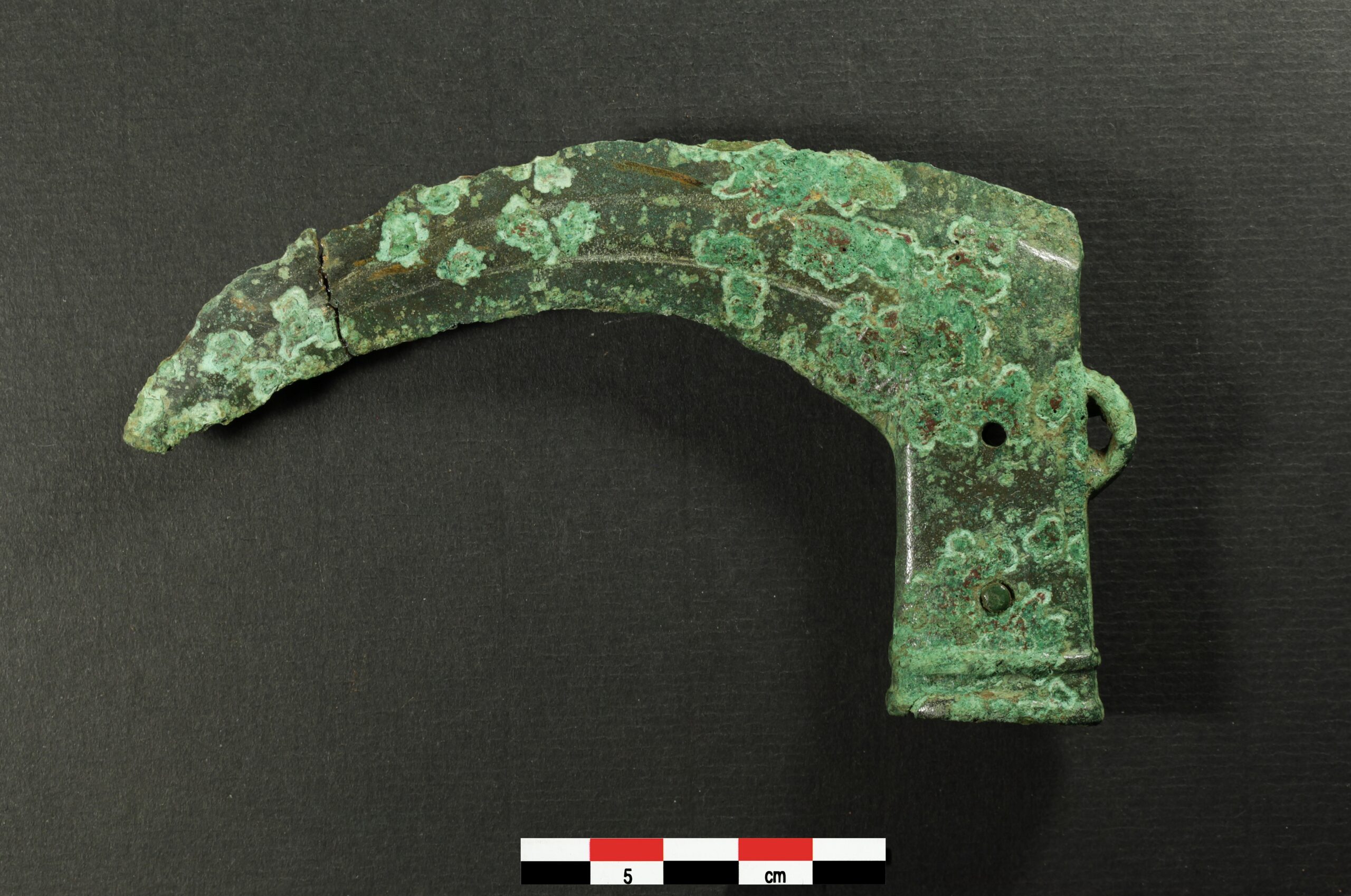
On August 6, 2025, France’s Inrap (Institut national de recherches archéologiques préventives) announced a remarkable archaeological find at Val-de-Reuil, in the Eure department: a rare British-style socketed sickle dating to the Late Bronze Age (10th–9th century BC).
A Legacy Buried in the Seine Valley
The sickle was found inside a small pit at the “Le Suret” site in the lower Seine Valley. Alongside it lay a cordoned pottery vessel and fragments of burnt sandstone, suggesting the deposit may have had ritual or symbolic significance.
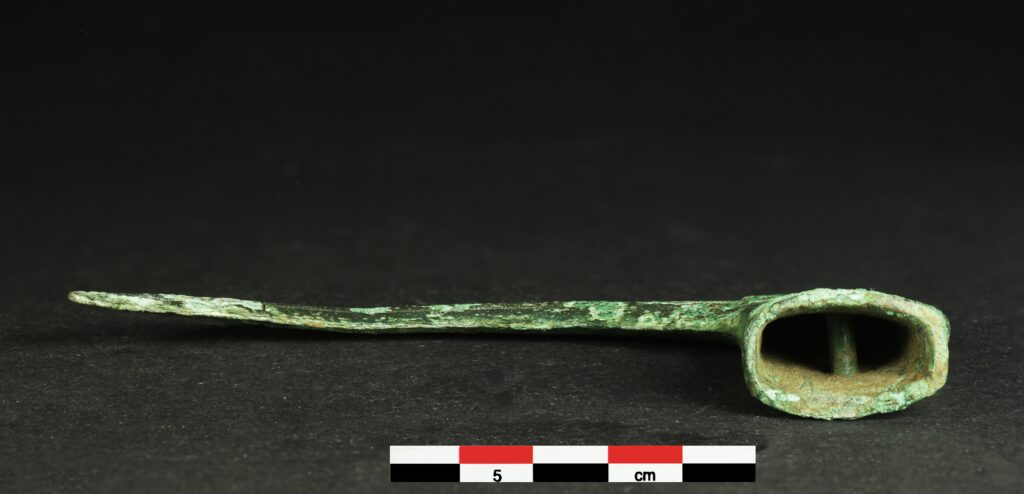
Made from a copper alloy, the tool measures 134 mm in length, 50 mm in height, and weighs 104 g. While the blade shows signs of wear with chipped edges and a broken tip, the socket is remarkably well preserved. It features two decorative mouldings, a lateral suspension ring, and two pin-holes that once secured a wooden handle. One of these pins—likely made from bone—still remains intact. Inside the socket, traces of the original handle were found, though the wood was too degraded for precise identification.
Botanical Clues: Tracing the Handle’s Origins
Specialized wood analysis narrowed the handle’s material to five possible tree species: willow, poplar, alder, hornbeam, or hazel. Evidence points most strongly to willow, a flexible and readily available wood in the region during the period. Radiocarbon dating places the artifact firmly in the Atlantic Final Bronze Age, around the 10th to 9th centuries BC.

A Rare Find That Speaks Volumes
Socketed sickles of this British style are exceptionally rare on the European mainland. Only about a dozen examples have been recorded, most from coastal regions along the English Channel, including the Somme and Seine valleys and the Atlantic seaboard. Before this discovery, only two other specimens were known from the Seine Valley—one in Vernon and another recovered from the Seine in Paris.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Val-de-Reuil sickle underscores the existence of extensive Bronze Age maritime and river trade routes, which connected both sides of the English Channel. These waterways played a central role in the movement of metals, tools, and ideas across what is now northern France and southern Britain.
Bridging Past and Present
Beyond its rarity, the sickle offers valuable insights into prehistoric craftsmanship, agricultural practices, and the cultural links between communities separated by sea but united through trade. Its sophisticated design reflects both functional utility and aesthetic care, marking it as an object of high skill in metalworking.
This discovery contributes to a broader understanding of the Bronze Age exchange systems and the strategic role of river valleys in fostering long-distance connections. It also enriches the archaeological record of the lower Seine Valley, offering a tangible link to a time when metal and water shaped the social and economic landscapes of Europe.
Cover Image Credit: S. Le Maho, Inrap