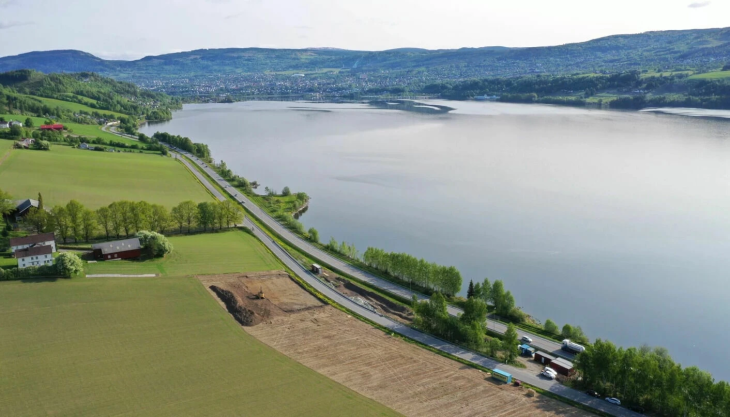
In the San Felice Canal, in the northern Venetian Lagoon, a material used as an additive in Roman concrete was discovered: pulvis puteolana, a volcanic ash from the Phlegraean Fields near Naples.
Researchers from the University of Padua, the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, and the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia collaborated to document this discovery, which was published in the scientific journal PLoS ONE.
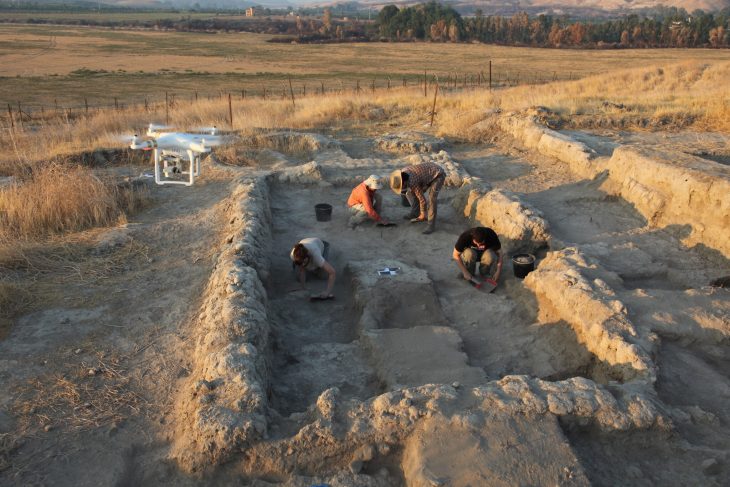
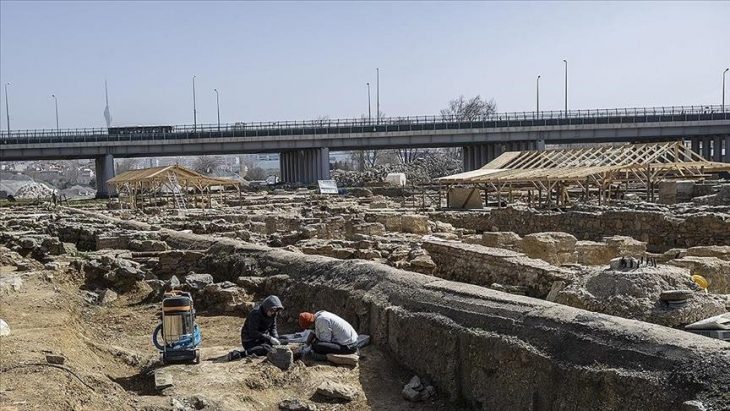
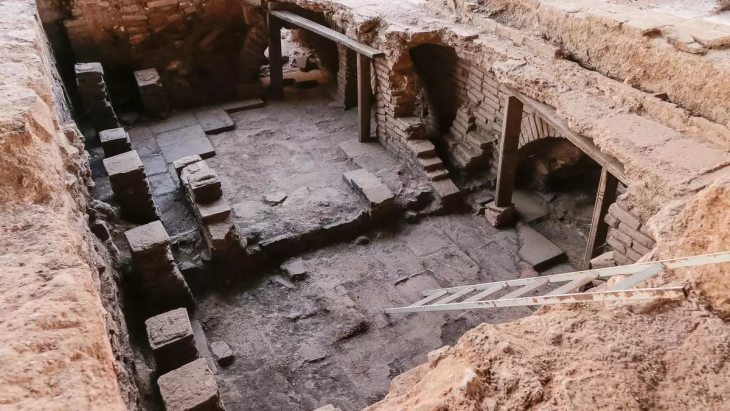
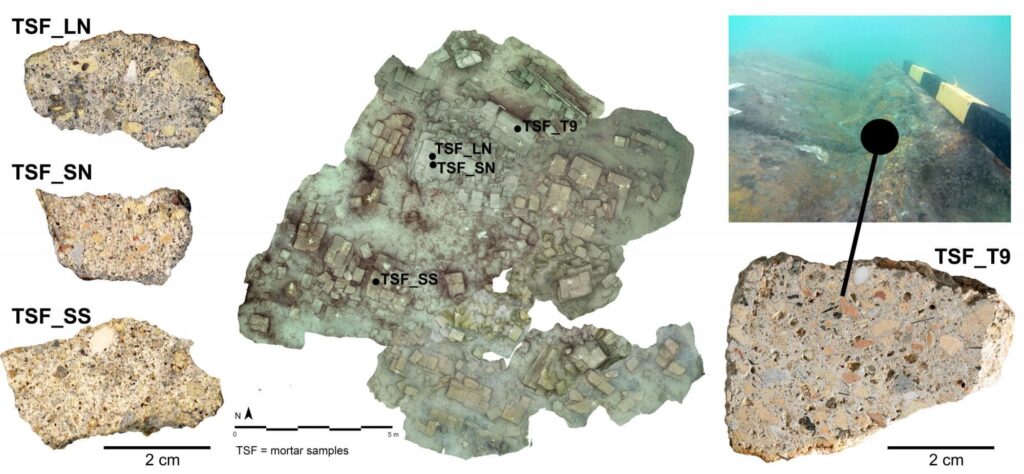
Researchers from the University of Padua detected the utterly unexpected presence of volcanic pumice from the Phlegraean Fields in Naples by analyzing samples of the mortars used to coat and bind the Roman well-cistern (1st c. CE), which is currently submerged more than three meters deep in the northern portion of the Venetian lagoon.
This material is described in detail by architects and treatise writers Vitruvius and Pliny the Elder as a powder (pulvis) with extraordinary properties, enabling ancient mortars and concretes to solidify in anaerobic environments and even underwater. Extracted from the area around ancient Pozzuoli (Puteoli), Latin authors recommended its use in the construction of port infrastructures made of concrete poured directly into the sea. 1,800 years before the discovery of Portland cement, pulvis puteolana gave ancient concretes exceptional resistance to structural loads, weathering, and the aggressive submerged environment, ensuring extraordinary durability that has recently revived the “myth” of Roman concrete.

The research sheds light on advanced Roman construction techniques and the commercial dynamics of the Mediterranean.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The subject of study is a 1st-century CE Roman hydraulic structure, considered a precursor to the “Venetian wells,” designed to capture and store fresh water.
The Venetian-style well is a hydraulic structure used since Roman times in the Upper Adriatic territories for the collection and storage of fresh water, which we have been able to document and study underwater, thanks also to innovative photogrammetric technologies, add Carlo Beltrame and Elisa Costa, a professor and a researcher from the Department of Humanities at the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice and authors of the underwater studies conducted under a permit from the Ministry of Culture, with the oversight of the Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio of the Municipality of Venice and the Lagoon.
Advanced laboratory technologies have made it possible to perform sophisticated microscopic and geochemical analyses on rocks and minerals, even when they have been finely ground into a micrometric-sized powder. These analyses were never performed on archaeological materials until a few years ago, but they have made it possible to determine the origin of the pulvis.
“The fingerprint of the volcanic pulvis,” emphasizes Tommaso Giovanardi, a professor in the Department of Chemical and Geological Sciences at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, “was traced thanks to ultra-high-resolution instruments, such as Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, which allow us to obtain extremely detailed geochemical data even on very tiny fragments of geological material.”
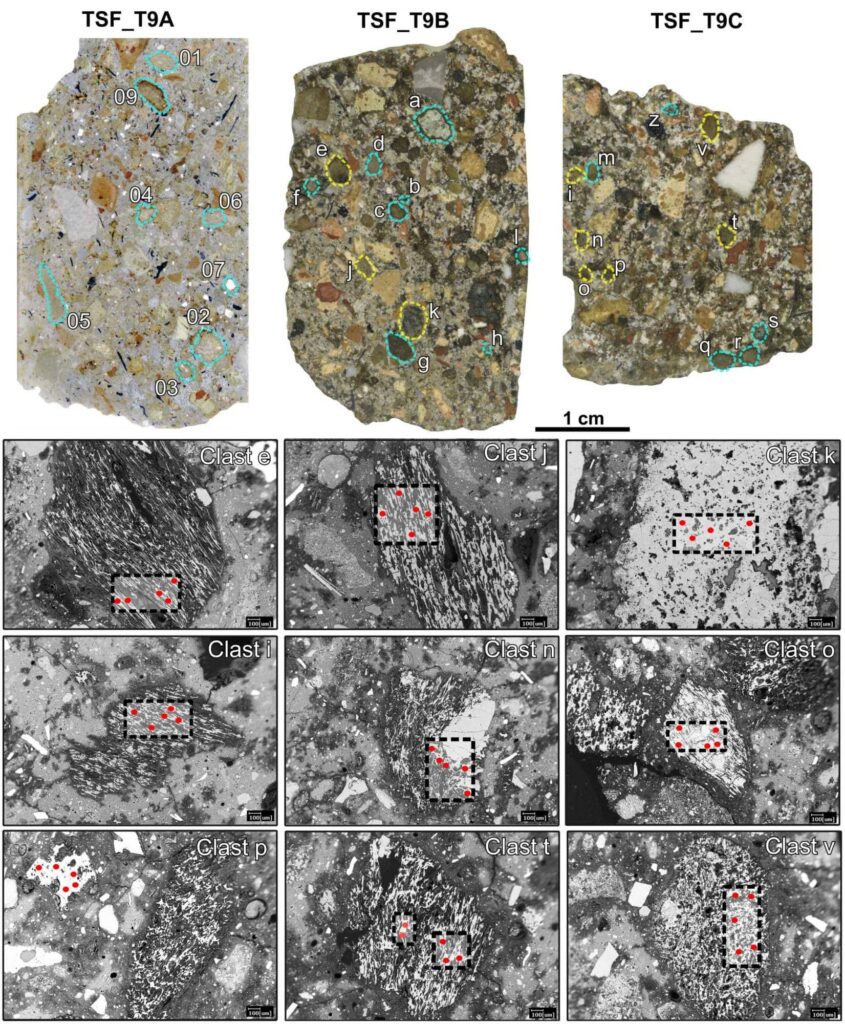
The profile of these small inclusions was then compared with a vast reference database created by researchers from the Departments of Cultural Heritage and Geosciences at the University of Padua, which gathers the compositional profiles of over 1,000 geological samples of compatible volcanic products. Through the comparison of chemical tracers, the compatibility with the volcanic dust from Campania was unequivocally certified.
Lastly, the study highlights the remarkable originality with which the Venetian ancestors adapted the prominent Vitruvian architectural forms to the unique architectural and environmental requirements of the Lagoon in its delicate balance between water and land, while also highlighting the close ties between Northern Italy and the most advanced Roman engineering knowledge.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313917
Cover Image: Wikipedia Commons
















