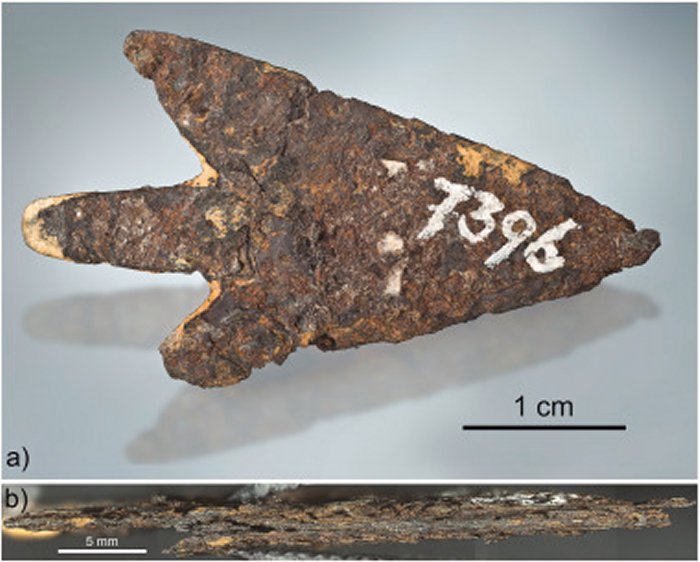
In a recent study of archaeological collections in the Lake Biel region in Switzerland, an arrowhead from the Bronze Age, which is currently housed in the Bern History Museum, has been revealed to be made from IAB meteoritic iron.
With a very specific goal in mind, a team of scientists recently completed a study of prehistoric metal artifacts collected in Switzerland over the previous couple of centuries. They were trying to determine if any of these ancient artifacts were possibly made of metal that had been recovered from meteorites that have been striking Earth for billions of years. To their great joy, the Swiss researchers were able to pinpoint one such artifact: a tiny, rusted Bronze Age iron arrowhead with a chemical and mineral makeup that was unquestionably extraterrestrial in origin.
The team of Swiss researchers focused their search on pre-Iron Age artifacts recovered from various locations nearby the Lake of Biel region of Switzerland, under the direction of geologist Beda Hofmann from the National History Museum of Bern.
The arrowhead was found during a 19th-century excavation of a stilt house settlement at Mörigen in the canton of Bern. The site was discovered in 1843 after water levels in Lake Biel dropped. The settlement dates from around 900 to 800 BC and was inhabited by people from the Urnfield culture, a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe.
Unfortunately, amateur excavations took place, resulting in some artifacts being removed from their original positions and ending up in private collections. To preserve the site, the Bernese government intervened in 1873, prohibiting private excavations and conducting a thorough survey led by Edward Jenner and Edmund Fellberg. The team found evidence of buildings, bridges, and various Bronze Age artifacts across the settlement.
The heavily rusted arrowhead was tiny, measuring just 1.5 inches (39.3 millimeters) in length and only one-tenth of an ounce (2.9 grams) in weight.
In a study published in the journal Science Directs, researchers employed several analytical techniques including gamma spectrometry, X-ray fluorescence, and Muon Induced X-ray Emission (MIXE) analysis to examine the arrowhead.
The arrowhead was made largely from iron and nickel, in a mixture consistent with a meteoric origin. Also, analyses showed that the arrowhead contained a radioactive isotope called Aluminium-26 (26Al), which is only found naturally in extraterrestrial objects. The latter particle does not occur naturally on Earth, because it can only form in the zero-gravity vacuum of space.
The scientists had discovered what they hoped and expected to find. But they determined that the metal used to make the arrowhead had traveled a longer distance to reach prehistoric Switzerland than they’d initially suspected.
The chemical composition of the arrowhead suggests that its material came from the Kaalijarv meteorite, which had fragmented around 1,500 BC in Estonia. This Estonian site is located in Northern Europe on the coast of the Baltic Sea, nearly 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) from the Bronze Age settlement at Mörigen.
Researchers have suggested that an iron meteorite trade network may have existed in Central Europe as early as 800 BC as a result of this discovery. They suggest that these meteorites, which came from the Baltic region, may have been traded along the same routes as amber.
Cover Photo: Journal of Archaeological Science
















