The Battle of Kadesh between the Hittites and Egyptians in Anatolia, the two superpowers of the Bronze Age period, has marked the world’s political and military history.
In the Battle of Kadesh, which took place between the Hittites and Egyptians, who came together to increase the influence by seizing the trade routes of the region, Egyptian Pharaoh II. Ramses’ tactical mistake determined the fate of this war.
Sethi I, who ascended the throne after the death of Ramses I, went on an expedition to establish domination in Palestine and Lebanon and organized operations on the Amurru Kingdom. These expeditions will replace II. It will be continued by Ramses and as a result the Amurru lands will be taken under Egyptian rule. That Amurru was captured by Egypt, IV. We learn by reading the introduction of the treaty between Tuthaliya and the Amurru King Shaushgamuva. In the text, the event is written as follows.
28 My sun’s father’s brother, Muwatalli,
29 when he was king, the people of Amurru to him
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
30 they sinned against and him
31 they declared: ‘We willingly
32 we became vassals. Now we are not your vassal ”
33 and they to the side of the king of Egypt
34 they passed. My sun’s father’s brother, Muwatalli
35 and the King of Egypt, the people of Amurru
36 they battle and him Muwatalli
37 he won. Amurru Land with gun
38 destroyed and made him his slave (= vassal)
39 and made Šapili king in the Land of Amurru. (CTH 105).
The Egyptian army, reaching as far as Ugarit, thus took control of the rear region in a war with the Hittite.
During these developments, king II. Murshili was dead. Instead of King II.Mursili, the hero king II. Muwatalli (1295-1272 BC) has passed.
Although Muwatalli, who made his brother Hattusili the army commander and king of the Upper Country Hakpish, is not known exactly, has been a radical decision to move the capital from Hattusa to Tarhuntassha in order to create a field of action against Egypt’s attempts against Syria’s. This situation is also described in Hattusili’s apolagya (CTH 81) as follows.
75 My brother Muwatalli, by the word of his god (= by order)
76 When he goes to the Lower Country, when he leaves Hattuša,
II.
1 Took Hatti’s (gods) and their dead souls
2 and took them [] to the Country.
II (§ 8)
52 Later he took displaced Hatti’s gods and dead souls
53 and took them to Tarhuntašša and kept Tarhuntašša (= sat there)
II. Ramses’ successful expeditions in Syria II. He angered Muwatalli. Also, IV. On the tablet written by Tuthaliya, the march with an enormous army started for the Amurru Country to break its oath to the Hittite king and the Egyptian threat and the re-establishment of Hittite rule in the region. He supported the formed army in Hattusili, King of Hakpish; In his apology, “When my brother went on an expedition to Egypt, I took the soldiers and fighters with cars from the regions I resettled to Egypt, to my brother’s expedition. He explained the situation by saying “I was the command.”
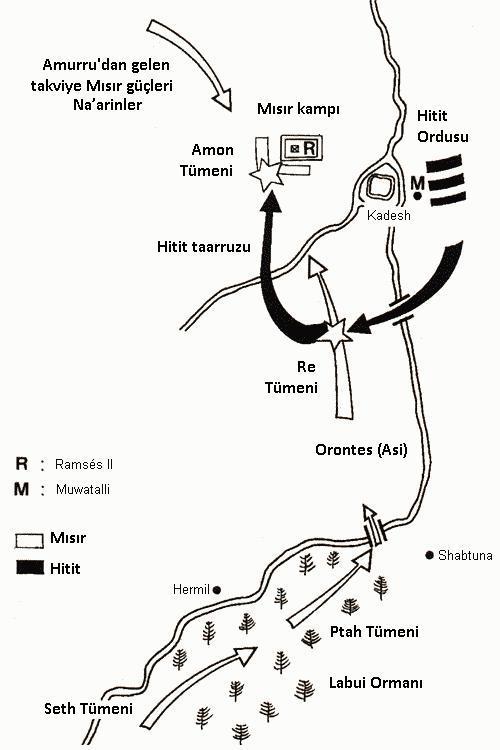
In Egypt immediately started preparations against II. Ramses prepared battalions named Amon (he himself commanded), Ra, Seth, and Ptah. Against these battalions, Muwattali had set up an army of 3,500 chariots and 37,000 infantry (the numbers are extracted from the records Ramses dictated to Karnak temples). The greatest and powerful armies of the period moved towards the Kadesh plain.
Qadesh, which comes from the root “Q-D-Š” in Semitic spelling, A city on the banks of the Orontes (Asi) river in the Land of Amurru, which was called Kinza in Hittite, Qidshu in Akkadian, Kodeşu by the Egyptians. The region was an indispensable land between Egypt and the Hittite, which always had aspiring on Syria.
Ramses’ tactical mistake becomes the fate of war
Ramses, who took action with the battalion he was in charge of, could not prevent the battalions from opening so much that they could disrupt the communication while moving towards Kadesh. In 4 battalions, their distance increased and they continued to walk.
Muwatalli cleverly devised a plan and sent two Bedouin spies to be captured by the Egyptian army. These Bedouins gave Ramses false information about the Hittite army. Relying on this information, Ramses began to wait for the battalions to gather. The Hittite army went on a sudden attack. Amon divisional disbanded. The defeat of the Ra battalion and the weakness of the other two battalions left Ramses in a difficult situation.
However, there was a moment when the wind started blowing in reverse. The efforts of the mercenaries in the Hittite army to get a share of the booty caused chaos. Meanwhile, Ramses attacked and upset the balance of the Hittite army. Two days of brutal war watered Kadesh with blood. At the end of the war it is difficult to determine its cauldron. According to Egyptian sources; II. According to the stories that Ramses had written on Karnak temples, Egypt was the winner of the war. However, after the war, Kadesh and Amurru were again under the control of the Hittites, The occupation of Damascus and its environs, which was under the control of Egypt, actually shows that the Hittites were the victor.
After the small and medium-scale conflicts after the Kadesh war, the Hittite-Egypt relations have evolved into a period of moderate diplomacy away from conflicts.
Source
Ali M. Dinçol, “Hititler Öncesinde Anadolu”, Anadolu Uygarlıkları Görsel Anadolu Tarihi
Ansiklopedisi, Görsel Yayınlar, İstanbul, 1982
Doç. Dr. Meltem Doğan Alparslan “II. Muwattali Dönemi” Yayınlanmamış Doktara Tezi. İstanbul Üniversitesi. 2007.
















