As the first civilizations began to emerge in Mesopotamia and Anatolia, significant transformations in social structure, economy, and culture took place. Among the most revealing archaeological sites shedding light on this period is Başur Höyük, an ancient royal cemetery located in eastern Türkiye. Recent studies indicate that this site offers crucial insights into the origins of inequality during the Bronze Age, situated at the margins of the Mesopotamian world.
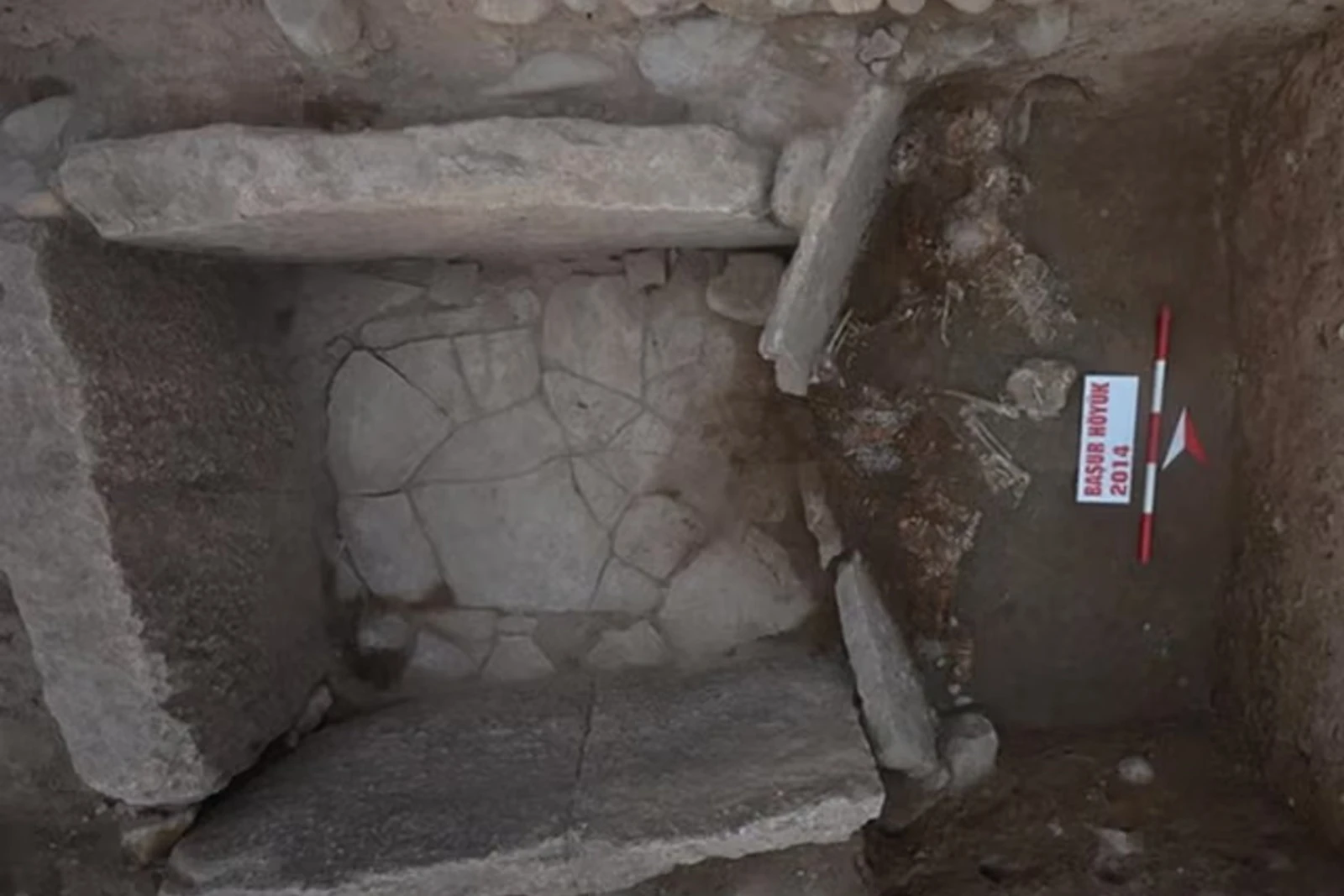
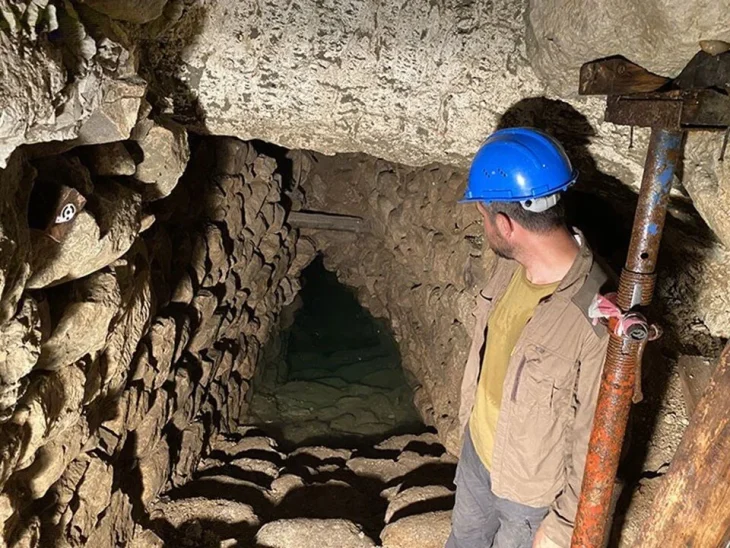
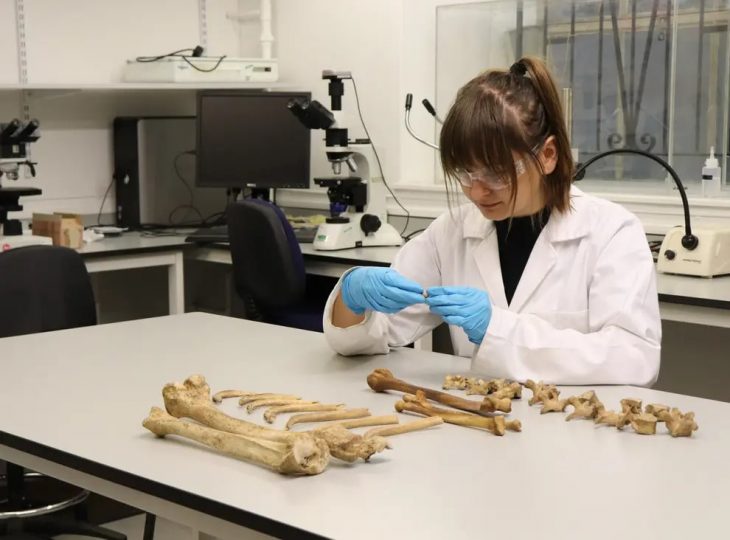
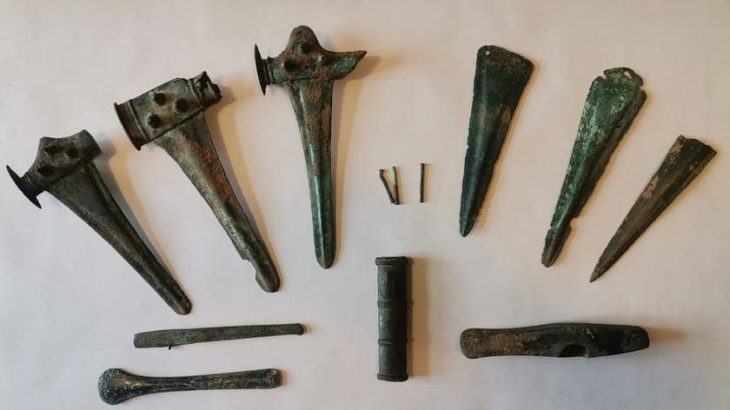
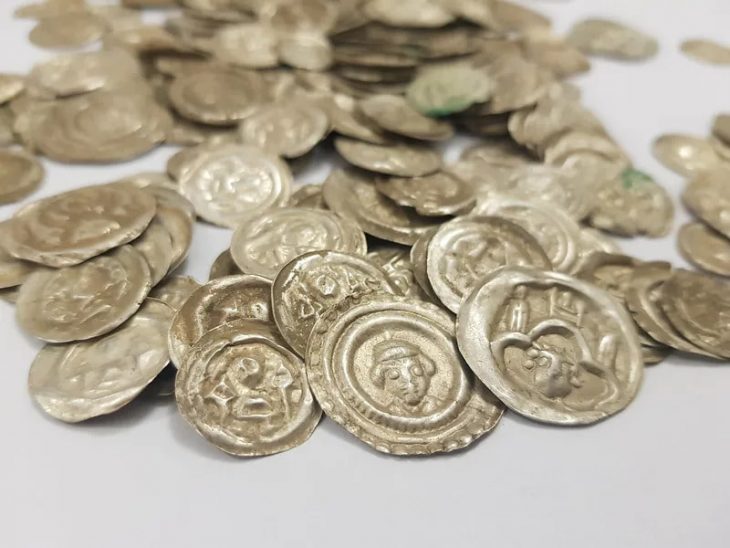
Başur Höyük, located in the Siirt province of modern-day Türkiye, has been identified as a significant settlement during the third millennium BCE. Excavations have uncovered monumental tombs belonging to the local elite, which contain exceptional burial goods such as weapons, prestige objects, and offerings. These findings suggest a clear social differentiation among the region’s inhabitants, indicating that Başur Höyük was a center of local power with strong connections to the major cities of Mesopotamia.
Recent archaeological studies are challenging long-held beliefs about the origins of kingship in Mesopotamia, particularly through findings from Başur Höyük. Excavations in this region have revealed evidence suggesting that kingship and warrior aristocracies may have emerged much earlier than previously thought, outside of urban centers.
Notably, at Arslantepe on the Malatya Plain of eastern Türkiye, a palace complex dating to around 3300 BC is documented from a non-urban setting, located far from the nearest centers of urban growth in lowland Mesopotamia, where evidence for secular rulership is either negligible or ambiguous at that time. This finding aligns with recent research indicating that palatial structures may have existed earlier than previously thought, challenging the traditional view that such buildings only appeared after the rise of cities. Additionally, the site has yielded what is identified as the earliest known “royal tomb,” containing a significant amount of metal weaponry and ornamentation. Surrounding this main burial are subsidiary graves interpreted as ritual sacrifice victims, further emphasizing the complexity of social hierarchies in early societies.
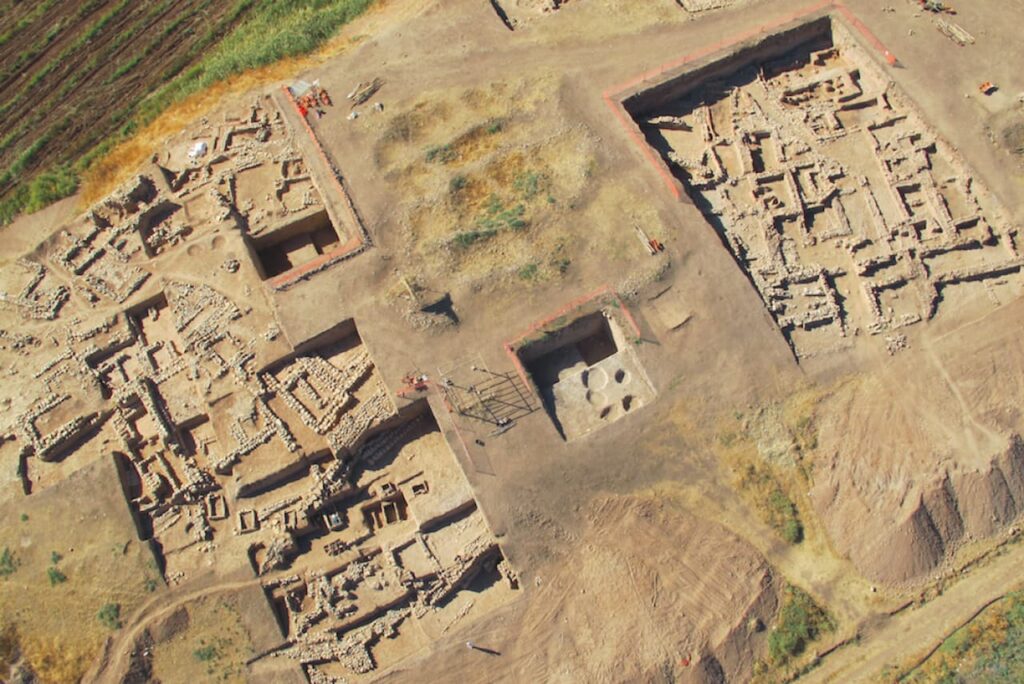

One of the most striking discoveries at the site is evidence of human sacrifices, a practice also documented in other ancient civilizations. Archaeologists have found remains of multiple individuals buried alongside rulers, symbolizing a ritual transition to the afterlife and the maintenance of social order even in death. Such sacrificial practices were common in hierarchical societies, where leaders utilized these rituals to demonstrate power and reinforce loyalty among their subjects. Bioarchaeological analyses reveal that the victims were often deliberately selected, predominantly teenage girls, highlighting the stark inequalities present in these early societies.
The burial goods found at Başur Höyük further illustrate the growing inequality in the region during the Bronze Age. Elite tombs contained bronze daggers, spearheads, cylinder seals, and intricate gold and silver jewelry, signifying privileged access to valuable resources and advanced technologies. These elements support the hypothesis that social inequality did not arise spontaneously but was the result of a gradual process driven by the consolidation of power, resource control, and the institutionalization of class differences.
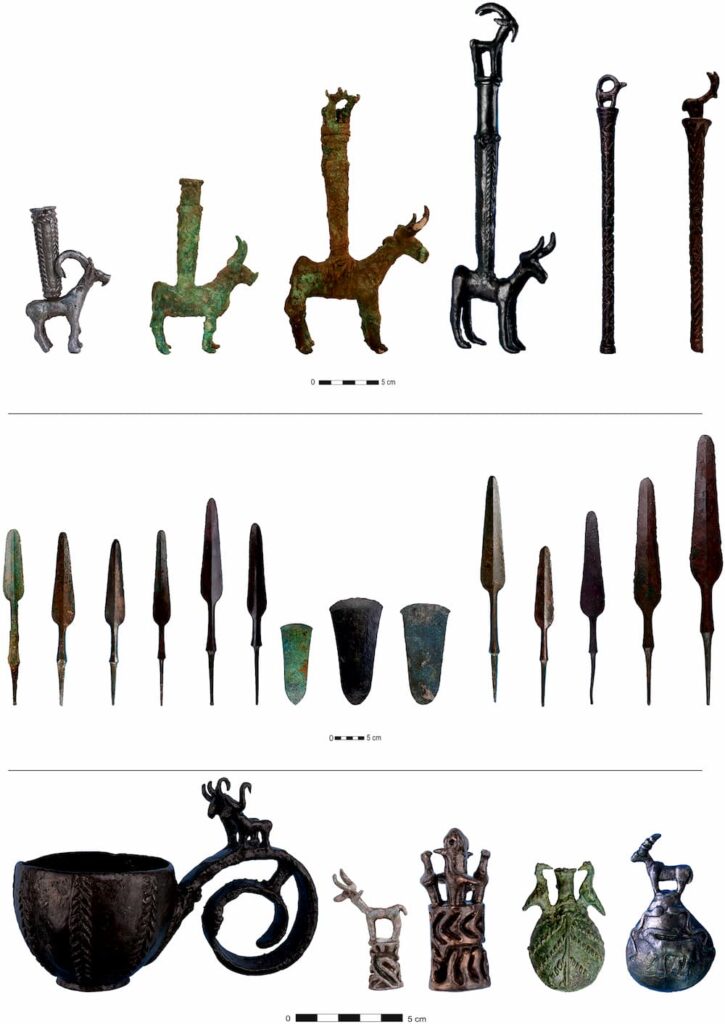

The analysis of this royal cemetery enhances our understanding of how human societies transitioned from egalitarian systems to highly stratified structures. Positioned between the Mesopotamian cities and the tribal populations of Anatolia, Başur Höyük played a crucial role in the diffusion of ideas, technologies, and power dynamics. Researchers argue that early state formation in Mesopotamia cannot simply be characterized as a combination of cities, bureaucracy, and dynastic elites. Instead, radical forms of inequality may have originated in small-scale communities before influencing broader political relations.
As new findings continue to emerge from Başur Höyük, they promise to reshape our understanding of the complexities of early social hierarchies and the processes that led to the establishment of inequality in ancient societies.
Wengrow, D., Hassett, B., Sağlamtimur, H., Marsh, W., Brace, S., Pilaar Birch, S. E., … Barnes, I. (2025). Inequality at the Dawn of the Bronze Age: The Case of Başur Höyük, a ‘Royal’ Cemetery at the Margins of the Mesopotamian World. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 1–12. doi:10.1017/S0959774324000398
Cover Image Credit: Başur Höyük Research Project/Cambridge Archaeological Journal 2025