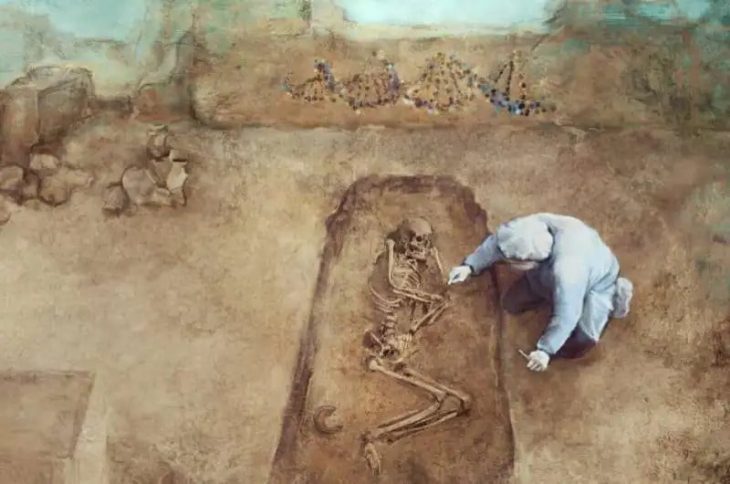
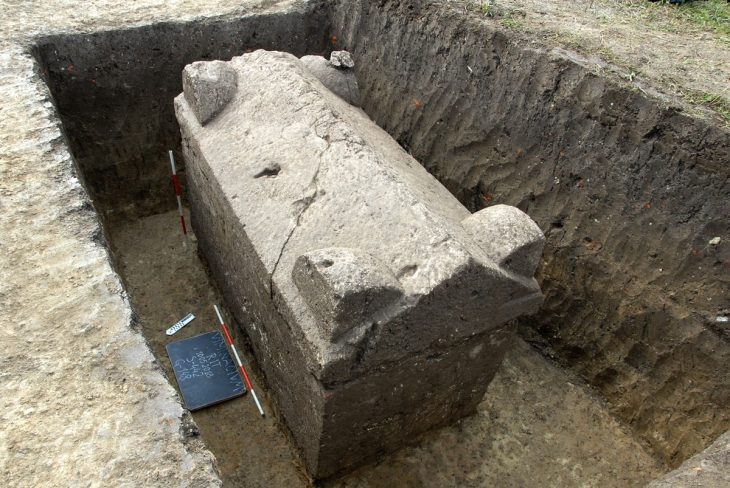
Heinrich Schliemann, a German businessman, excavated the ancient city of Troy in northwest Canakkale province 150 years ago. Archaeologists are still working to restore the damage he made to the historical site today.
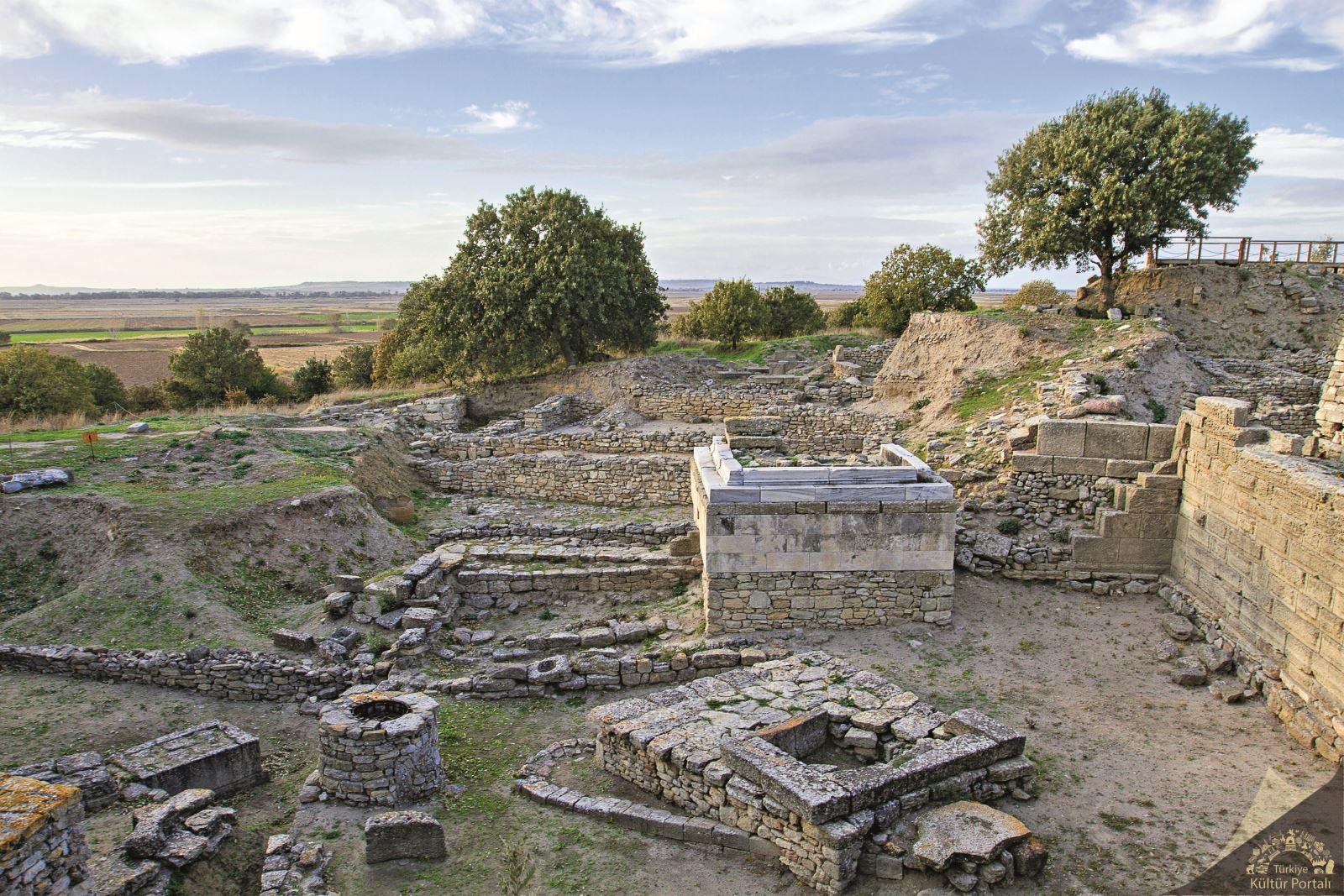
Excavations at Troy’s old city, an open-air museum on UNESCO’s World Cultural Heritage List, provide insight into history. To date, several archaeological finds have been made at the location where the initial excavations were begun 150 years ago.
Professor Rüstem Aslan of the Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University (ÇOMÜ) department of science and department of archeology of letters and head of the excavation of Troy told the Anadolu (AA) agency that Troy was first excavated by Frank Calvert in 1863 and official excavations were carried out first Heinrich Schliemann in 1871. While the work was later resumed by Wilhelm Dorpfeld and Carl W. Blegen, the ancient site has been exposed as one of the important areas of archaeological work in the world.
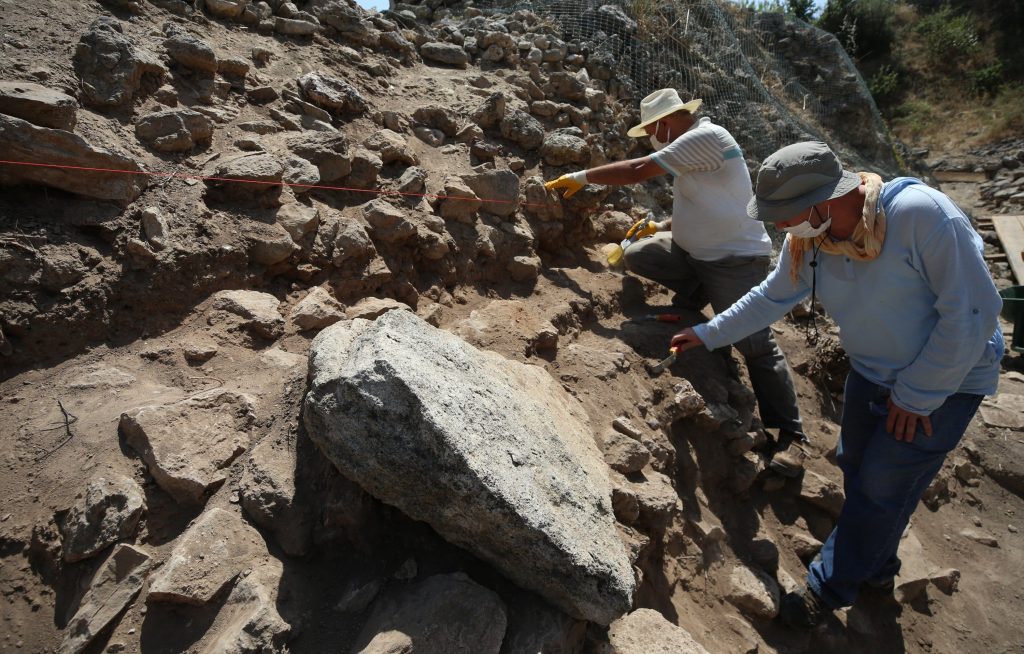

Aslan continued, noting that they continue to excavate the site throughout the year: “Troy has been excavated for 150 years. During the official excavations of Schliemann, which started in 1871, both damages to the site and the theft of some artifacts from the site were two major issues. Recently, we have been mostly working to repair the damage caused during the Schliemann period.”
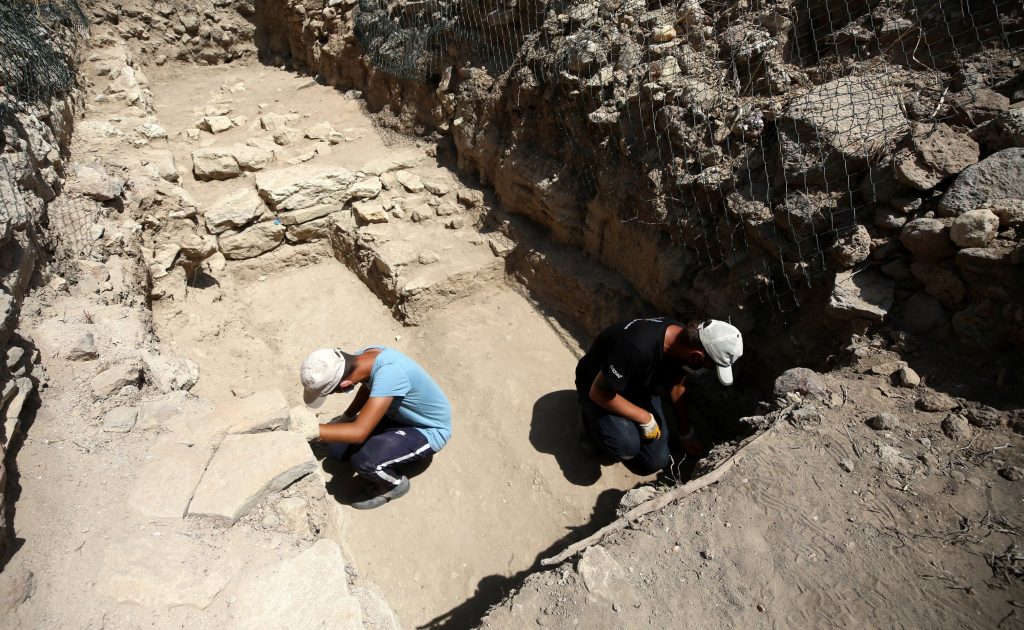

Aslan pointed out that the area where they had been working in the area called “Troy II City Entrance” for the past few years was a research area excavated during Schlieman’s time. Aslan continued: “Schliemann cut the mound from top to bottom and destroyed it. Then, he stole the finds he had unearthed here in 1872. We are trying to eliminate the damage in this area. We are trying to repair what he destroyed, especially in the area called the Troy II castle, perhaps the richest city of the Troy period.”
“We are doing preliminary studies of restoration and conservation here. At the same time, we are trying to explain some of the dating problems of the place he destroyed in the archaeological sense with our findings,” he added.
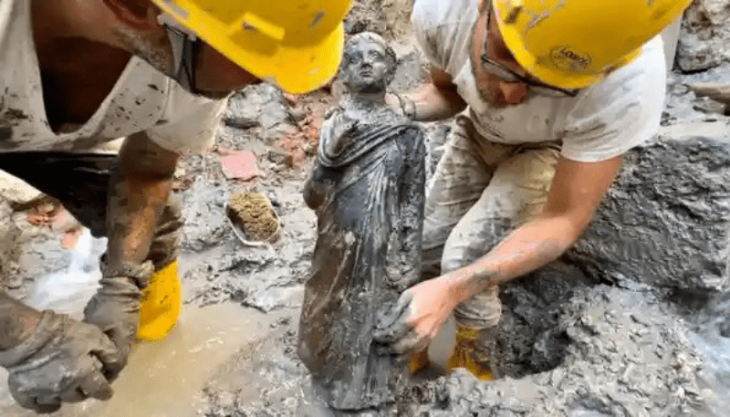
Finally, Aslan hinted that the Troy Museum is the best place to store the treasures excavated and smuggled from these regions and that it is waiting for these artifacts to be returned.