A new study of stone tools from southern China reveals the earliest evidence of rice harvesting, dating back 10,000 years. The researchers discovered two methods of harvesting rice, which aided in the domestication of rice.
Wild rice differs from domesticated rice in that when the seeds are ready to be shed, the mature wild rice naturally scatters them to the ground, whereas the mature seeds of domesticated rice remain on the plants.
To harvest rice, some sort of tool would have been required, and the use of a tool meant that early rice cultivators were selecting the seeds that primarily remained on the plants. Domestication occurred as the proportion of seeds that remained on the plants increased over time.
“For quite a long time, one of the puzzles has been that harvesting tools have not been found in southern China from the early Neolithic period or New Stone Age (10,000 – 7,000 BCE) — the time period when we know rice began to be domesticated,” said lead author Jiajing Wang, an assistant professor of anthropology at Dartmouth, in a statement. “However, when archaeologists were working at several early Neolithic sites in the Lower Yangtze River Valley, they found a lot of small pieces of stone, which had sharp edges that could have been used for harvesting plants.”

The team’s early hypothesis was that some of those small stone pieces were tools that harvested rice, which the results confirm.
In the Lower Yangtze River Valley, the two earliest Neolithic culture groups were the Shangshan and Kuahuqiao.
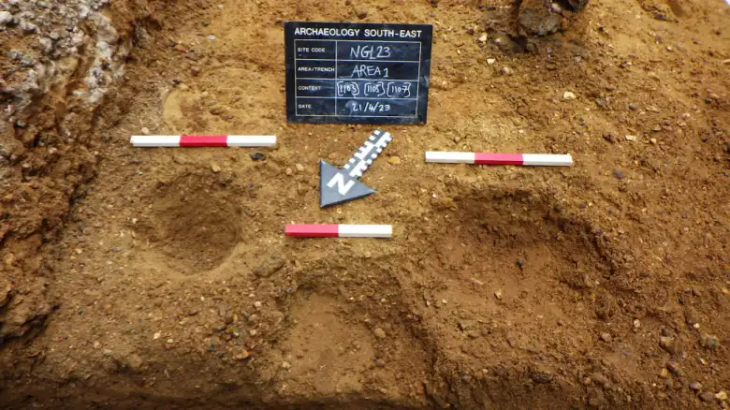
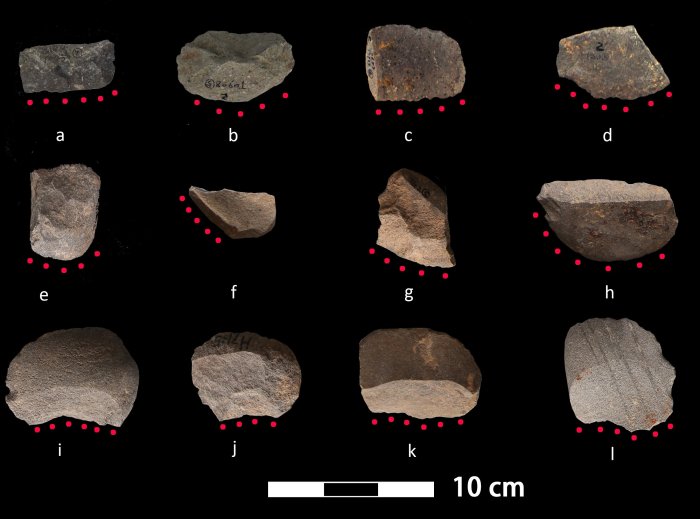
The researchers examined 52 flaked stone tools from the Shangshan and Hehuashan sites, the latter of which was occupied by Shangshan and Kuahuqiao cultures.
The stone flakes are rough in appearance and are not finely made but have sharp edges. On average, the flaked tools are small enough to be held by one hand and measured approximately 1.7 inches in width and length.
To determine if the stone flakes were used for harvesting rice, the team conducted use-wear and phytolith residue analyses.
For the use-wear analysis, micro-scratches on the tools’ surfaces were examined under a microscope to determine how the stones were used. The results showed that 30 flakes have use-wear patterns similar to those produced by harvesting siliceous (silica-rich) plants, likely including rice.
Fine striations, high polish, and rounded edges distinguished the tools that were used for cutting plants from those that were used for processing hard materials, cutting animal tissues, and scraping wood.
Through the phytolith residue analysis, the researchers analyzed the microscopic residue left on the stone flakes known as “phytoliths” or silica skeleton of plants. They found that 28 of the tools contained rice phytoliths.
“What’s interesting about rice phytoliths is that rice husk and leaves produce different kinds of phytolith, which enabled us to determine how the rice was harvested,” says Wang.
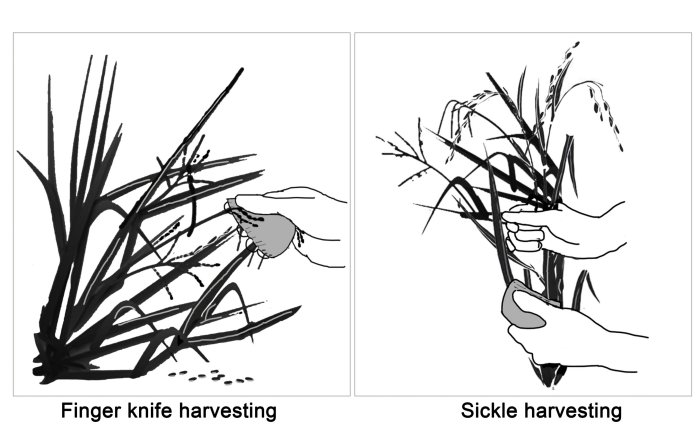
The findings from the use-wear and phytolith analyses illustrated that two types of rice harvesting methods were used — “finger-knife” and “sickle” techniques. Both methods are still used in Asia today.
The stone flakes from the early phase (10,000 – 8,200 BP) showed that rice was largely harvested using the finger-knife method in which the panicles at the top of the rice plant are reaped. The results showed that the tools used for finger-knife harvesting had striations that were mainly perpendicular or diagonal to the edge of the stone flake, which suggests a cutting or scraping motion, and contained phytoliths from seeds or rice husk phytoliths, indicating that the rice was harvested from the top of the plant.
“A rice plant contains numerous panicles that mature at different times, so the finger-knife harvesting technique is especially useful when rice domestication was in the early stage,” says Wang.
The stone flakes however, from the later phase (8,000 – 7,000 BP) had more evidence of sickle harvesting in which the lower part of the plant was harvested. These tools had striations that were predominantly parallel to the tool’s edge, reflecting that a slicing motion had likely been used.
“Sickle harvesting was more widely used when rice became more domesticated, and more ripe seeds stayed on the plant,” says Wang. “Since you are harvesting the entire plant at the same time, the rice leaves and stems could also be used for fuel, building materials, and other purposes, making this a much more effective harvesting method.”
Wang says, “Both harvesting methods would have reduced seed shattering. That’s why we think rice domestication was driven by human unconscious selection.”
















