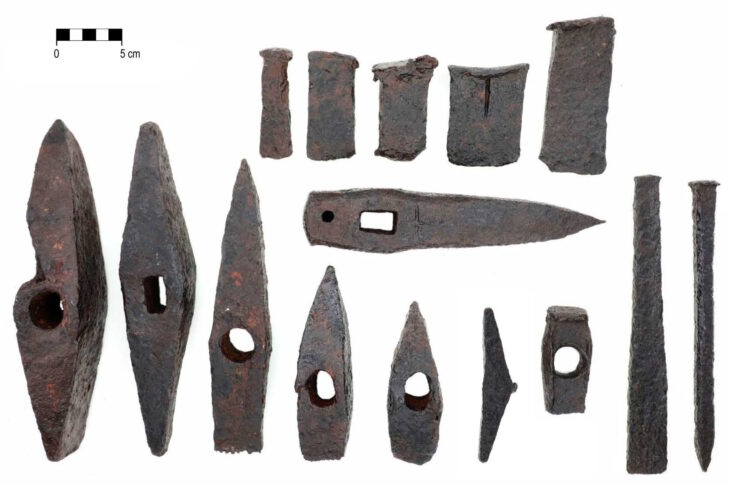
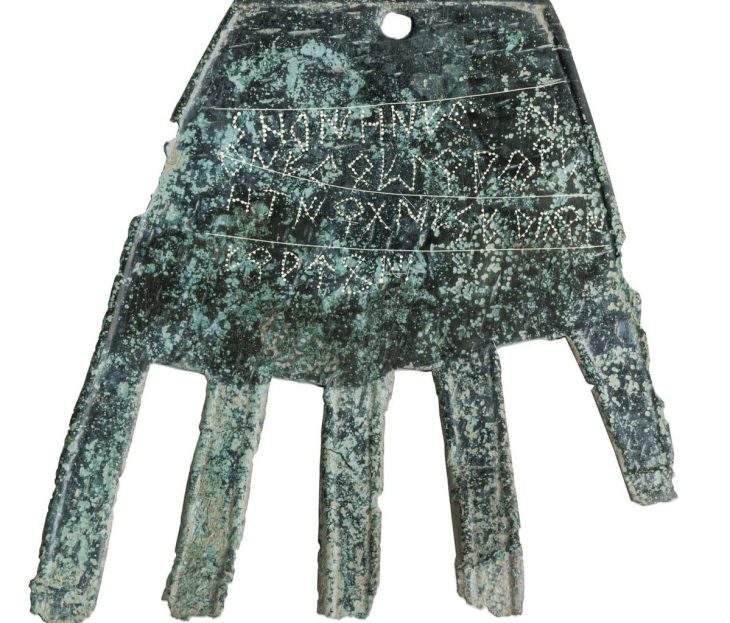
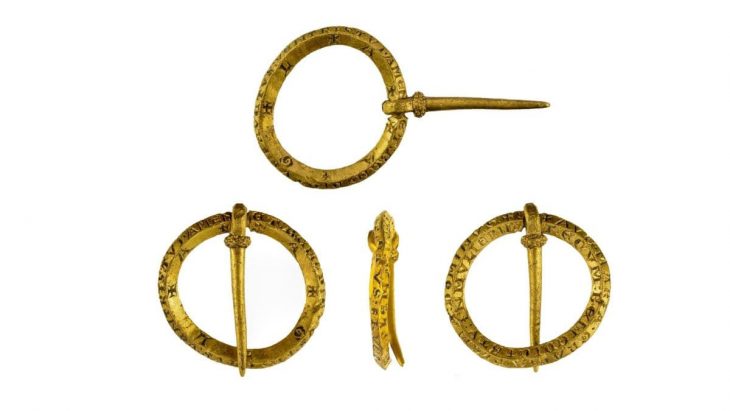
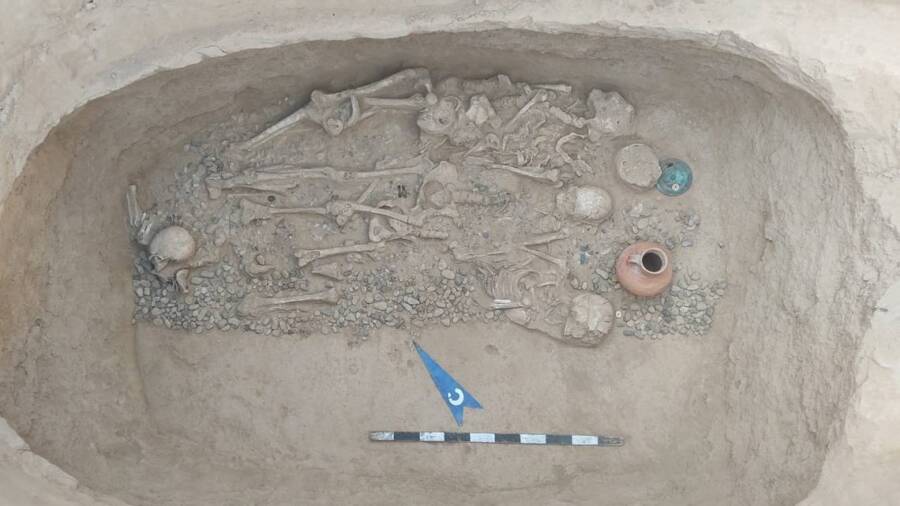
Archaeologists in Kazakhstan have unearthed gold jewelry, arrowheads, and a large, bronze mirror from three burial mounds in the Tolebaitobe cemetery, Turkestan region.
In what is now Kazakhstan, some time ago, some looters discovered a series of old graves. Two of them were looted, and they fled with looted goods. However, they were unaware of a third grave close by. Now, archaeologists have excavated it and discovered a wealth of grave goods.
The artifacts are believed to be created during the reign of the Kangju state, a little-known political entity that governed the area between the fifth and fourth centuries B.C.
The discoveries demonstrate the highly skilled craftsmanship of the area during the period when the Kangju state traded with ancient Rome, ancient China, and the Kushan Empire further south, according to a statement translated by representatives of Turkistan’s regional government.
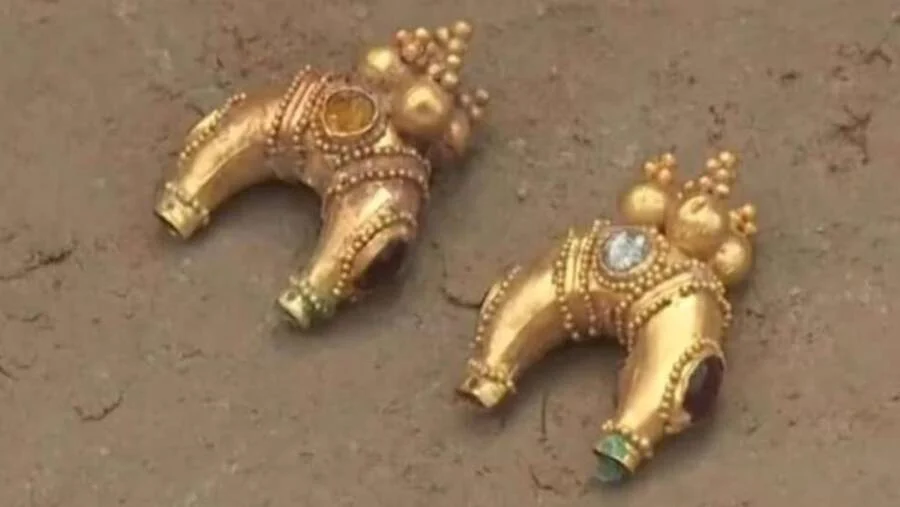
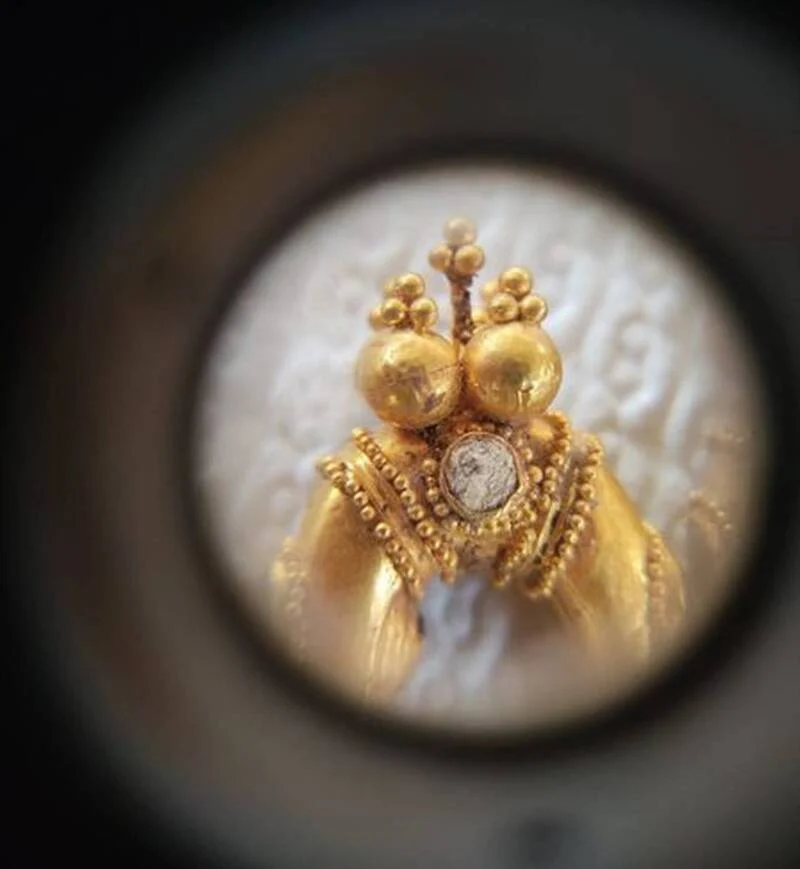
The grave included a pair of moon-shaped earrings decorated with blue amethyst and ruby from the first century B.C.E., a Roman fibula, which would have been used as a pin to fasten clothing, large and small beads to be worn on the hands, a shoe, a belt, a buckle, and arrowheads for hunting birds.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

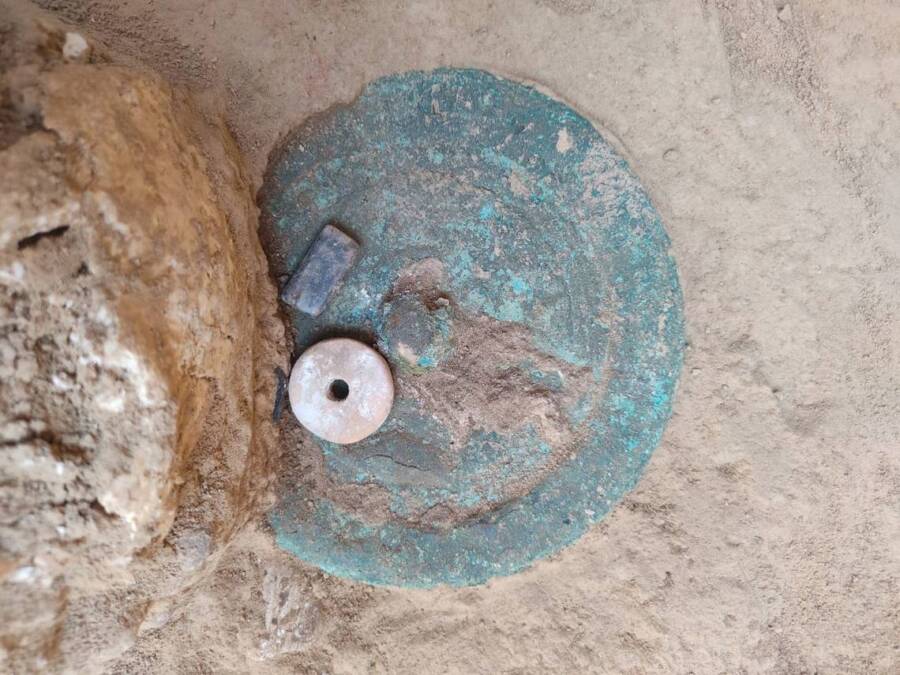
Remarkably, the archaeologists also discovered a circular bronze mirror that seemed to have originated in China during the Han dynasty, which lasted from 206 BCE to 220 CE.
According to the statement, such objects were highly valued throughout Eurasia (similar mirrors have been discovered in Afghanistan and the southern Ural region). It also indicated that the woman buried next to it had been wealthy and influential.
Ozbekali Zhanibekov South Kazakhstan Pedagogical University statement, the items found in the grave suggest that the woman buried there must have been one of society’s elites.

Between the fifth and fourth centuries B.C.E., the mysterious ancient power known as the Kangju state ruled the region, during which time it appears that she lived.
“Looking at the found artifacts, it is possible to know that the [Kangju state] was in contact with strong and powerful empires,” the university statement notes. “Rome, Byzantium, Kushan…[and] China had equal diplomatic relations with the [Kangju state].”

Kangju state was located along the Silk Road. It was thus advantageously placed for trade between East and West.
Because of this, the finding of this old grave and the abundance of grave goods it contained provide a fascinating glimpse into a little-known civilization and one of its elites. Life in the Kangju state offered a taste of many ancient cultures to those who could afford it, such as the woman buried here.
Ozbekali Zhanibekov South Kazakhstan Pedagogical University
Cover Photo: Ozbekali Zhanibekov South Kazakhstan Pedagogical University