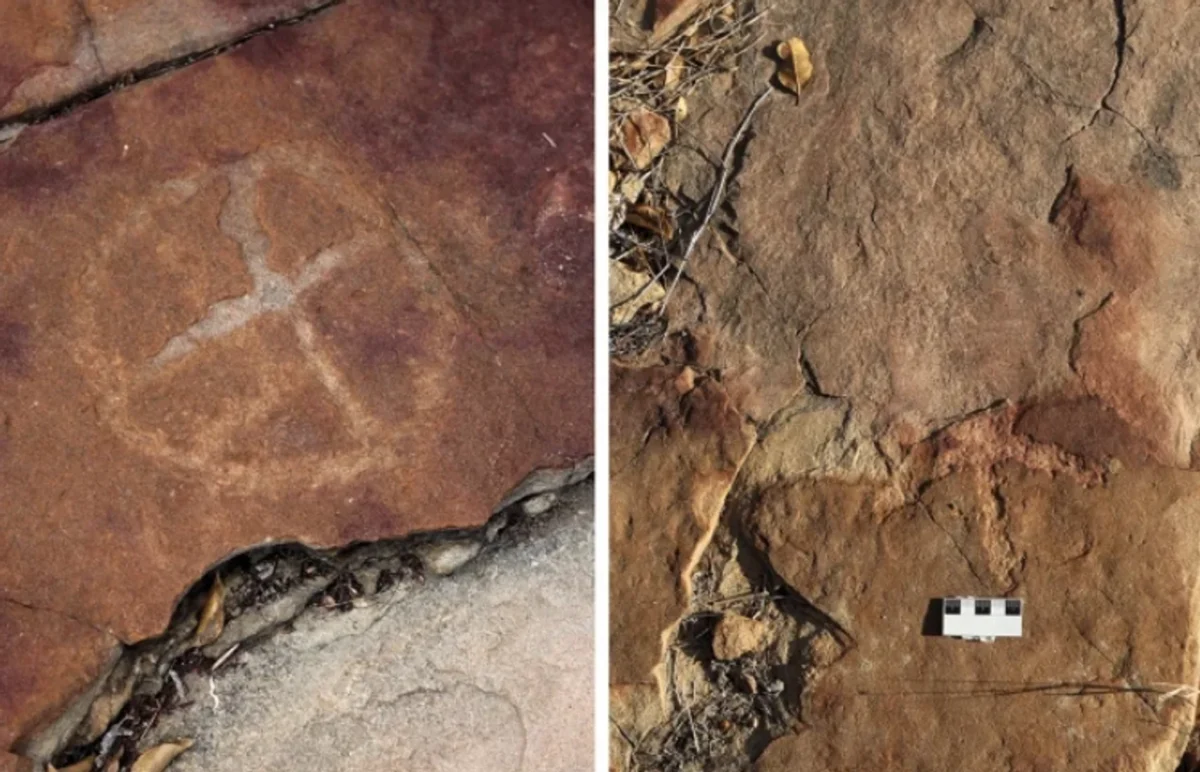
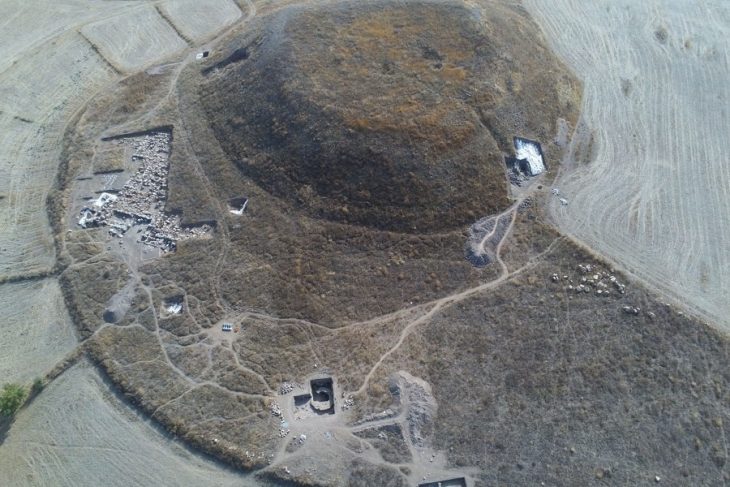
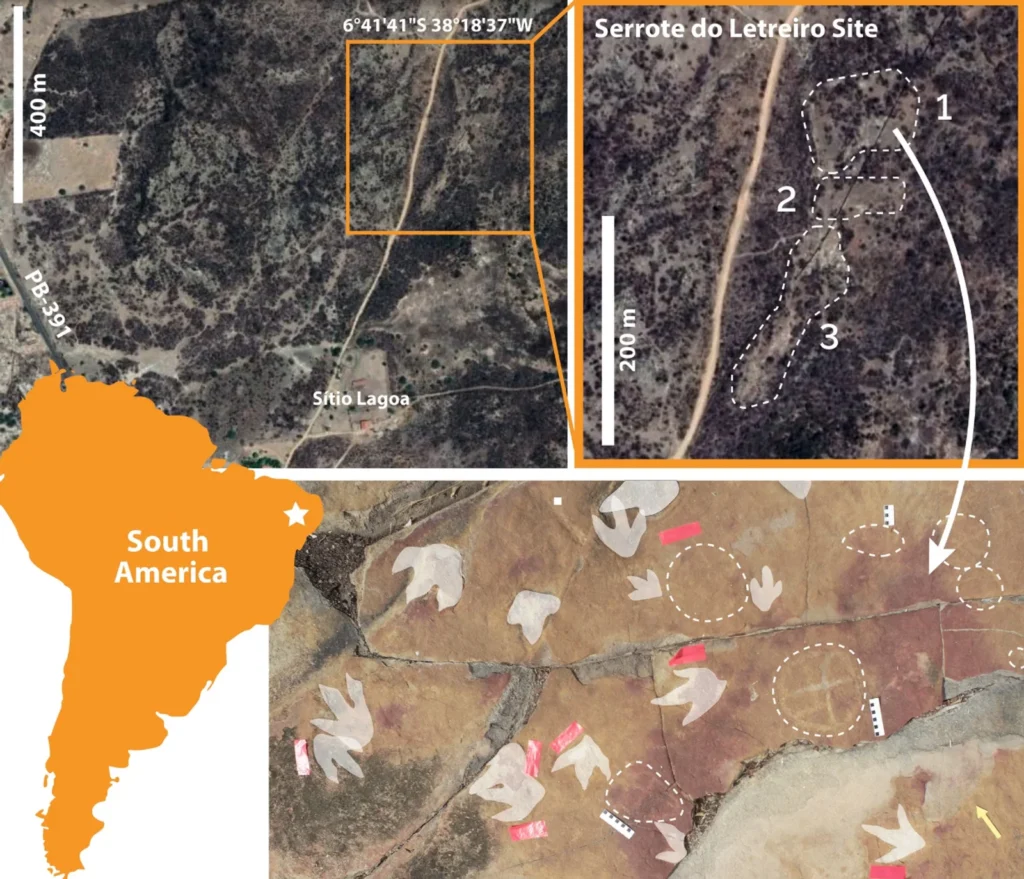
In Brazil, researchers have made an extraordinary discovery of ancient rock art dating back over 9,000 years, found alongside dinosaur footprints from the Cretaceous Period, approximately 66 million years ago. This significant find took place in Serrote do Letreiro, located in the Sousa Basin.
The research has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Led by researchers Leonardo P. Troiano, Heloísa B. dos Santos, Tito Aureliano, and Aline M. Ghilardi, the study indicates that prehistoric hunter-gatherers in Brazil crafted enigmatic rock art designs, referred to as petroglyphs, alongside dinosaur footprints. These discoveries provide important insights into the relationship between paleontology and archaeology, especially at the Serrote site.
The study conducted by Leonardo P. Troiano and his team has uncovered important insights into ancient rock art in Brazil. Although the petroglyphs were initially discovered in 1975, it is only recently that researchers have found these carvings situated near substantial dinosaur footprints, aided by the cutting-edge application of drone technology. These footprints are thought to be from dinosaurs that roamed during the Cretaceous Period, which concluded approximately 66 million years ago.
The researchers propose that prehistoric humans intentionally placed these carvings next to the dinosaur prints, with some petroglyphs located just 2 to 4 inches away and potentially depicting the footprints themselves. This suggests that ancient people were not only aware of the footprints but also interacted with them meaningfully.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Leonardo Troiano, the study’s lead author and an archaeologist from Brazil’s National Institute of Historic and Artistic Heritage, emphasized that the individuals who created the petroglyphs were likely drawn to the footprints, selecting the location specifically because of their presence.
Troiano noted that these ancient humans found the footprints significant, which aligns with the location of Serrote do Letreiro, or “Signpost Hill,” situated near the Valley of the Dinosaurs, a conservation area famous for its numerous fossilized dinosaur footprints.
In 2023, Troiano and his team conducted research with a group of middle-school students who helped survey the site. The students not only learned about the intersection of paleontology and archaeology but also assisted in photographing the specimens. The team identified tracks from various dinosaur types, including meat-eating theropods, long-necked sauropods, and two-legged ornithopods, such as iguanodontian dinosaurs.
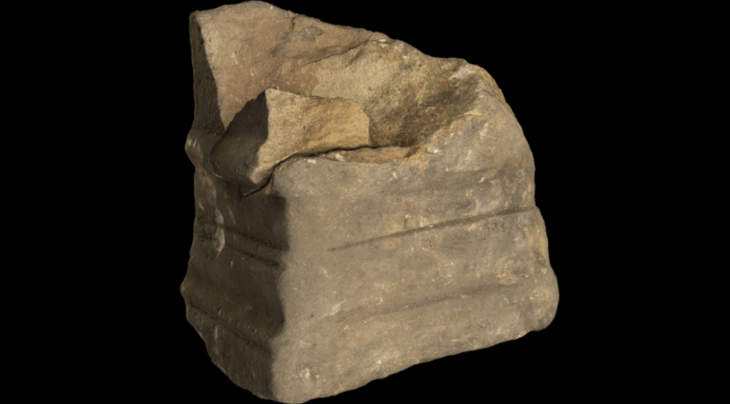
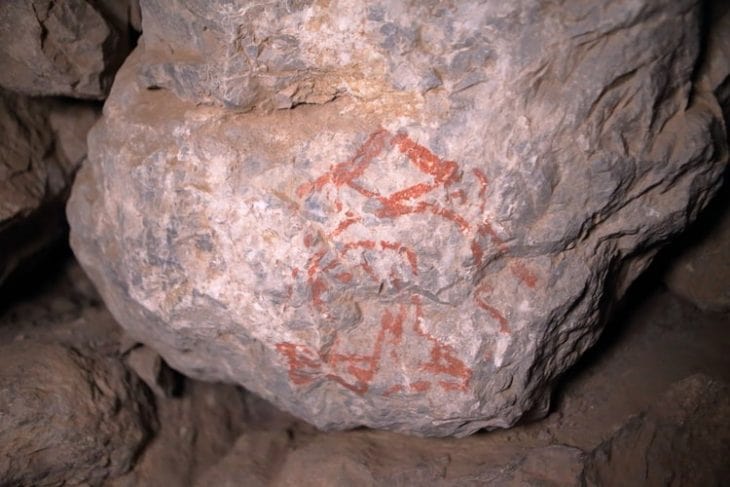
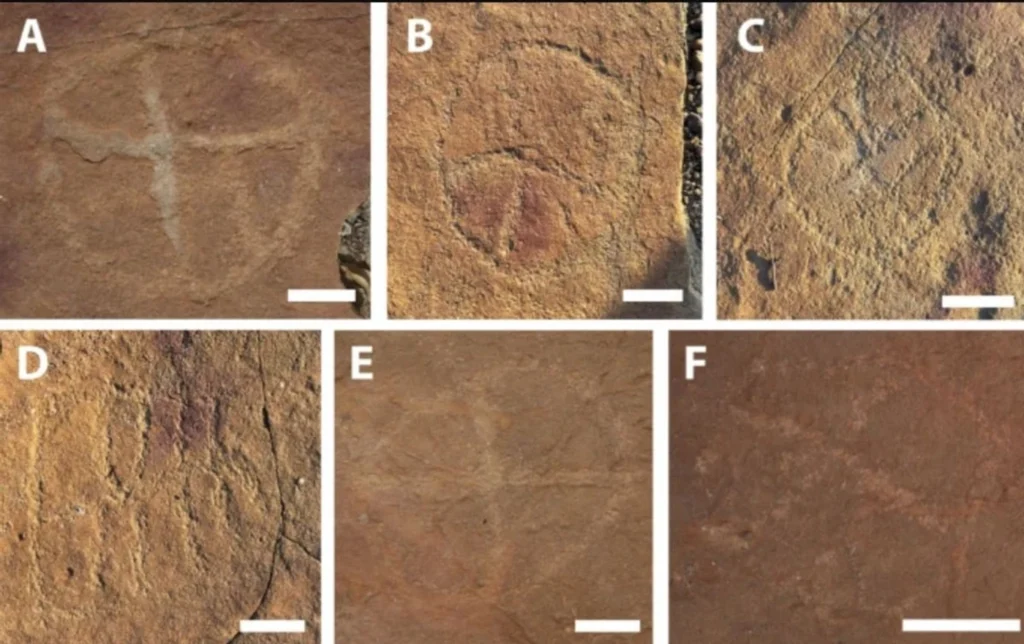
The petroglyphs discovered primarily consist of circles filled with lines and other geometric shapes, attributed to humans who lived in the region between 9,400 and 2,620 years ago. Troiano described these ancient people as small, seminomadic groups of hunters and gatherers who utilized stone tools. The rock carvings were created using two techniques: perforation and scraping. Perforation involves using a stone hammer to create depressions, while scraping entails rubbing a stone against the surface to form engravings.
The petroglyphs offer crucial evidence about the historical population and shed light on the rituals and practices of that time. “I think rock art creation was embedded in some sort of ritual context: people gathering and creating something, perhaps utilizing some psychotropics,” said Troiano, adding that these people were interested in “what the footprints represent.”

Supporting Troiano’s hypothesis, Jan Simek, a distinguished professor of anthropology at the University of Tennessee, remarked that the study presents a compelling example of how ancient people observed and integrated fossils into their spiritual experiences and interpretations. He noted that this case exemplifies the human tendency to connect the spiritual realm with unexplained phenomena in the surrounding world.
Troiano, L.P., dos Santos, H.B., Aureliano, T. et al. A remarkable assemblage of petroglyphs and dinosaur footprints in Northeast Brazil. Sci Rep 14, 6528 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56479-3
Cover Image Credit: Journal Scientific Reports