The inscription on a bronze shield purchased by the Rezan Has Museum revealed the name of an unknown country.
It is thought that the bronze shield belonging to the Urartian King Argişti was found within the borders of Ağrı-Patnos or Muş in eastern Turkey.
At the panel “Evaluations on the Urartian Collection of Rezan Has Museum,” organized by Kadir Has University, Van Yüzüncü Yıl University Faculty Member Associate Professor Orhan Varol said they had identified the name of a previously unknown country on the bronze shield belonging to Argişti, one of the Urartian kings.
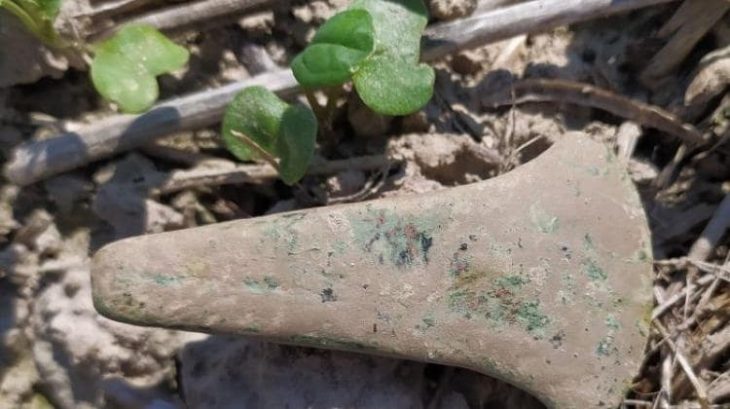
Associate Professor Orhan Varol said that on the bronze shield belonging to Argişti, one of the Urartian kings and currently in Rezan Has Museum, the existence of a new country called Qarini, written with the KUR ideogram, which is the country sign, was detected.

Orhan Varol, who stated that most of the Urartian inscriptions consisted of the military campaigns and victories of the kings inscribed on stone blocks such as andesite, basalt, and limestone, or on rocky areas, said, “We also get information about war and victory in Urartian war tools. It is understood that besides the use of Urartian shields on the battlefield, they could also function as a badge of victory for the kings. It is sometimes indicated on the shield that the conquered country or weapon of war was dedicated to the chief god. In the hands of the king or a great warrior, the shield, which plays an important role in winning the war, gains a symbolic meaning and value by being processed in cuneiform,” said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The shield is 40 centimeters wide. Apart from the inscription, there are dotted and curved stripes on the surface of the shield.
The shield contains new information about Urartian expansion during King Argishti’s reign, as well as Urartu’s linguistic features.

The Urartians adapted the Assyrian cuneiform writing system. All the rulers except Sarduri I wrote in Urartu. Except for Sarduri I. his son Ishpuini (r. ca. 830–810 B.C.) and later rulers all wrote in the Urartian language (distantly related to the isolated non-Indo-European, non-Semitic Hurrian language).
Argishti I. was the sixth known king of Urartu, reigning from 786 BC to 764 BC. He conquered the northern part of Syria and made Urartu the most powerful state in post-Hittite Asia Minor. He also expanded the borders of the country up to the Caucasus.
From early in the Urartian kingdom’s history, very characteristic artifacts were manufactured, including hundreds of bronze belts along with shields, quivers, helmets, bells, horse equipment, jewelry, and ceramic and metal vessels of many forms. Many of these artifacts bear royal inscriptions and are decorated with characteristic motifs and scenes, which consist of various deities and composite otherworldly creatures, royal rituals, hunts, battles, and genre scenes.
A detailed study on the bronze shield and the Qarini settlement will be published soon by Van Yüzüncü Yıl University Faculty Members Prof. Dr. Rafet Çavuşoğlu and Associate Dr. Orhan Varol.