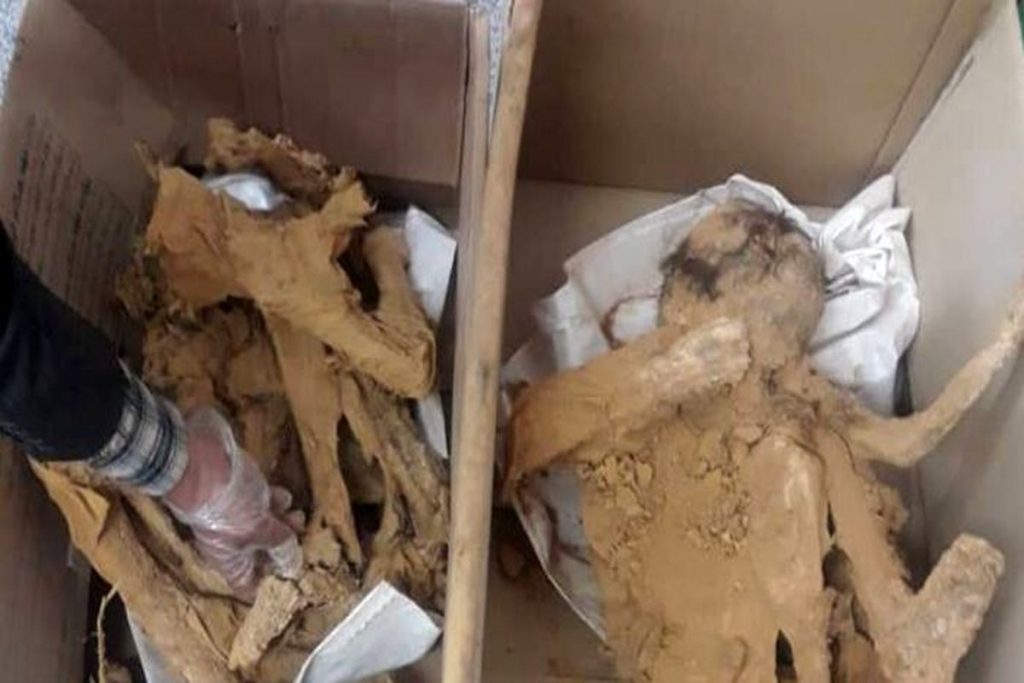
Archaeologists from the University of Tehran have discovered the remains of children dating back 3,000 years during excavations in an ancient cemetery in the Segzabad region of Qazvin province in central-west Iran.
The excavations, conducted under the supervision of Dr. Mustafa Deh Pahlavan found the remains of some children along with babies and fetuses, also found the remains of two horses, two goats, and a sheep.
The discovery made by Iranian archaeologists was made in an area of five square meters.
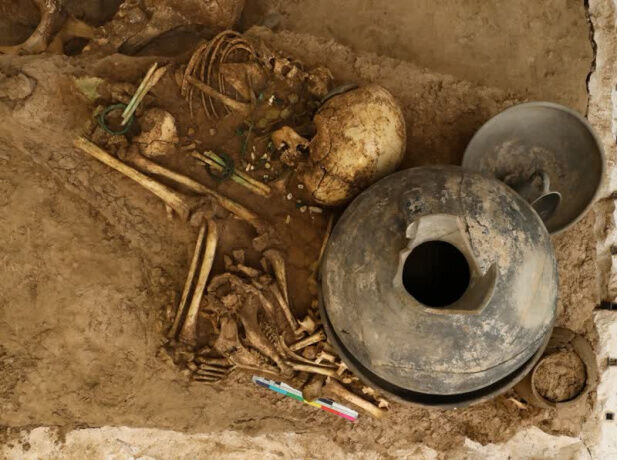
“This complex with an area of five square meters and a height of 120 cm, weighing about 10 tons, includes the remains of nine children, a baby, and a fetus, the remains of two adult horses, two goats, and a sheep,” Dr. Mostafa Dehpahlavan said.
Dehpahlavan, who presides over the Institute of Archeology of the University of Tehran, stated that the foundation work has three parts, adding the first part contains the burial remains of a child along with the remains of an immature goat.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dehpahlavan said: In the eastern cemetery of Qara Tepe, important evidence of five layers of burials and graves on top of each other was obtained on a wide scale. In this cemetery, the graves do not have a specific direction. Their borders are surrounded by several clay ridges. Aborted fetuses and babies were buried in clay cooking pots. Without exception, the remains of animals such as goats, immature sheep, cows, camels, and horses were found in all the graves, which indicates that animals were buried next to the dead.

Based on criteria such as the growth of teeth and the length of long bones, the child’s skeleton is estimated to be less than six years old.
In describing the second part, the archaeology said: “In this part, the burial remains of two adult horses of different breeds can be seen. First, the remains of an adult horse lying on its left side without a skull. Another smaller adult horse (probably of the Caspian breed) was buried in a huddled form on its right side. Its skull is above the surface of the body in a semi-raised form. This horse has a necklace with bronze beads and a part of the iron bridle of this horse can be seen in the mouth area.”
In his explanation about the third part of this collection, Dehpahlavan stated: This part contains human and animal remains that are in a very chaotic state. Based on the number of visible skulls, a total of eight people were buried in this section. Next to a gray clay cave, the remains of a human fetus can be seen.
In addition, an adult sheep skull can be identified next to the skulls of human fetuses. Also, a container with a vertical handle and a small jug along with a part of the body of a pot with pea color and rope decoration constitute the pottery findings of this section.
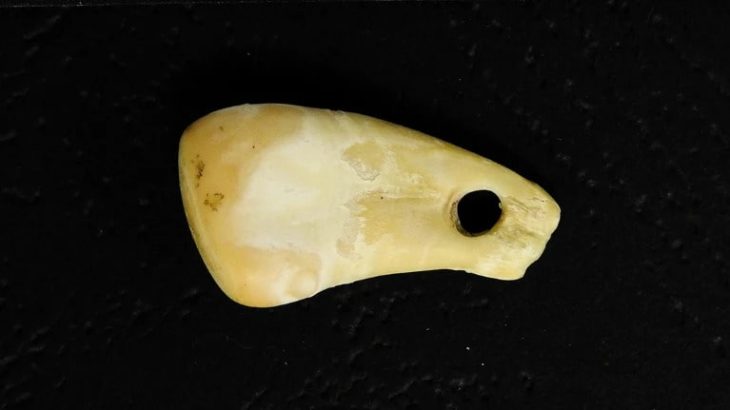
The cemetery also found a child’s skeleton next to clay dishes, which can attest to his special social status, as well as burial ornaments like bronze bracelets, a ring, and the remnants of a necklace made of stone, bronze, and ivory beads.
The discovered collection has been moved to Segzabad municipality for display and preservation in accordance with conservation and restoration standards due to the unfavorable conditions in the Qara Tepe cemetery.