The Hittites, which left their mark on the Bronze Age period in Anatolia, is a society that draws attention with the importance they give to water resources.
Water and water resources were of vital importance for the Hittites, who were an agricultural society. The vital value of water was not only related to agriculture. In the Hittites, which was a society strictly adhering to belief values, water and water cleaning were very important. The water used as a cleansing tool in rituals against Gods and Goddesses should definitely be far of dirt. So much so that the person responsible for cleaning the water could pay for his slightest carelessness with his life. In addition, the frequent occurrence of plague in the territory of the country increased the value given to water even more. For these reasons, the Hittites gave utmost importance to water resources within the borders of the state.
In many cuneiform tablets obtained, water monuments belonging to the Hittites and libations made there, as well as springs and dams are mentioned.
The Hittites considered the water coming out of the mountain or underground as sacred due to the connection between the holes opened in the earth and the underground world. The places where the water flows were used as sacred places where rituals were held. There are many rituals performed with water in the Hittites. These differ, such as purification, death, birth, prayer, magic, and divination rituals.
The Hittites used water in their religious rituals and libations during holidays. In even, washing the mouth was one of the first steps to be taken during bodily purification. Because the mouth was the place where God’s word came out and it should have been clean.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
We read the use of water in the tablets where the ceremonies called “itkalzi” of Hurri origin are written.
12-17 “… As soon as they finish (this), the victim owner comes to bathe and is washed. As soon as he finishes the washing process, the Priest holds the cleansing water. And he leads her to the bathing tent. And as soon as the victim owner has finished the washing process… ” 18-23 “… Pours the same [water] into an empty bathtub of copper or bronze, the other (priest) also comes, holding nothing. And he puts (the bath bowl) next to other cult items… ” 24-28 “… Then he pours it (water) on his head. Besides, he does not pour other water on his head. It puts it down. As soon as he threw the shirt into it and sat on a stool, the priest speak / prayed in Hurri… ”
As an agricultural society, the Hittites built water monuments in many water springs, both because of their religious beliefs and because they were aware that all diseases, especially plague, were caused by not being clean.
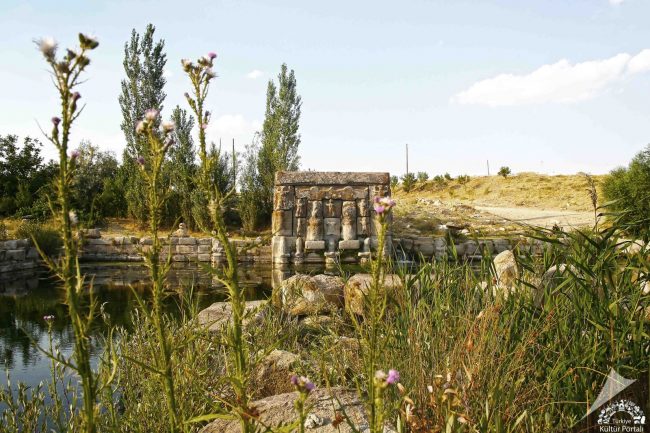

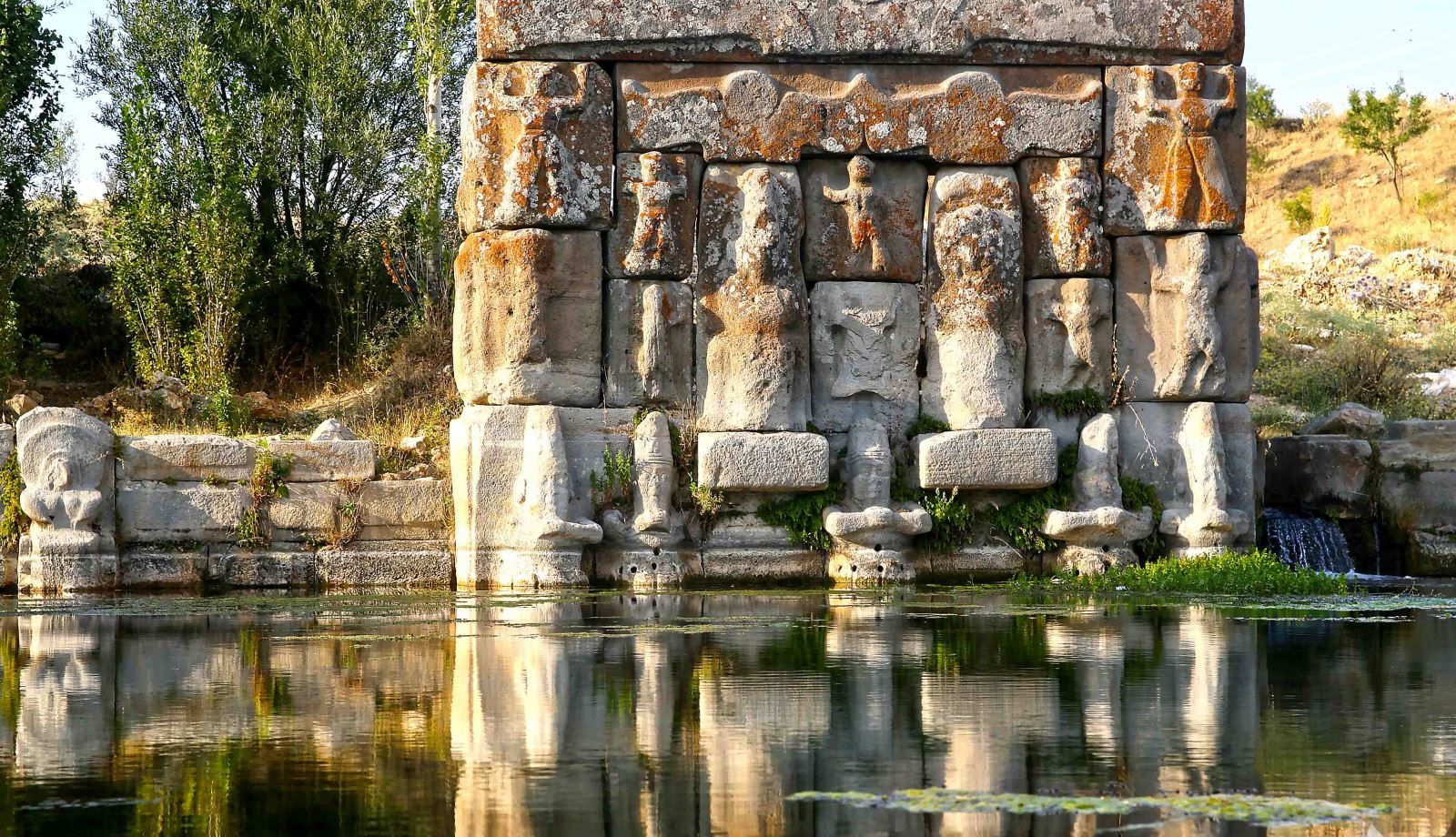
Eflatunpınar Hittite Water Monument
More water cult structures were built’s during Tuthaliya IV. (1250-1220 BC). Especially in Konya Region, these cult structures are seen more. In addition to the water systems that can be described as small dams established in the capital Hattusa, with the water monuments around the water springs built in various regions of Anatolia, water springs were kept under control and measures were taken against the water problems in the future. One of these monuments is the Eflatunpınar Hittite Water Monument, which is located within the borders of the Beyşehir District’s Sadıkhacı Town of Konya.
Hittite King IV. The Eflatunpınar Monument, built in the time of Tudhaliya (there is controversy on this issue), is the rare architectural water system that has survived until today without losing its function. B.C. The Eflatunpınar Hittite Water Monument, dated to the 13th century, is a workmanship’s product of the stone specific of the Hittites. The monument was built on solid one piece rock. It was built by meticulously combining andesite blocks cut in appropriate with each other.
Eflatunpınar Hittite Water Monument was not built only to control the spring where it was established. The compositions drawn on the stones are also considered as an open-air temple with god and goddess figures. With this feature, Eflatunpınar Hittite Water Monuments Are separated from other rock monuments.
The Water Monument consists of a large pool built on a natural water source and god and goddess figures made in relief technique on rocks shaped in rectangular form. Horizontal water channels parallel to the wall of the pool provide important information about the water system and water technology of the period by allowing the water to flow into the pool.
In 2014, it was included in the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List as the Hittite Sacred Water Temple.
Outstanding Universal Values Justification for Inclusion in the List: The feature of the Eflatunpınar water pool is that it is one of the rare water systems that are used economically when necessary by collecting the flowing water with the central pool system. This monument is one of the rare monuments not only in terms of its appearance, layout and iconography, but also in terms of technology and craftsmanship used during its construction.
Source: https://www.kulturportali.gov.tr/
Leyla Murat, Hititlerde su kültü. Tarih Araştırmaları Dergisi, 31, 51. 2012
Dr. Öğr. Üyesi İsmail COŞKUN, Nesim KILIÇ, Hitit Kutsal Su Tapınaklarında Eflatunpınar ile İlgili Değerlendirmeler, 3. Uluslararası Sosyal ve Beşeri Bilimler Kongresi, Van, 2019.