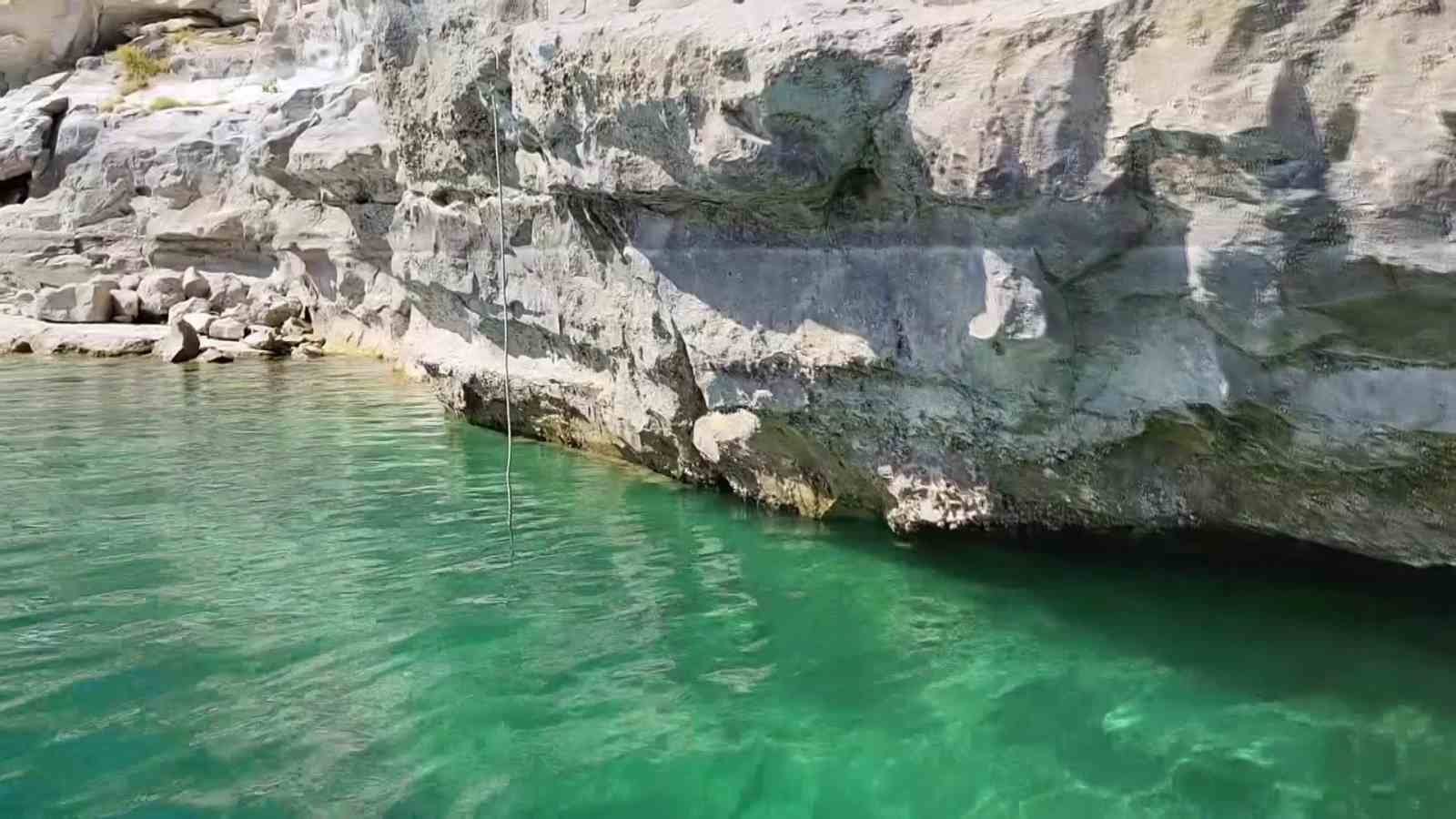
Archaeologists and museum officials in Adıyaman, southeastern Türkiye, have captured underwater images of rock carvings estimated to be 12,000 years old. The carvings, located on the main rock formation along the shores of the Atatürk Dam in Kahta district, belong to the Epipaleolithic Period and depict stylized hunting scenes featuring both humans and animals.
The ancient site was first discovered by local fishermen eight years ago when drought conditions caused the water level of the Atatürk Dam to drop significantly. This year’s prolonged dry season prompted officials to return to the site to check if the carvings had resurfaced again. However, they found the carvings still submerged about one meter underwater near the Belören area of Kahta.
Underwater Documentation and Preservation Efforts
A team from the Adıyaman Museum Directorate conducted a detailed underwater examination using diving and photographic equipment. According to Museum Director Mehmet Alkan, the rock surface is now covered with layers of mussel shells, making documentation challenging. “Despite the shells, we were able to verify that the carvings remain intact,” Alkan said. “We plan to clean the area and produce a detailed replica to display at the Adıyaman Museum.”
Museum Deputy Director Mustafa Çelik noted that reaching the site is nearly impossible during times of high water levels. “This season marks the lowest water level in the dam, giving us a rare chance to inspect the carvings. Even so, they remain about one and a half to two meters below the surface,” he explained.
A Glimpse into Prehistoric Anatolia
The carvings, which span approximately 8 meters in length and 70 centimeters in height, were created using the engraving technique, one of the earliest known artistic methods. The detailed depictions include stylized human figures, mountain goats, horses, wolves, foxes, and storks, illustrating a vivid hunting scene believed to represent daily life and spiritual beliefs during the Epipaleolithic era.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Experts suggest that these carvings provide rare insights into prehistoric Anatolian life and early human artistic expression long before the rise of settled agriculture in the region. Similar findings have been made in other parts of southeastern Türkiye, such as Göbekli Tepe and Karahan Tepe, reinforcing the region’s reputation as a cradle of early human civilization and symbolic art.
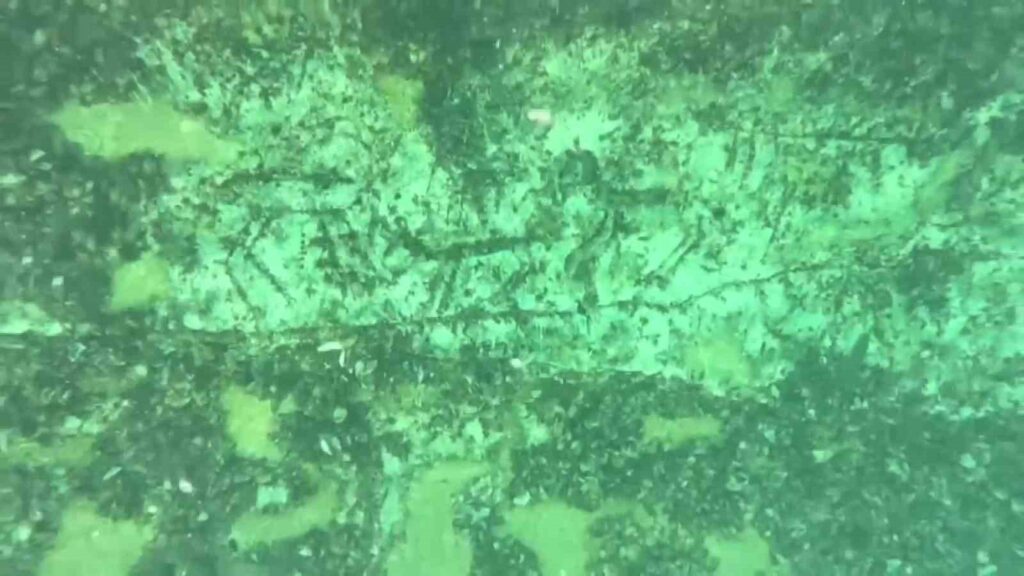

Preservation Amid Environmental Challenges
The Atatürk Dam, one of the largest in Türkiye and a vital part of the Southeastern Anatolia Project (GAP), has significantly altered the local environment since its completion in 1990. As water levels fluctuate due to drought and seasonal changes, submerged archaeological sites like this one face increasing threats of erosion, biological growth, and sediment buildup.
Archaeologists emphasize the importance of digital documentation and 3D modeling to preserve underwater heritage exposed to such conditions. Future plans include conducting a comprehensive cleaning project, high-resolution scanning of the carvings, and the creation of a museum replica to make this prehistoric art accessible to the public without disturbing the original site.
Reviving the Past Beneath the Water
The rediscovery of these 12,000-year-old carvings underlines Türkiye’s vast archaeological richness and the delicate balance between development and cultural preservation. As researchers continue to explore the submerged heritage of the Euphrates basin, each new finding sheds light on humanity’s earliest symbolic expressions — silent stories carved into stone, now resting beneath the waters of modern engineering.
Cover Image Credit: İHA