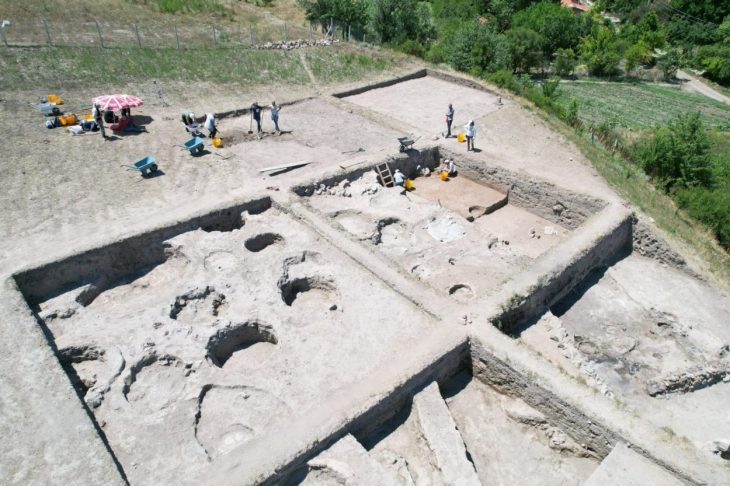
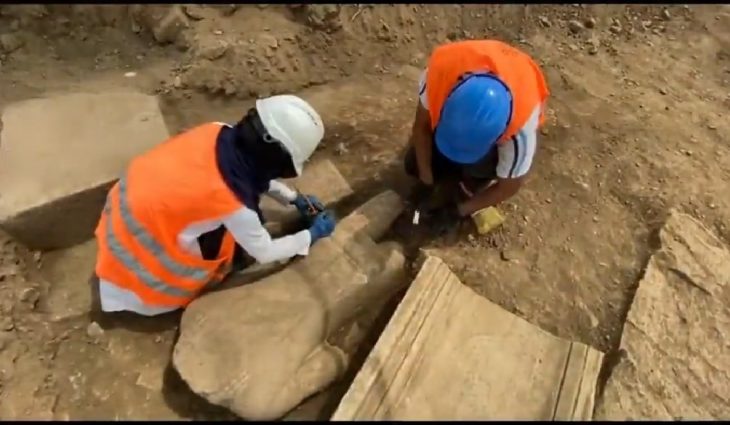
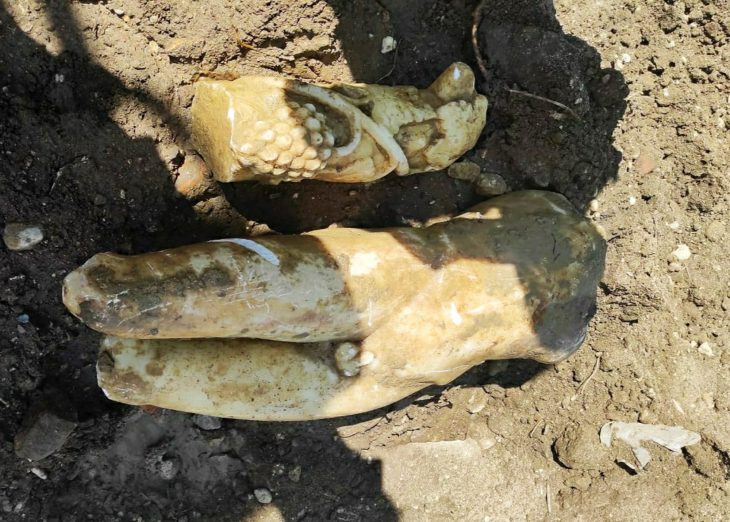
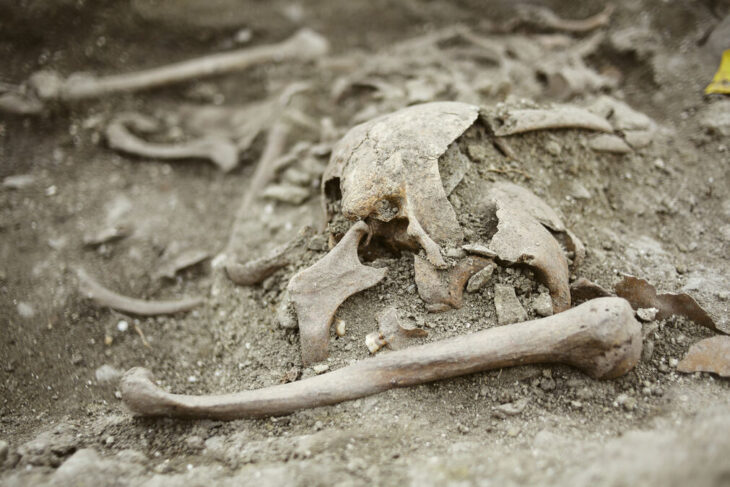
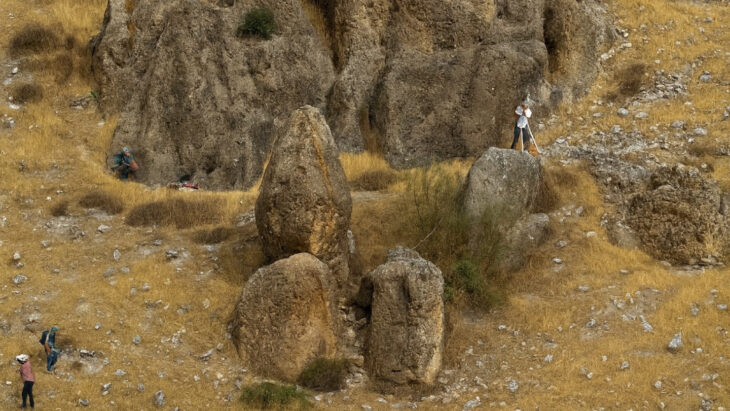
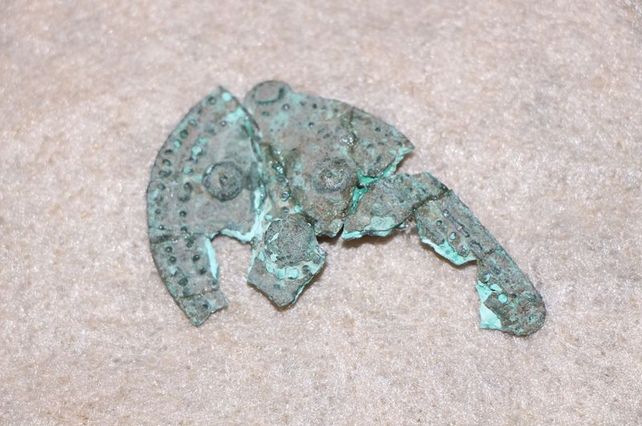
During the Oluz Höyük excavations in Amasya, artifacts dating back to the Med Kingdom period were found, dating back to 2,600 years.
Head of the excavation Professor Şevket Dönmez said, “One of the important results of our excavations this year is that we have reached archaeological findings related to the Med culture for the first time in Anatolian archeology.”
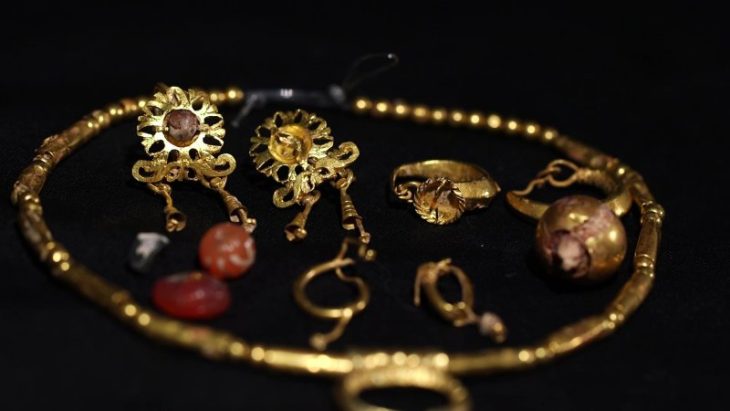
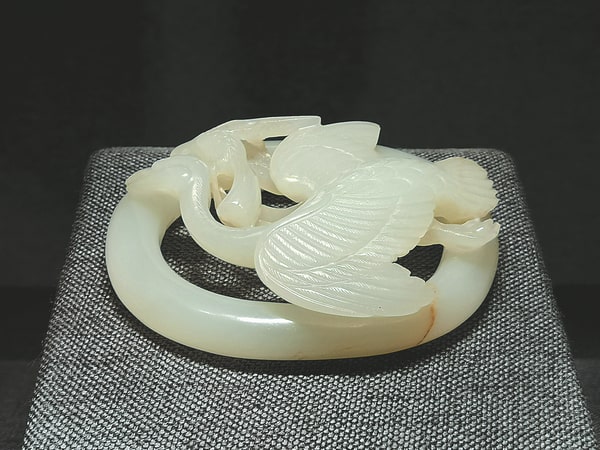
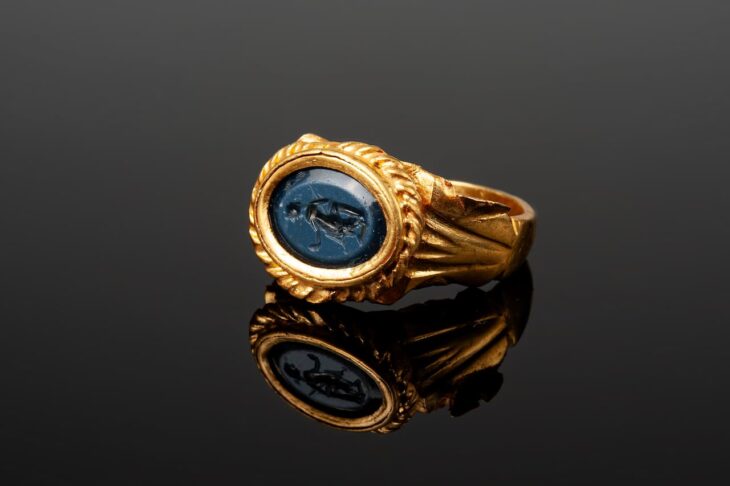
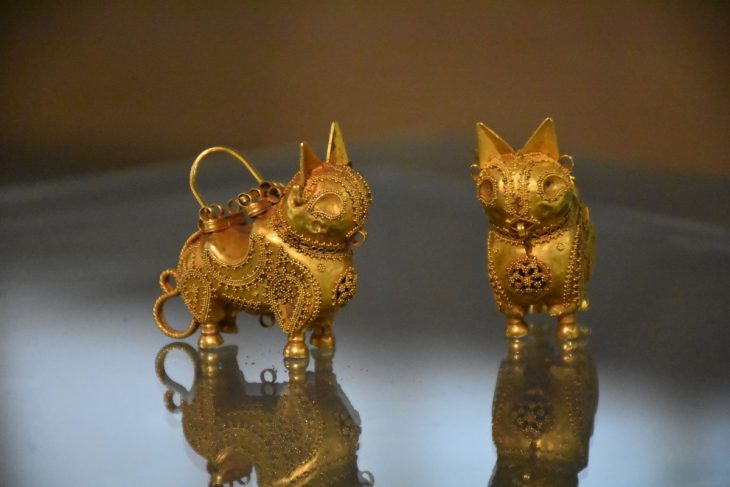
Evaluating the results of this year’s work on the architectural layer, which they describe as the Late Phrygian period, covering the years between 600 and 550 BC, in the 4 layers of Oluz Höyük, Istanbul University Archeology Department Lecturer Prof. Dr. Dönmez said, “We found Medes pottery, a decorated bronze plate, and a bronze arrowhead. These proved the existence of the Medes in Oluz Höyük and the existence of archaeological findings belonging to the Medes in Anatolia,”.

Reminding that the Med Kingdom of Iranian origin conquered Anatolia up to the Kızılırmak in 590 BC and ruled for 40 years, however no findings attributed to this kingdom have been encountered so far, Professor Şevket Dönmez said:
“Archaeologists were always surprised by the scarcity of findings in Anatolia, regarding the Medes, which Herodotus mentioned for pages and states that there were 6 tribes.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
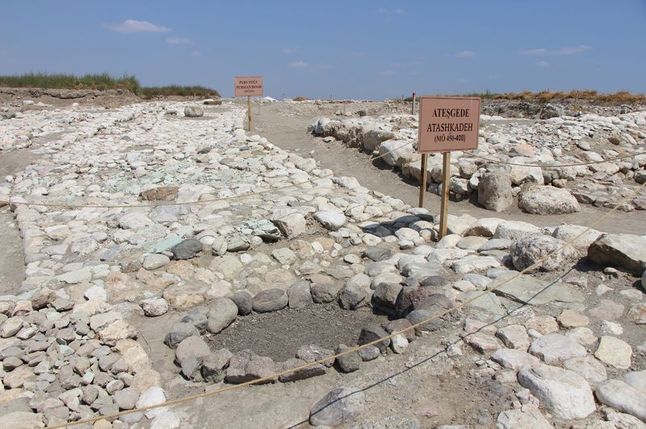
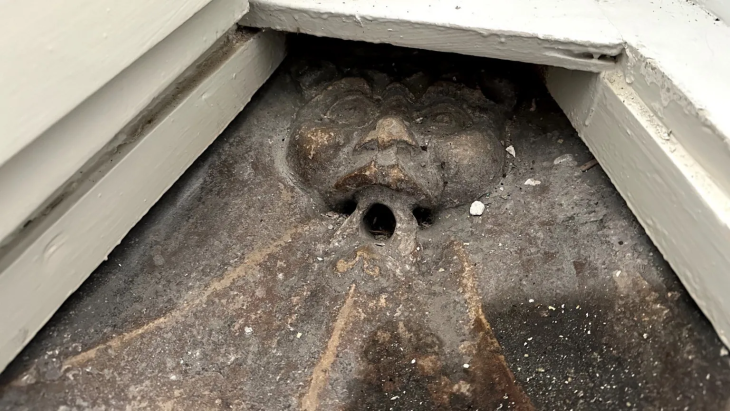
Dönmez also said that the excavations, where they came across a religious complex such as the 2,500-year-old Persian road, the fire houses (Ateşgede) found for the first time in Anatolia, and a multi-column temple, had exciting results every year.

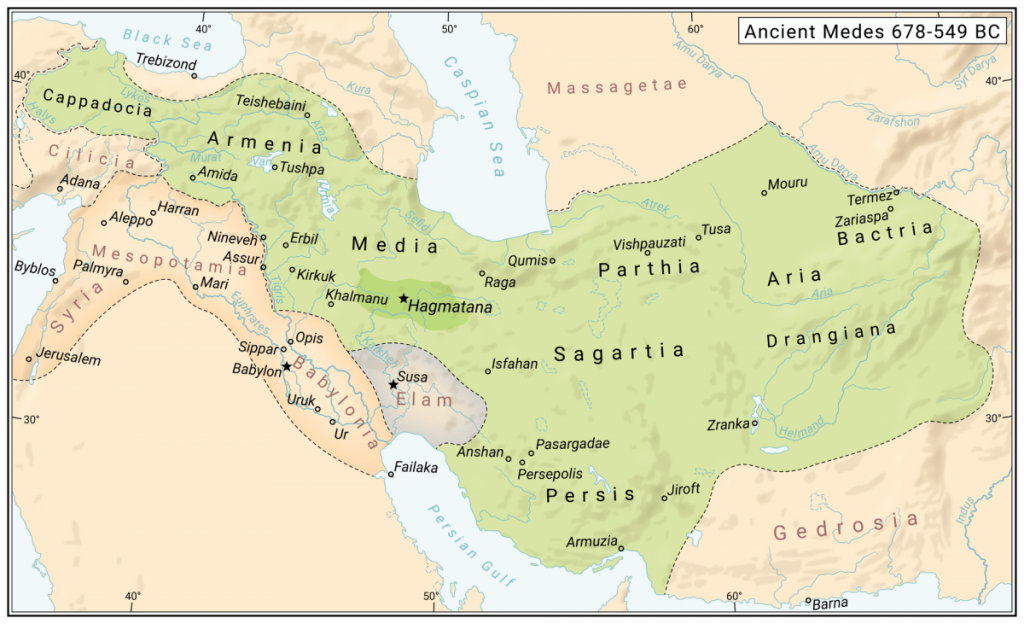
The Medes were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran.
They occupied the mountainous region of northwestern Iran, as well as the northeastern and eastern regions of Mesopotamia in the Hamadan region, around the 11th century BC (Ecbatana). Their establishment in Iran is thought to have occurred in the 8th century BC. All of western Iran and some other territories were under Median rule in the 7th century BC, but their precise geographic extent is unknown.
The accounts of the Medes that Herodotus recorded have left the impression of a strong people who would have established an empire at the beginning of the 7th century BC that lasted until the 550s BC, played a significant role in the fall of the Assyrian Empire, and competed with the strong kingdoms of Lydia and Babylonia.
Oluz Höyük made us distinguish some evidence regarding Anatolian Iron Age archaeology and ancient history that we haven’t noticed until today.
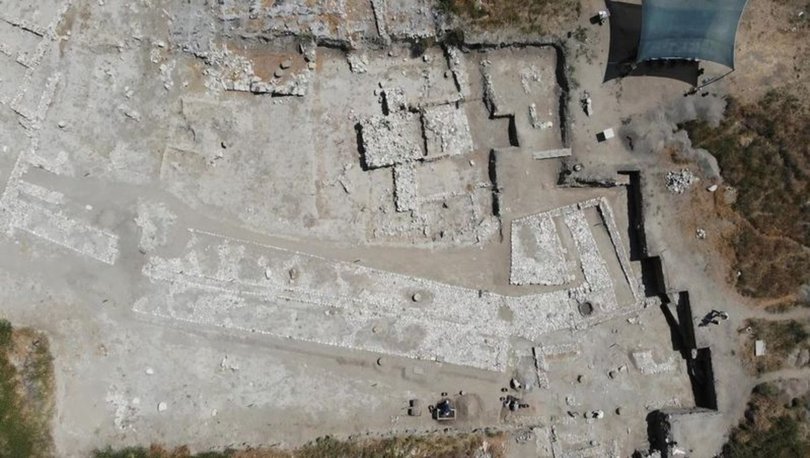
Oluz Höyük, located 25 kilometers west of Amasya, is an ancient city which has rich findings of religious structuring.
During the excavations that have been going on for 15 years, 10 settlement layers were encountered, each of them had a religious structure.
You can read our article about the subject: Evidence of the Birth of Archaic Monotheism in Anatolia found at Oluz Höyük, “Havangah prayer at Oluz Höyük”.
















