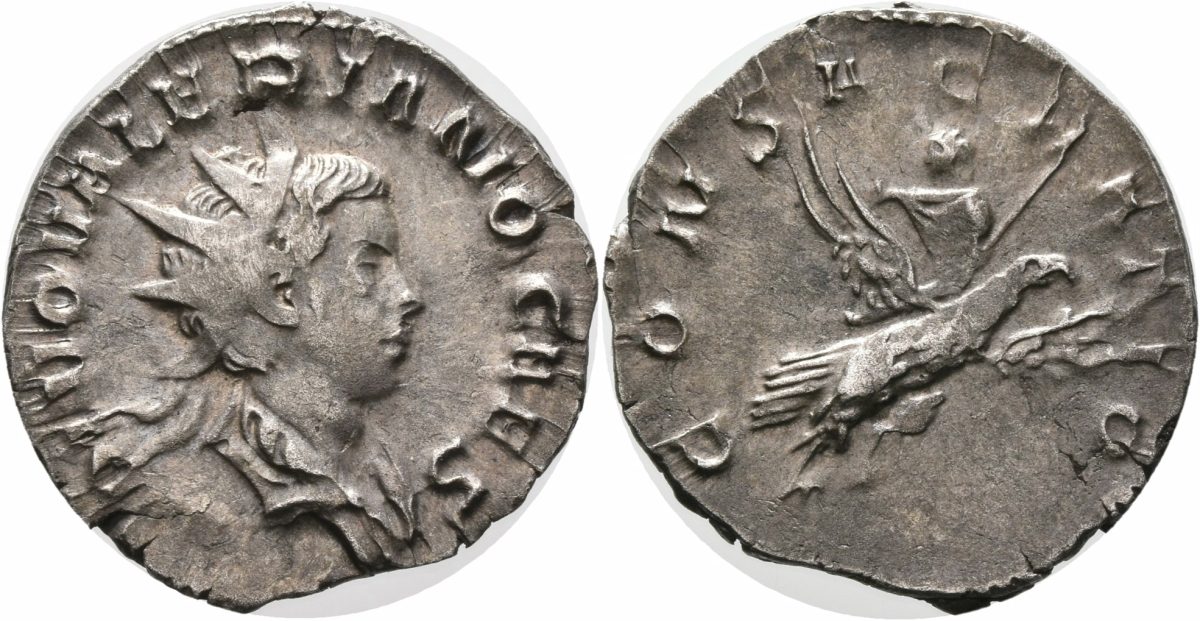
Historical coins are much more than just pieces of jewelry for collections and exhibitions and are of particular interest for research. The University of Trier has had a collection of mainly ancient coins for several years. The more than 500 copies have now been digitized and made accessible in portals.
“The digitization of coin collections is a great benefit for science. Integration into databases and permanent access to a large number of coins opens up new options for research, but also for teaching,” explains Prof. Dr. Frank Daubner, the ancient historian responsible for the collection at Trier University.
Researchers can derive insights into the economy, trade, mobility, and cultural and social phenomena of the time from the design of coins, for example how rulers are depicted on them, from their distribution, and from the depiction of historical events.
The more than 500 coins in the Trier collection, most of which date from the Roman period, were photographed with a special camera and described scientifically in an accompanying information text.
“There are some very beautiful coins, for example, one with a portrait of Emperor Constantine,” explains Professor Frank Daubner.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
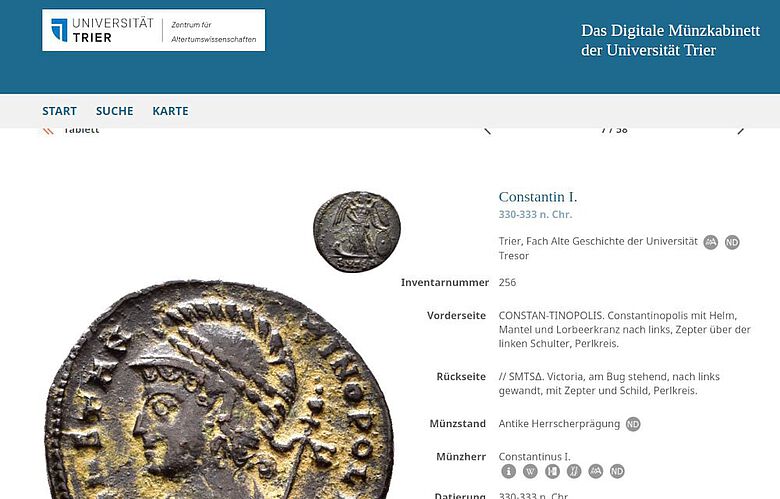
However, ancient historians are more interested in coins as a source of data and information than aesthetics. A special feature of the Trier collection is that the place where most of the objects were found – predominantly in Trier and the region – is known. The comparison between the place of origin of the coin, the mint, and the place of discovery can reveal information about trade relationships and travel routes at the respective time.
The digitization of the Trier coin collection is also an enrichment for studying and teaching in history. In addition to student teaching and research projects, the digitized objects from the databases can be used to create virtual exhibitions, for example.
The collection is represented on three online platforms under the name “Digital Coin Cabinet of the University of Trier”. At www.ikmk.uni-trier.de, those interested can only find objects from the Trier collection.
The University of Trier is also a partner in the “Network of University Coin Collections in Germany” (NUMID), which was founded in 2015. To date, 34 universities with 42 coin collections belong to this research and digitization network. NUMID uses the “Interactive Catalogs of Coin Cabinets” database provided by the “Münzkabinett Staatliche Museums zu Berlin”.
In addition to the NUMID collections with a total of around 30,000 objects, other large non-university collections are integrated here, for example over 40,000 objects from the numismatic holdings of the Coin Cabinet of the State Museums in Berlin. When the portal opened in 2021, a total of more than 90,000 data sets on objects were available, and there are now more than 130,000. All three portals can be used free of charge and the photos can be used freely for teaching and publications.
- Digitales Münzkabinett der Universität Trier
- NUMID – Netzwerk universitärer Münzsammlungen in Deutschland
- Interaktive Kataloge der Münzkabinette
Cover Photo: Sophie Kröner – University of Trier
















