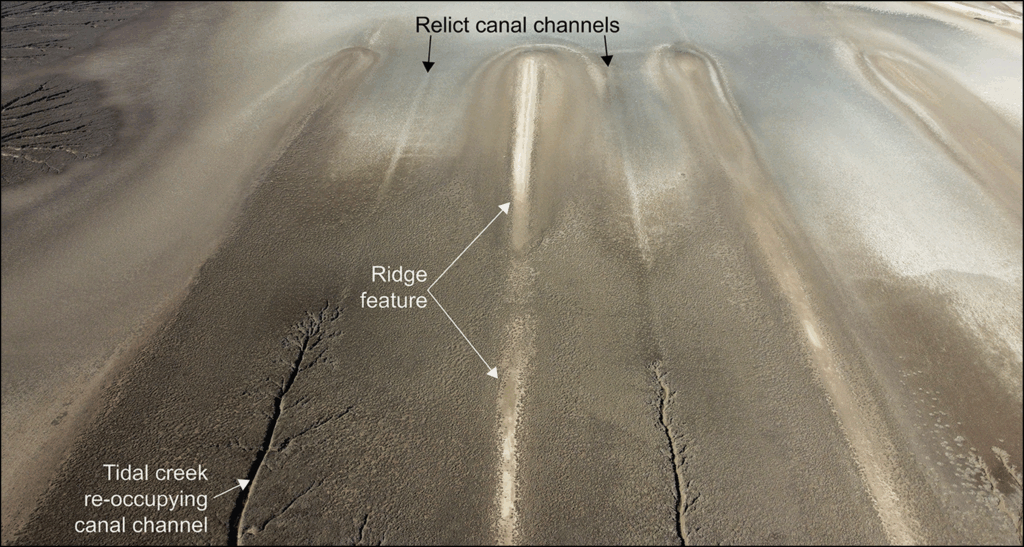
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Zanj Rebellion (869–883 CE) has long been recognized for its scale and brutality, but this new research highlights the lasting environmental and economic impacts of the uprising. Rather than marking the end of slave labor, the study implies that exploitation continued—possibly even intensified—in the rebellion’s aftermath.
The study authors argue that this engineered landscape represents both a physical and political legacy, constructed by marginalized people whose voices have been historically silenced.
Dr. Jaafar Jotheri, a participating archaeologist from the University of Al-Qadisiyah, emphasized the importance of the discovery in an interview with AP News, stating: “Their history has not been actually written or documented very well in our history,” highlighting the urgent need to preserve these structures as part of Iraq’s national heritage.
A Revival of Archaeological Interest in Iraq
This study arrives amid a resurgence of archaeological endeavors in Iraq, following decades of conflict and artifact looting that hindered historical research. The renewed focus aims to reclaim and protect the nation’s rich archaeological heritage, offering deeper insights into its complex past.
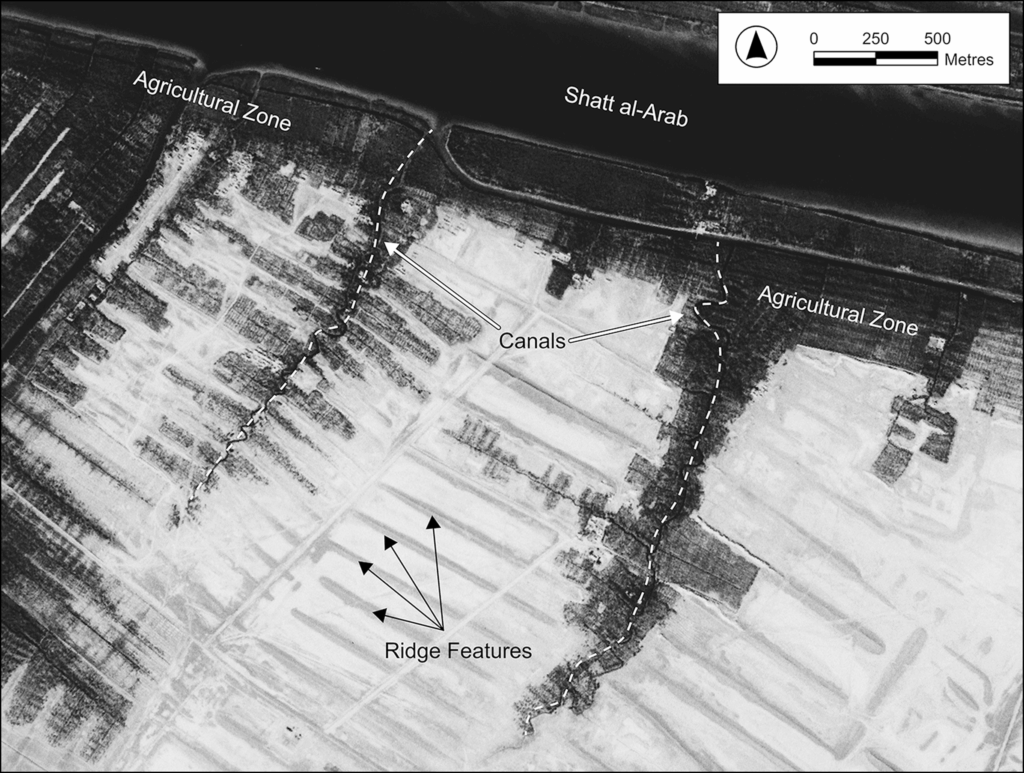
The full research findings are detailed in the journal Antiquity, providing a comprehensive analysis of the agricultural system’s scope and its implications for understanding the socio-economic dynamics of the period.
Brown, P. J., Jotheri, J., Rayne, L., Abdalwahab, N. S., & Andrieux, E. (2025). The landscape of the Zanj Rebellion? Dating the remains of a large-scale agricultural system in southern Iraq. Antiquity, 1–17. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.72
Cover Image Credit: Antiquity- doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.72
















