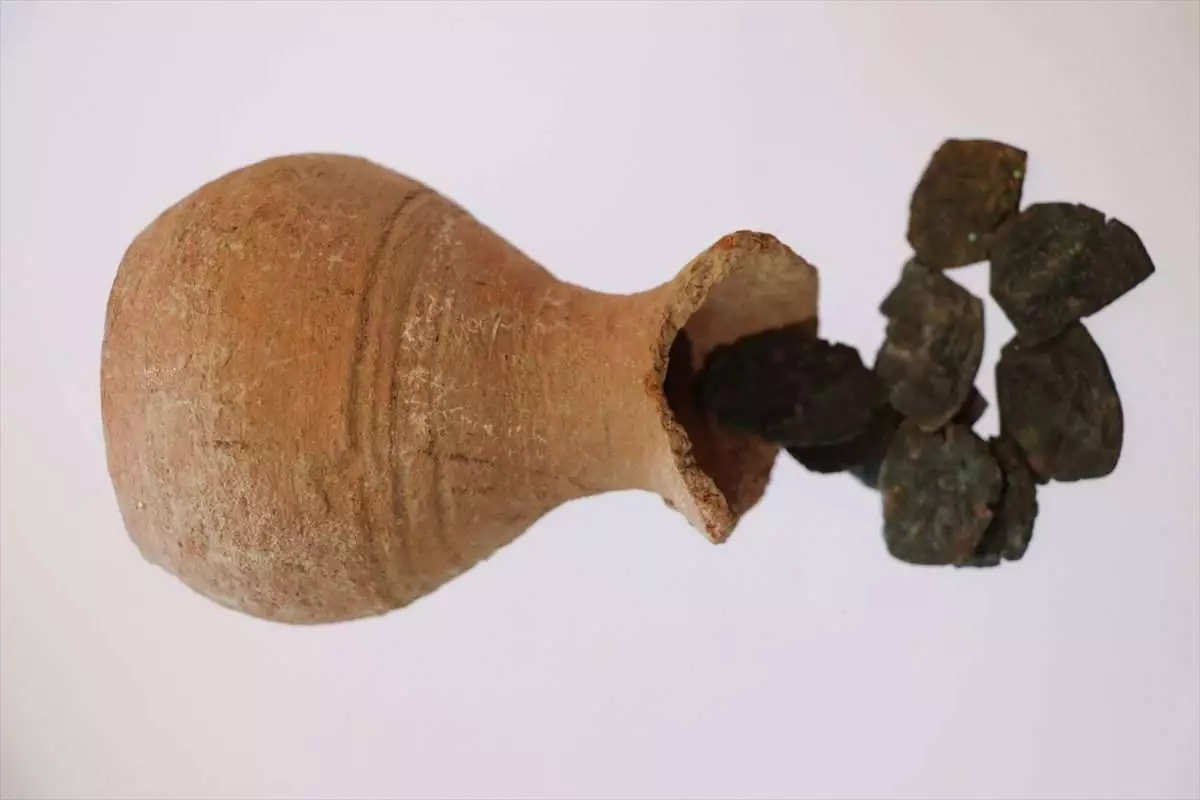
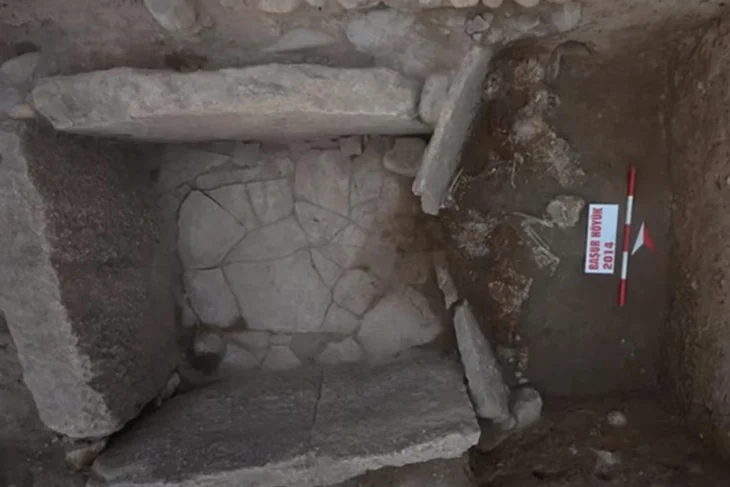
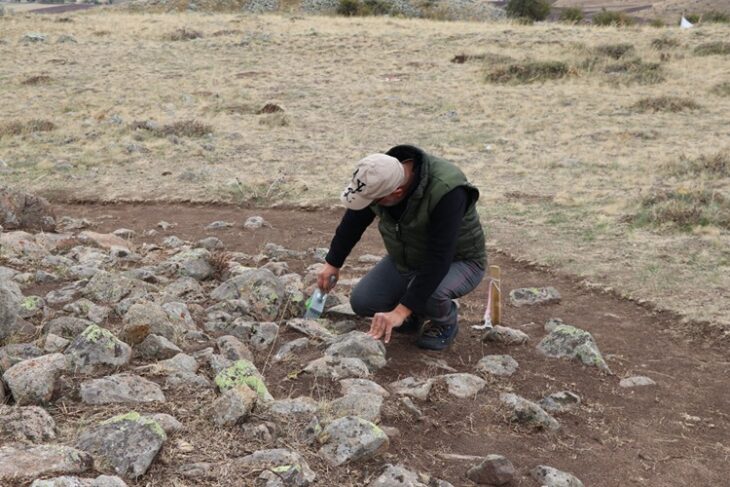
Archaeologists unearthed a collection of 10 coins believed to date back nearly 1,400 years, retrieved from what appears to be a piggy bank in the ongoing excavations at the ancient city of Hadrianopolis in Karabük’s Eskipazar district, Türkiye.
Excavations started in 2003 at the structures in Hadrianopolis and continue in periods under the direction of Ersin Çelikbaş, a lecturer at the Archaeology Department of Karabük University (KBÜ).
The ancient city is known as “Zeugma of the Black Sea” due to its mosaics depicting various animals such as horses, elephants, panthers, deer, and griffons. Zeugma is a mosaic museum in Gaziantep, Türkiye’s southeastern province.
Hadrianopolis, known for its churches decorated with mosaics, has produced important discoveries that include walls, villas, defensive fortifications, rock tombs, theaters, arched and domed structures, and monumental cultic niches.
Discussing the recent findings with Anadolu Agency (AA), Çelikbaş highlighting their efforts to uncover new structures across extensive areas with a dedicated team of approximately 60 individuals.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Explaining the discoveries within a particular building whose exact function remains partially ambiguous, Çelikbaş suggested: “We presume it might have served as a kitchen based on the artifacts found within. Various vessels and kitchen utensils were among the unearthed items. Stratigraphy indicates the building’s prolonged use, though specifics about its final phase remain elusive.”
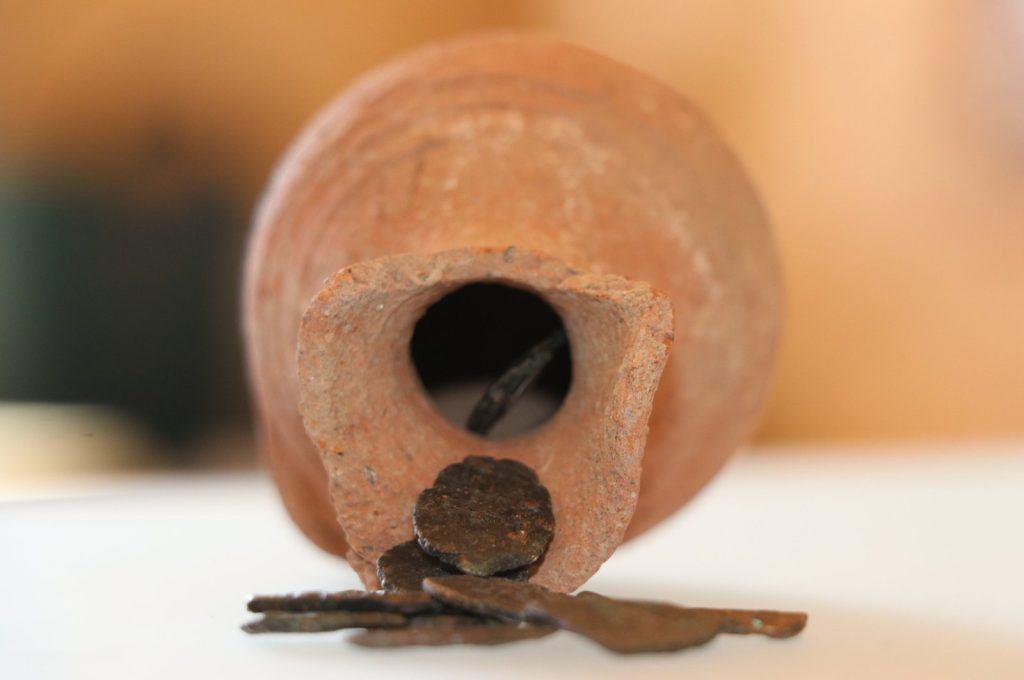

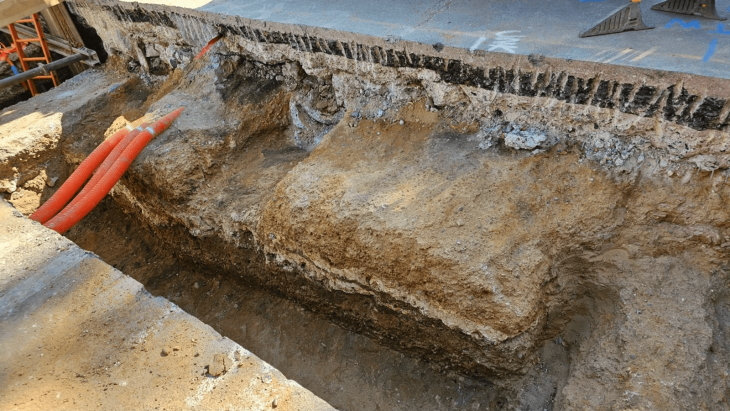
Remarkably, a significant archaeological finding emerged from this area in the form of a money box containing 10 coins dating back to the era of Constans II, believed to span from A.D. 641 to 666, marking the apparent culmination of the building’s usage during the seventh century.
While defining these coins as a treasure in archaeological terms, Çelikbaş suggested an alternative use, saying: “We suspect it was employed as a primitive form of a piggy bank, possibly by a female member of the household during that era, rather than for hiding or burying money.”
The unearthing of these coins provides a glimpse into the final phase of the building’s utilization. It offers valuable insights into ancient domestic practices, highlighting the intersection of archaeology and everyday life in antiquity.
Hadrianopolis in Paphlagonia, also known as Eskipazar, was a city situated in southwestern Asia Minor, located approximately 3km west of the modern town of Eskipazar in the Karabuk Province. The city was inhabited from at least the 1st century BC until the 8th century AD and was named after the Roman emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century AD.
Hadrianopolis was established during the late Hellenistic, Roman, and early Byzantine periods. When Emperor Theodosius I (347-395) established a new province called Honorias, combining Paphlagonia and Bithynia, the city became known as Hadrianopolis in Honorias. It was largely due to its Christian diocese that it was listed among the current titular sees in the Annuario Pontificio.