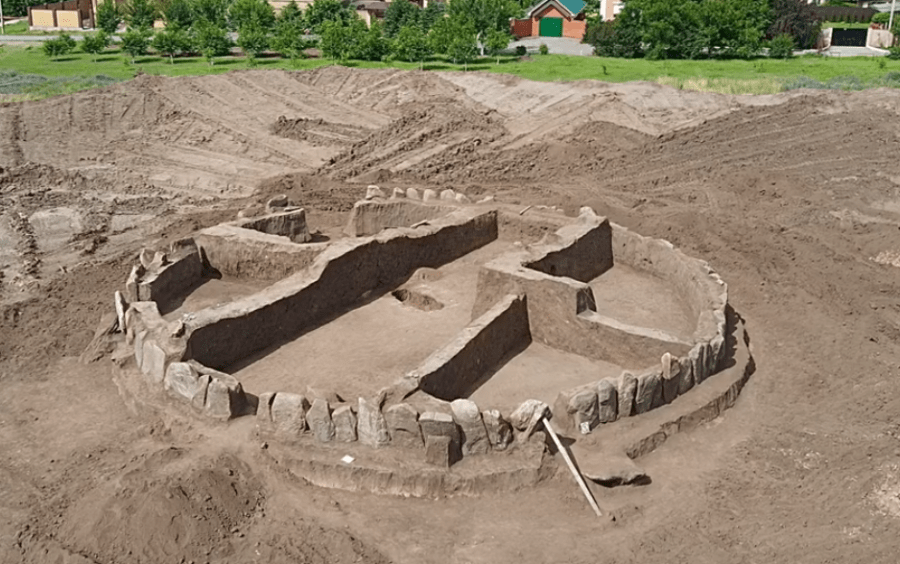
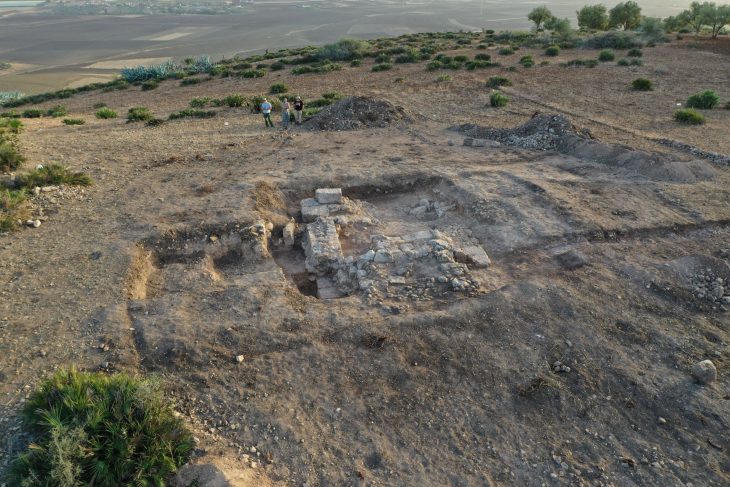
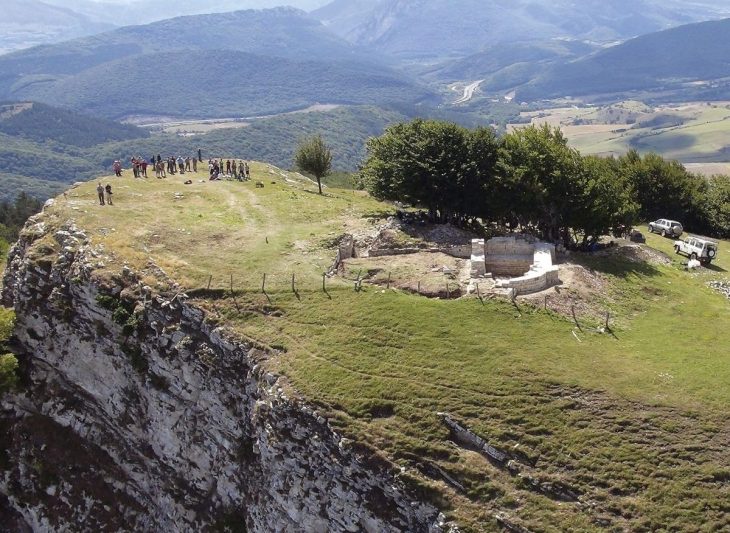
It has almost become a tradition to compare the structures surrounded by stones to the Stonehenge monument. This ancient cemetery, which dates back to the Bronze Age, is commemorated as the “Ukrainian Stonehenge”.
According to archaeologists, this “Ukrainian Stonehenge,” an ancient burial site, dates back to the Bronze Age and is more than 5,300-5,500 years old.
There are many kurgans dispersed throughout eastern and southern Ukraine, and archaeologists and historians are concerned that urban development may destroy these ancient burial mounds in many cases. As a result, they are hurrying to unearth as many as they can in order to rescue and protect precious treasures from bulldozers and increasing urbanization.
A mound of this type was discovered near the settlement of Novooleksandrivka in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. Items and artifacts unearthed in this almost eight-meter mound attest to the flourishing of Indo-Aryan tribes, who created an intricate burial practice that was used by the whole community.
These tombs are notable not only for their quantity, density, and scale, but also for features like burial chambers, burial presents, and mummified remains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Early semi-nomadic pastoral tribes from the Ukrainian steppes left few towns but many graves. They are recognized by the presence of a kurgan above the grave and the body being positioned on its back with bowed legs and coated in red ochre.
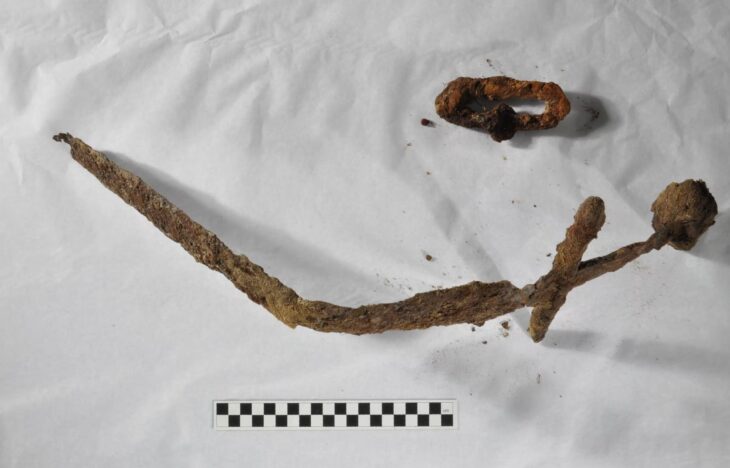
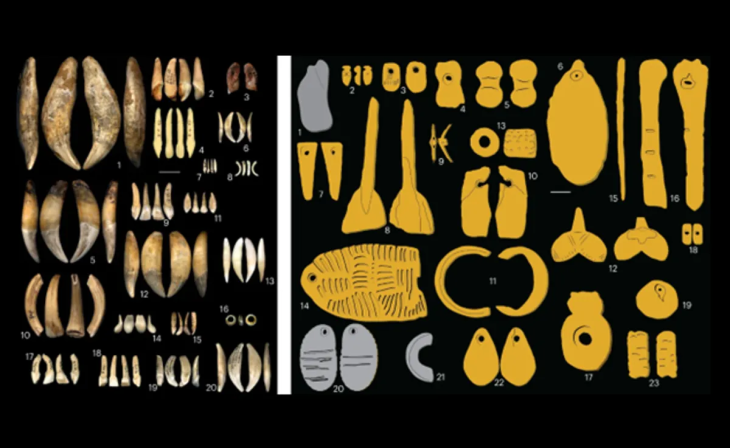
Weapons (stone war hammers and clubs), arrowheads, and rough clay pots with rope impressions were found in several burials. Some have wheels in the corners to represent funeral wagons.
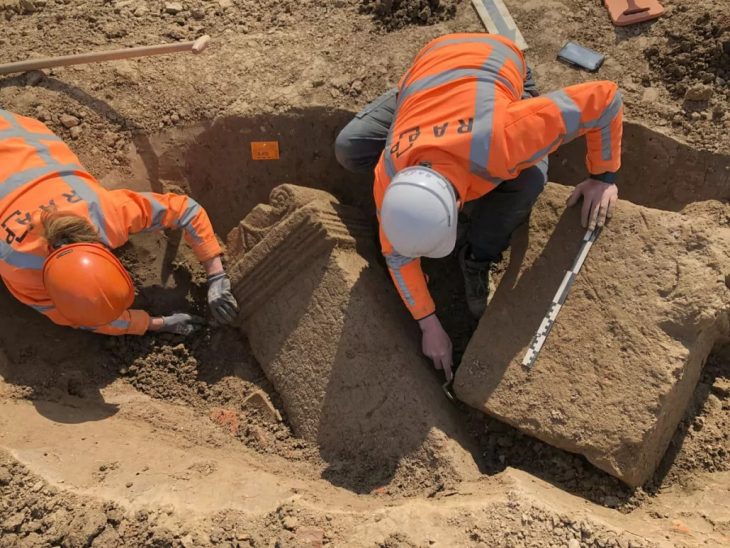
Excavations in the Novooleksandrivka region began in early April 2021, and hundreds of multi-layered burials from the Bronze Age, Scythian period, and Middle Ages have been uncovered in the mound.

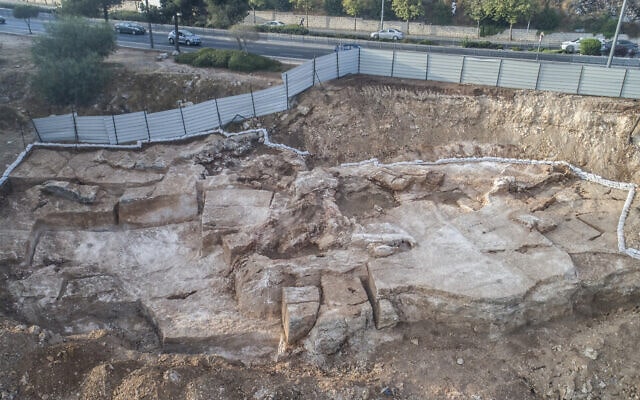
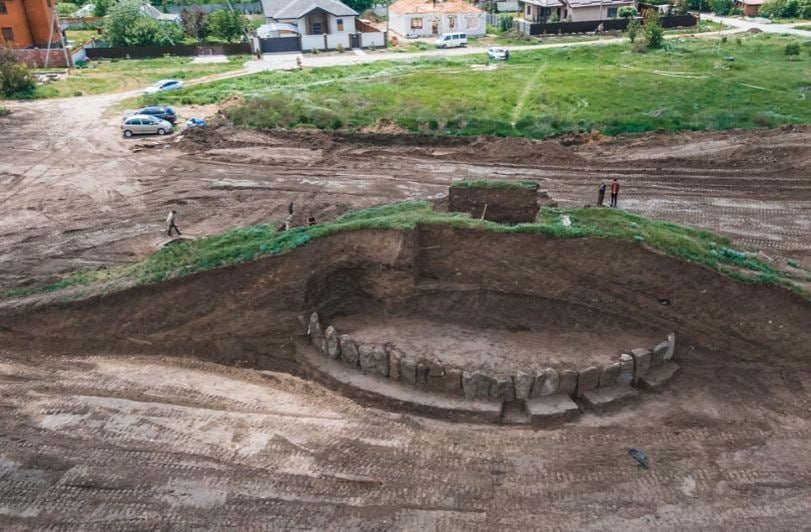
This kurgan, which may be dubbed the “Ukrainian Stonehenge,” first emerged around 5,000 years ago; it is 7.5 meters high and 5 meters broad and was most likely used as a common burial site for over a thousand years.
Archaeologists discovered skeletons buried in eleven alcoves, shattered jugs, and massive rocks surrounding the area a week after the excavations began. Experts and historians believe that chieftains and shamans were buried on this mound.
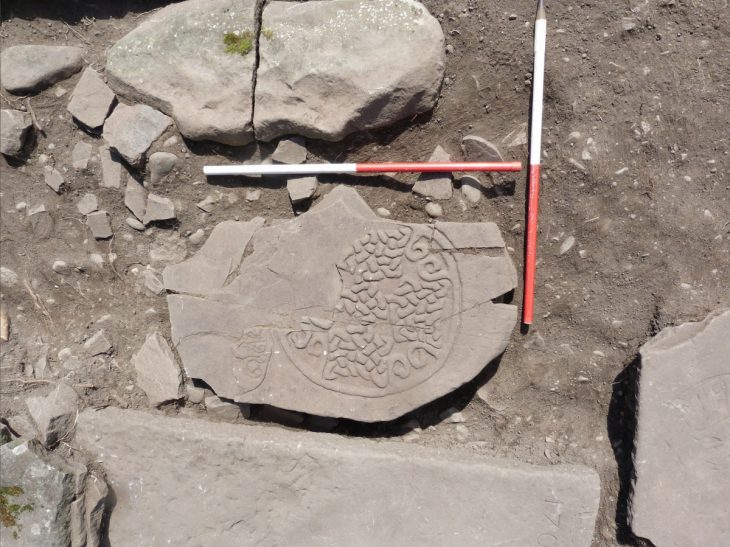
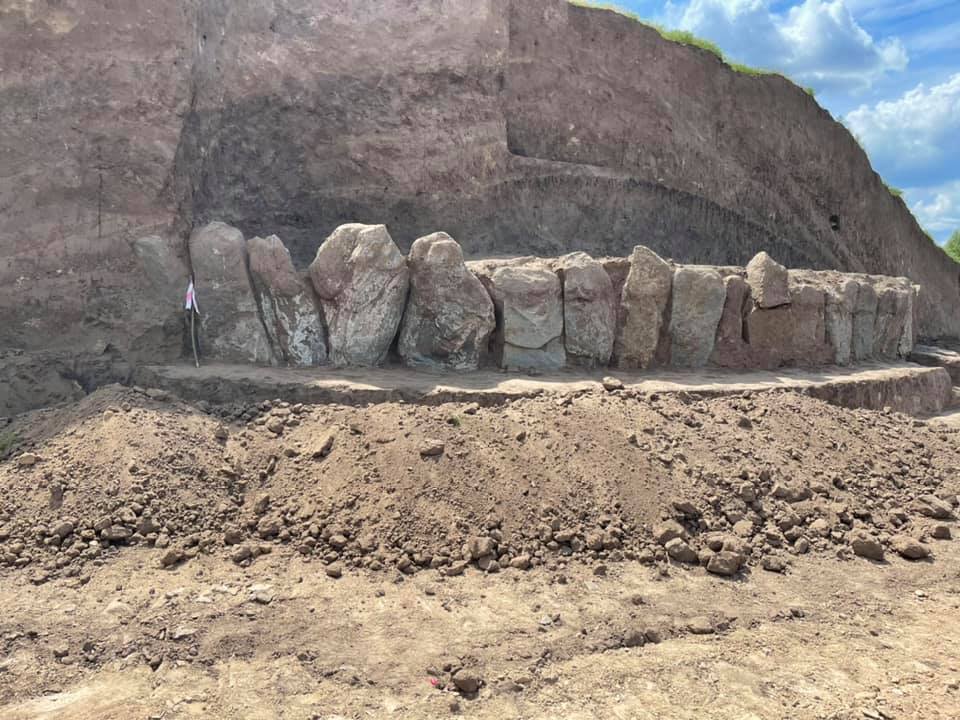
Ancient tribes erected massive stone slabs in a circle, which they carefully adjusted to reinforce the entire construction, according to archaeologists. In the winter, the tombstones were carved by hand and brought by water, horse cart, or even sled to the burial site. These stones are 500 years older than Egypt’s Giza Pyramids, according to experts.
“This cromlech (megalithic construction made of large stone blocks-Ed) has two functions. First, the boulders act as a retaining wall to hold back the soil, and second, they are sacred fences, separating the world of the dead from the world of the living,” explains Yaroslav Yaroshenko, a researcher of the Dnipro Archaeological Expedition. (Euromaidan Press)
During excavations, archaeologists discovered 64 stone boulders that they thought were of sacred significance.
In one of the old tombs going back to the Early Bronze Age, archaeologists discovered evidence of mummification.
Local officials intend to establish an open-air museum when the excavation is done and all artifacts have been properly documented. Cromlech will be located in the heart of the museum. The building business has pledged to cover all costs. In response, local people organized a working group and petitioned the Ministry of Culture to keep the excavated area on the list of memorial sites.
According to some estimates, 100,000 burial mounds dot Ukraine’s fields, many of which were substantially flattened in the twentieth century as part of a Soviet strategy to level the terrain for cultivation. Many are at risk today.