A team of international researchers led by the University of Arizona reported last year that they had uncovered the largest and oldest Maya monument – Aguada Fénix. That same team has now uncovered nearly 500 smaller ceremonial complexes that are similar in shape and features to Aguada Fénix.
The find transforms previous understanding of Mesoamerican civilization origins and the relationship between the Olmec and the Maya people.
The team’s findings are detailed in a new paper published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour. UArizona anthropology professor Takeshi Inomata is the paper’s first author. His UArizona coauthors include anthropology professor Daniela Triadan and Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Lab director Greg Hodgins.
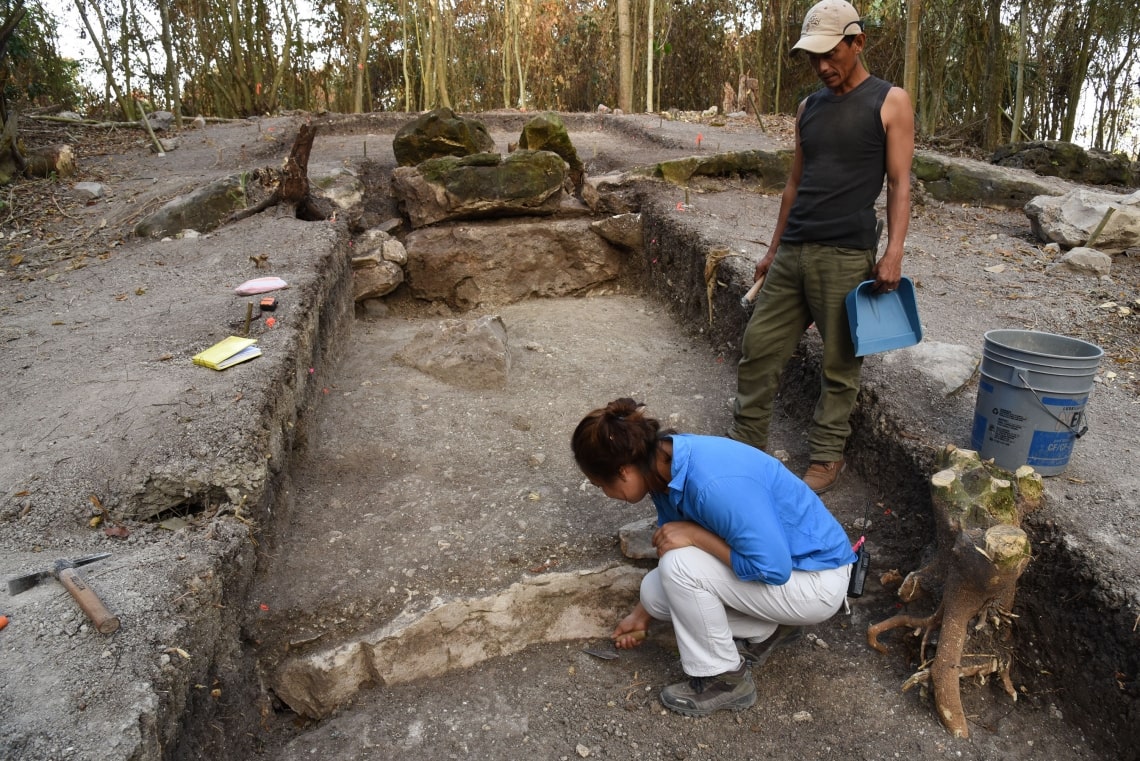
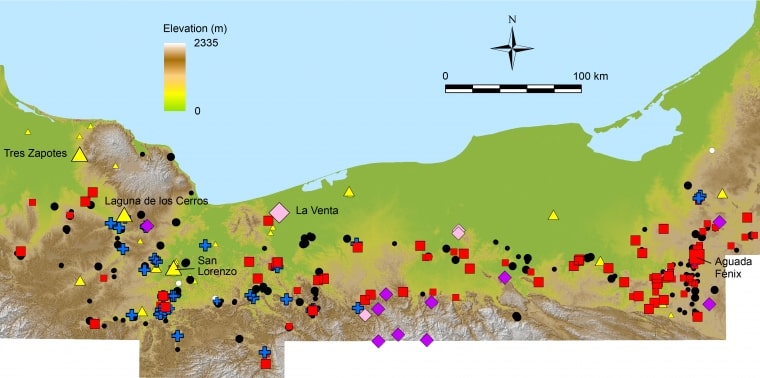
Using data gathered through an airborne laser mapping technique called lidar, the researchers identified 478 complexes in the Mexican states of Tabasco and Veracruz. Lidar penetrates the tree canopy and reflects three-dimensional forms of archaeological features hidden under vegetation. The lidar data were collected by the Mexican governmental organization Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía and covered a 32,800-square-mile area, which is about the same size as the island of Ireland.
Publicly available lidar data allows researchers to study huge areas before they follow up with high-resolution lidar to study sites of interest in greater detail.
“It was unthinkable to study an area this large until a few years ago,” Inomata said. “Publicly available lidar is transforming archaeology.”
Missing Links?
There’s a longstanding debate over whether the Olmec civilization led to the development of the Maya civilization or if the Maya developed independently.
The newly uncovered sites are located in a broad area encompassing the Olmec region and the western Maya lowlands. The complexes were likely constructed between 1100 B.C. and 400 B.C. and were built by diverse groups nearly a millennium before the heyday of the Maya civilization between A.D. 250 and 950.
The researchers found that the complexes share similar features with the earliest center in the Olmec area, San Lorenzo, which peaked between 1400 and 1100 BC. Aguada Fenix in the Maya area and other related sites began to adopt San Lorenzo’s form and formalize it around 1100 BC.
At San Lorenzo, the team also found a previously unrecognized rectangular space.
“The sites are big horizontally but not vertically,” Inomata said. “People will be walking on one and won’t notice its rectangular space, but we can see it with lidar really nicely.”
The researchers’ work suggests that San Lorenzo served as a template for later constructions, including Aguada Fénix.

“People always thought San Lorenzo was very unique and different from what came later in terms of site arrangement,” Inomata said. “But now we show that San Lorenzo is very similar to Aguada Fénix – it has a rectangular plaza flanked by edge platforms. Those features become very clear in lidar and are also found at Aguada Fénix, which was built a little bit later. This tells us that San Lorenzo is very important for the beginning of some of these ideas that were later used by the Maya.”
Sites Were Likely Ritual Spaces
The sites uncovered by Inomata and his collaborators were likely used as ritual gathering sites, according to the paper. They include large central open spaces where lots of people could gather and participate in rituals.
The researchers also analyzed each site’s orientation and found that the sites seem to be aligned to the sunrise of a certain date, when possible.
“There are lots of exceptions; for example, not every site has enough space to place the rectangular form in the desired direction, but when they can, they seem to have chosen certain dates,” Inomata said.
While it’s not clear why the specific dates were chosen, one possibility is that they may be tied to Zenith passage day, which is when the sun passes directly overhead. This occurs on May 10 in the region where the sites were found. This day marks the beginning of the rainy season and the planting of maize. Some groups chose to orient their sites to the directions of the sunrise on days 40, 60, 80, or 100 days before the zenith passage day. This is significant because the later Mesoamerican calendars are based on the number 20.
San Lorenzo, Aguada Fénix, and some other sites have 20 edge platforms along the eastern and western sides of the rectangular plaza. Edge platforms are mounds placed along the edges of the large rectangular plazas. They define the shape of the plazas, and each is usually no taller than about 3 feet.

“This means that they were representing cosmological ideas through these ceremonial spaces,” Inomata said. “In this space, people gathered according to this ceremonial calendar.”
Inomata stressed that this is just the beginning of the team’s work.
“There are still lots of unanswered questions,” he said.
Researchers wonder what the social organization of the people who built the complexes looked like. San Lorenzo possibly had rulers, which is suggested by sculptures.
“But Aguada Fénix doesn’t have those things,” Inomata said. “We think that people were still somehow mobile because they had just begun to use ceramics and lived in ephemeral structures on the ground level. People were in transition to more settled lifeways, and many of those areas probably didn’t have much hierarchical organization. But still, they could make this kind of very well-organized center.”
Inomata’s team and others are still searching for more evidence to explain these differences in social organization.
“Continuing to excavate the sites to find these answers will take much longer,” Inomata said, “and will involve many other scholars.”
















