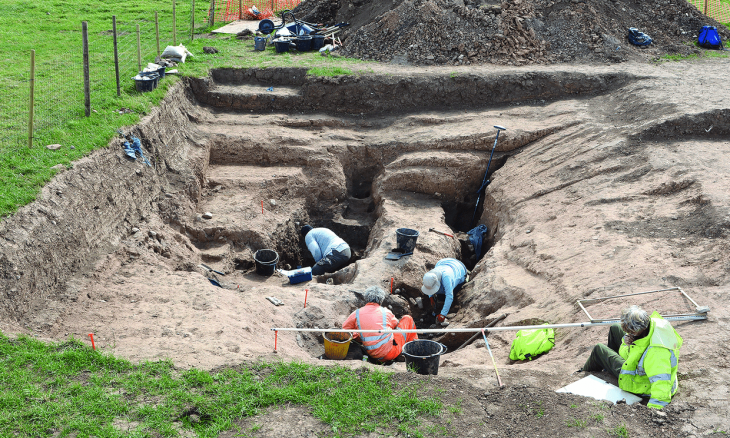
In preparation for a planned residential building project in suburban Tel Aviv, archaeologists from the Israel Antiquities Authority have begun excavating to ensure that no historical artifacts would be harmed.
The scope of the new discoveries in Ramat Hasharon indicates that this contemporary suburb was constructed on land that had previously been utilized for a variety of profitable industries such as agricultural farming, winemaking, glassmaking, and much, much more.
Archaeologists and historians were taken aback when they discovered a thriving and prosperous farmhouse 1,500 years ago in the area north of Tel Aviv. There is no reference of such a village or large-scale farm elsewhere in the historical record, and there are no above-ground ruins nearby that could indicate the region was populated long ago. The site for the new housing in Ramat Hasharon is treeless and desert-like now but apparently was capable of producing an abundance of crops in the first millennium AD.
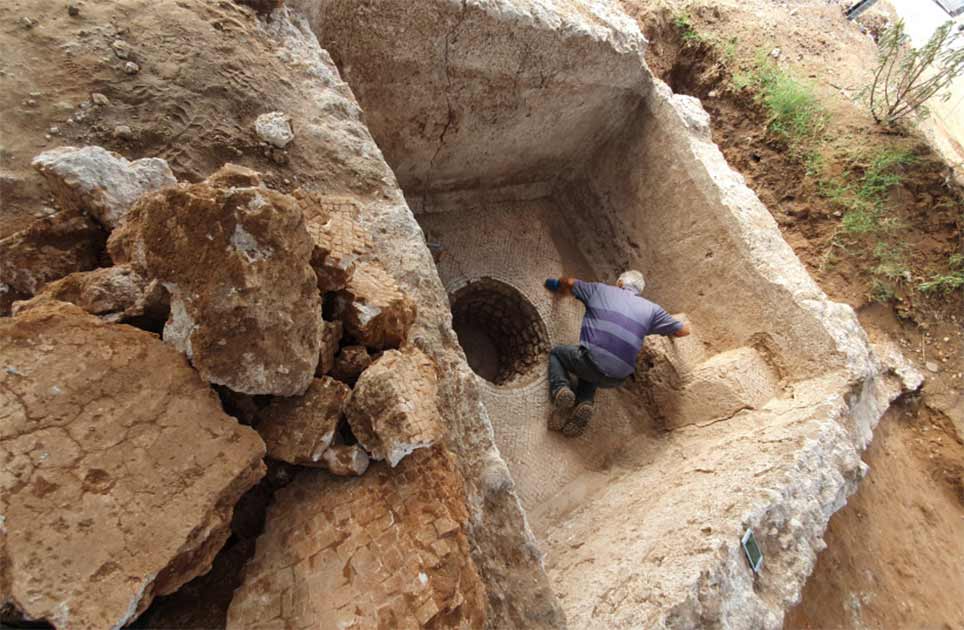
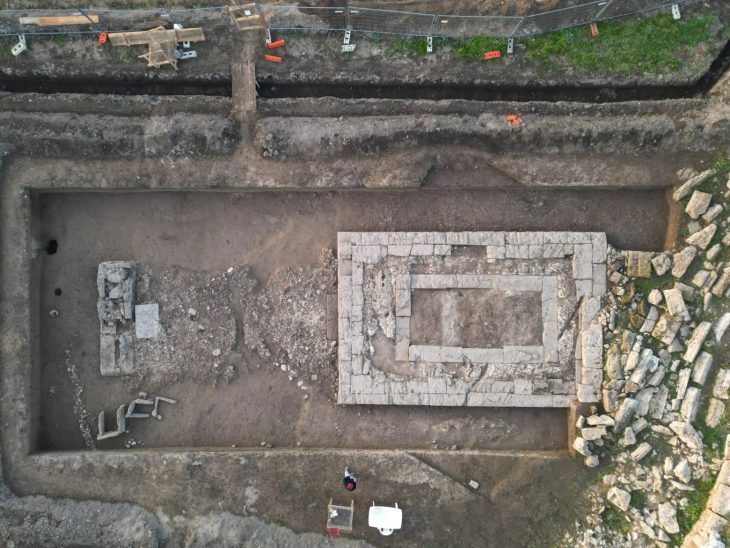
“The excavation unearthed evidence of agricultural-industrial activity at the site during the Byzantine period about 1,500 years ago,” Dr. Yoav Arbel director of the excavation said in a statement released by the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA).
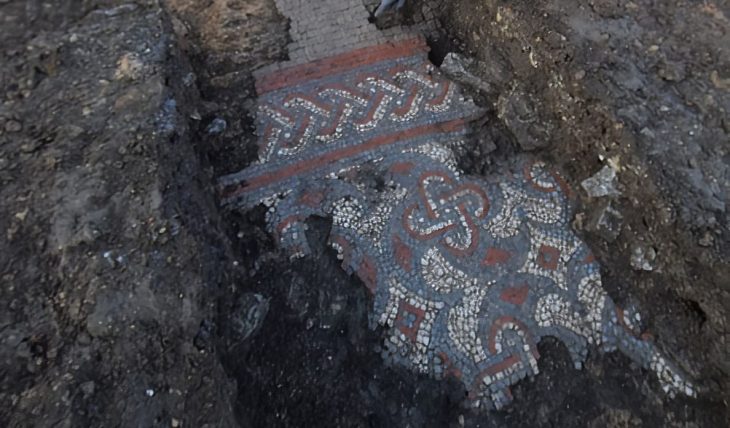
“Among other finds, we discovered a large winepress paved with a mosaic, as well as plastered installations and the foundations of a large structure that may have been used as a warehouse or even a farmstead,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
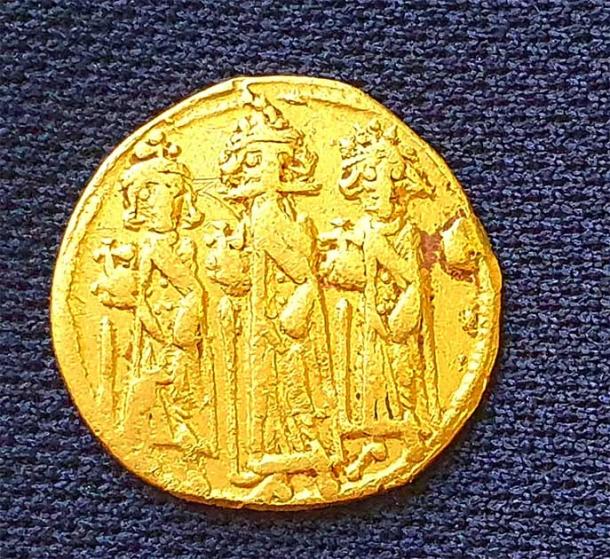

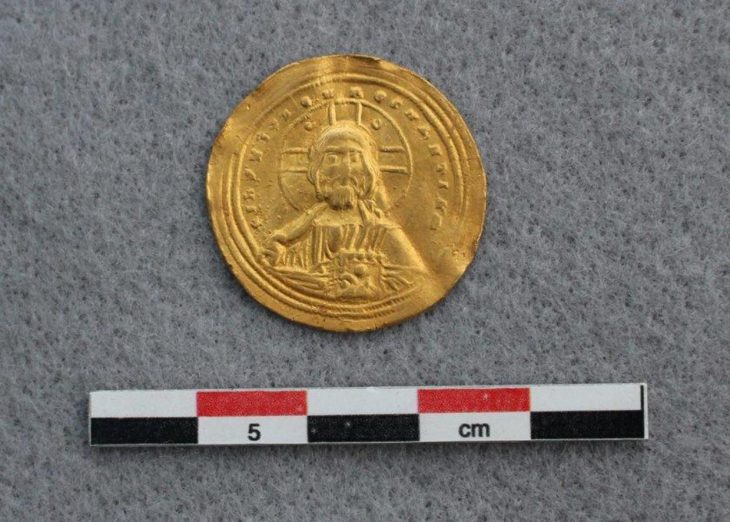
A single gold coin
A single gold coin produced in perhaps 638 or 639 AD, when ancient Palestine was part of the Byzantine empire governed by Emperor Heraclius, was one of the more fascinating finds. This coin was struck just two or three years before Byzantine forces in that area of the world were destroyed by invading armies from Arab regions, who brought with them the new faith of Islam.
On one side, the emperor and his two sons were shown, while on the other, the hill where Jesus was crucified (known as Golgotha) was depicted. An inscription in a language that might have been either Greek (the official language in Byzantine-era Palestine) or Arabic was scratched into the coin’s surface (the language of the post-641 AD occupiers of Palestine).
“The coin encapsulates fascinating data on the country’s decline of Byzantine rule and contemporary historical events, such as the Persian invasion and the emergence of Islam, as well as information on Christian and pagan symbolism and the local population who lived here,” said Dr. Robert Kool, the Antiquities Authority’s numismatics department head.
Ramat Hasharon was created in 1923 by Polish Jewish immigrants. Preparations for the community’s 100th anniversary have already begun, and Mayor Avi Gruber has stated that the area’s unique history would be emphasized during these celebrations.
Cover Photo: Top image: The winepress discovered at the Byzantine-era farmstead found under the modern suburb of Ramat Hasharon, Tel Aviv, Israel. Source: Yoli Schwartz / Israel Antiquities Authority