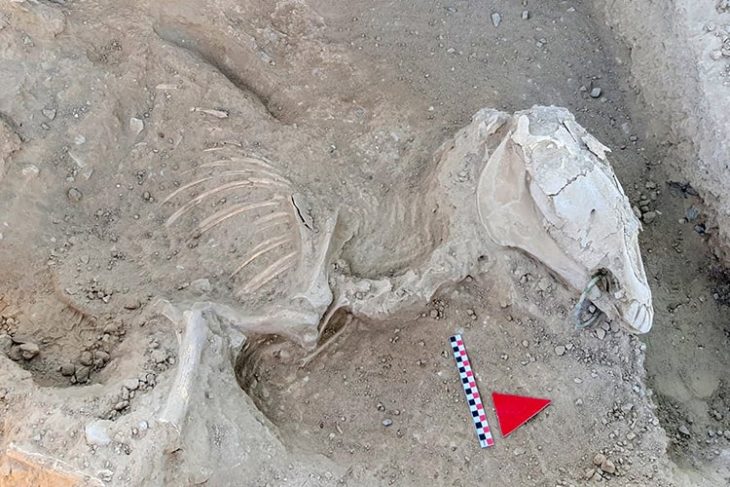
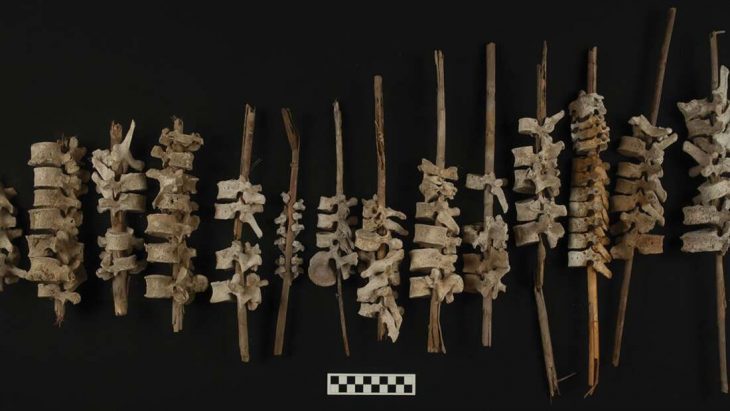
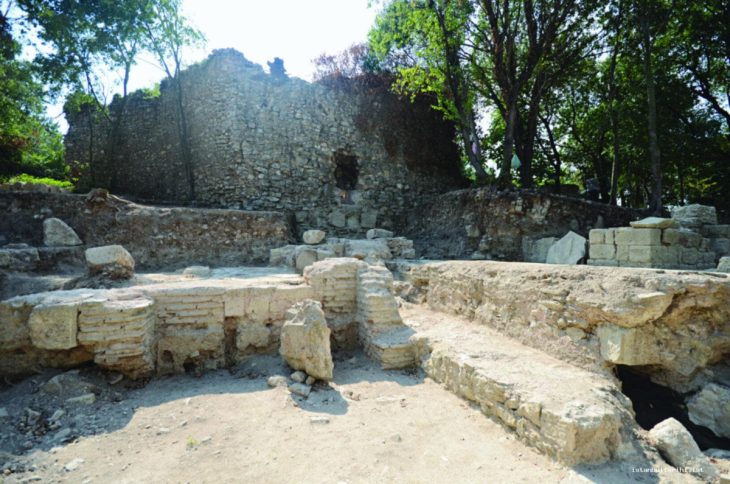
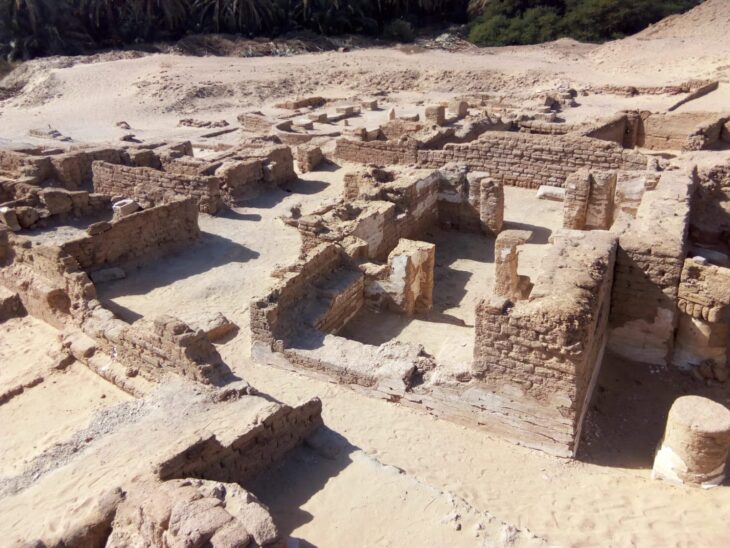
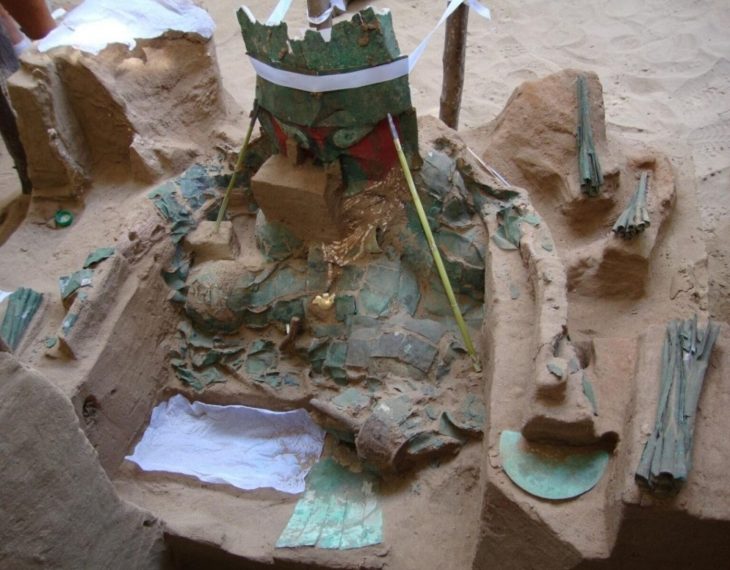
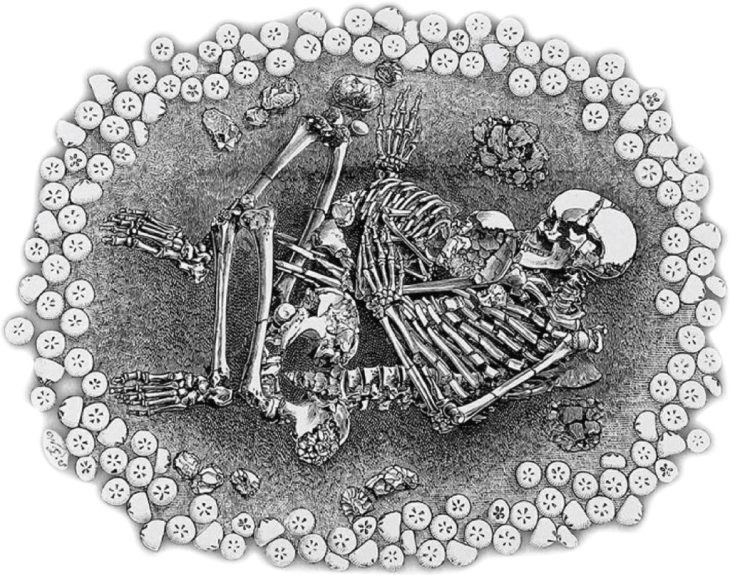
The human remains of 29 people buried as sacrificial offerings have been discovered in a pre-Inca temple in northern Peru.
These remains could help experts rewrite pre-Inca Wari history, the lead researcher said Friday.
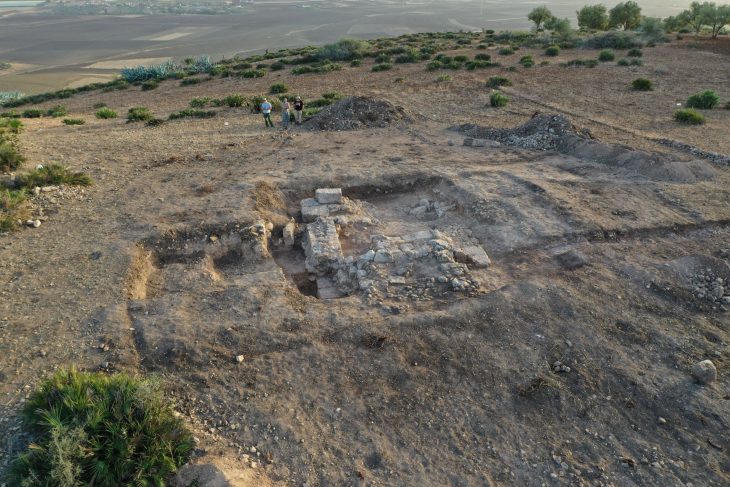
Researchers discovered four graves containing the bones of toddlers and teens at the Huaca Santa Rosa de Pucalá excavation site in Peru’s Lambayeque area.
It is the first time a discovery linked to the Wari civilization has been made this far from their area of influence, Edgar Bracamonte, the lead researcher, told AFP
“These discoveries allow us to rethink the history of the Lambayeque region, especially the links to Wari and Mochica occupations in the area,” said Bracamonte.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
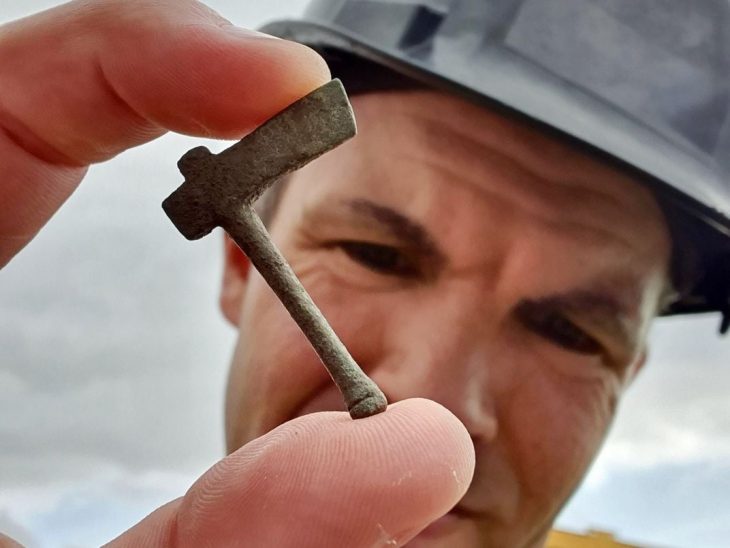
As well as the human remains, the team discovered camelids and guinea pigs showing signs of sacrificial practices.

It is the first time scientists have recorded this form of human offering associated with the Wari civilization, a civilization that lived between 500 and 1000 CE in the south-central Andes and coastal area of modern-day Peru. So far three of the enclosures discovered at the site have been excavated.
Researchers believe that the bones of humans and animals were part of a probable ceremony performed at the time of the start of building on Wari-style holy facilities.
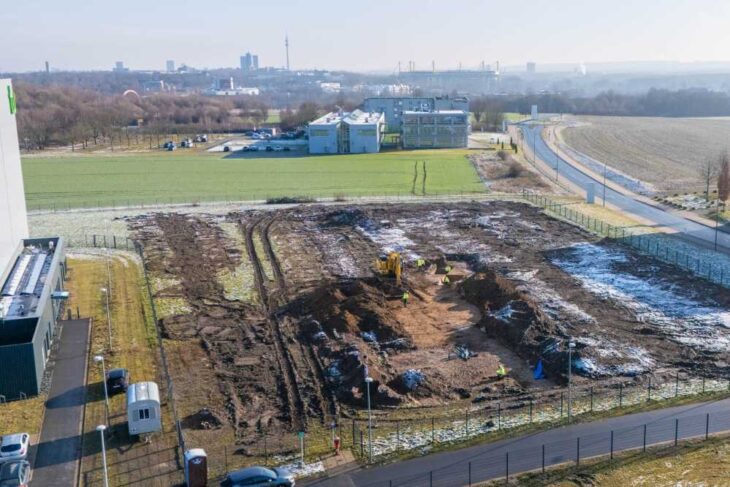
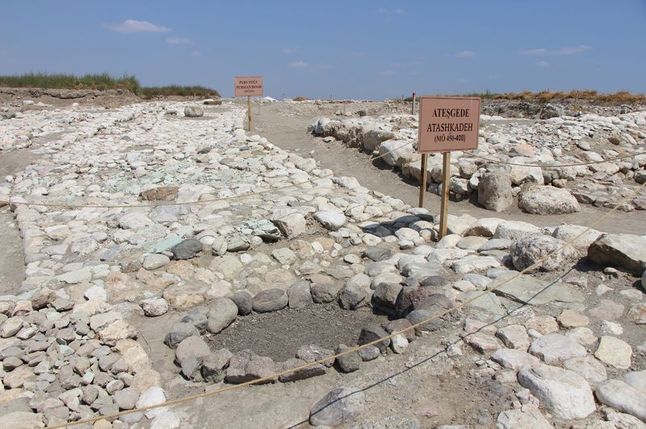
A ceremonial temple was also unearthed during the excavation.
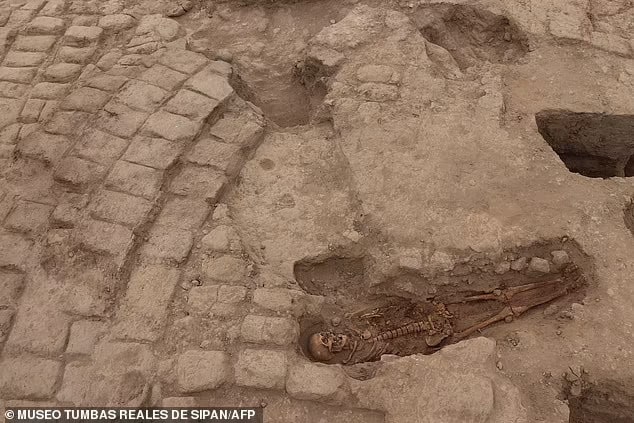

Bracamonte said: ‘It is a temple built with walls made of clay as formwork and that include clay maces as prototypes of adobes inside the walls. The upper part of the temple presents very well elaborated floors, ceilings of vegetal remains, and evidence of the incineration of objects were found.’
Bracamonte said the temple was built by a group of people with local characteristics, showing that during the years 400 to 200 BCE.
These fresh findings have increased the number of Wari-period ritual places, compelling experts to reinterpret Lambayeque’s past.