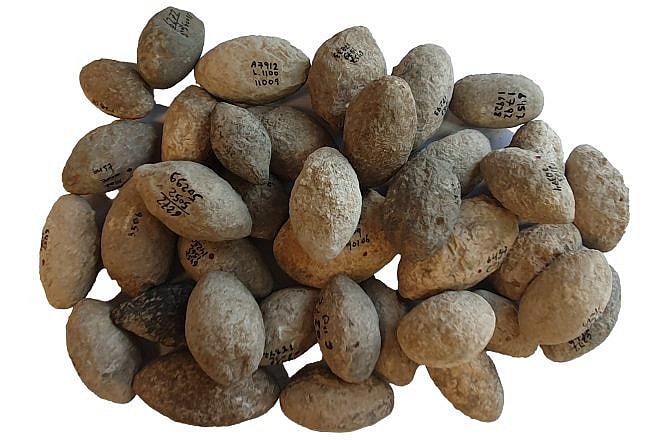
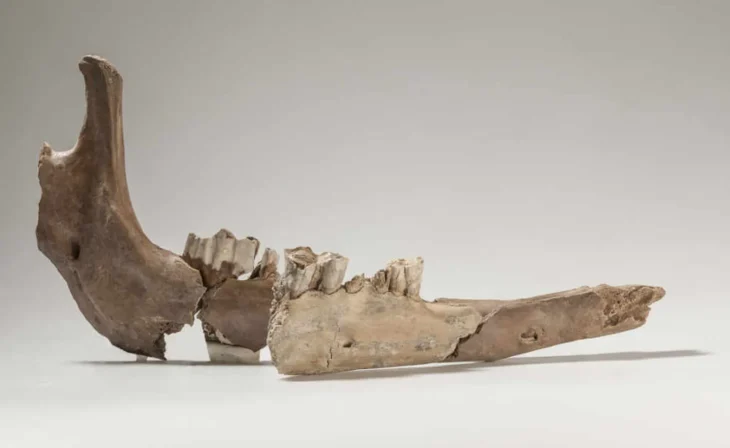
Israel Antiquities Authority researchers have unearthed the earliest evidence of warfare and organized arming in the Southern Levant, dating back approximately 7,200 years. The 424 sling stones from the Early Chalcolithic period point to organized preparation for battle.
This discovery, which is focused on what is now modern-day Israel, shows that mass weapon production—in the form of lethal sling stones—occurred much earlier than previously thought.
The newly published research, which has been published in the journal Atiqot, examined hundreds of sling stones from the Early Chalcolithic period (c. 5800–4500 BCE) that were uncovered at two large archaeological sites, one at Esur in the northern Sharon Plain, and the other En Zippori in the Lower Galilee.
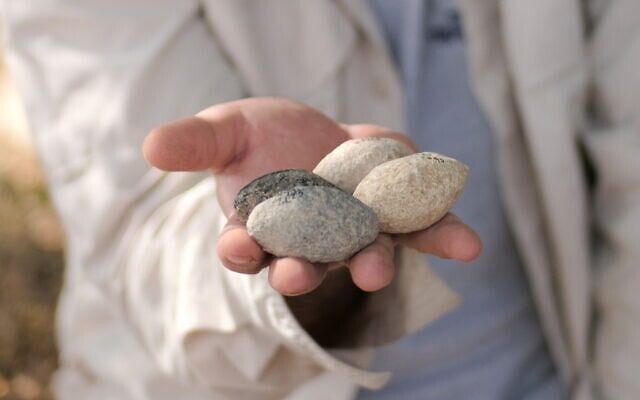
The researchers found that the stones were nearly identical in size, shape and composition: mostly manufactured from hard limestone, were almost identical, with an average length of 52 mm (just over 2 inches), a width of about 321 mm (a bit over 12.6 inches), and an average weight of 60 grams (around 2.1 ounces). Indicating they were mass-produced and organized, almost certainly with warfare in mind.

The use of slings is known in many parts of the world from ancient times. The sling was used to launch rocks at the enemy in the famous battle between David and Goliath in the 9th century BC, according to anecdotal evidence.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The stones, which were intended to be projected from a sling, are smoothed, with a specific biconical aerodynamic form, enabling exact and effective projection,” researchers said.
Similar sling stones have been discovered in other parts of the country, primarily from the Hula Valley and the Galilee in the north to the northern Sharon Plain, but this is the first time they have been discovered in such large concentrations.
In their article, the researchers conclude: “The proliferation, formalization, standardization, and labor-intensive manufacturing all point toward an organized production of weapons, interpreted as an escalation in the preparations for war, attesting to the probable existence of local power centers in the region.”
Cover İmage: Slingstones from En Zippori in the Galilee. Photo by Gil Haklay/IAA.