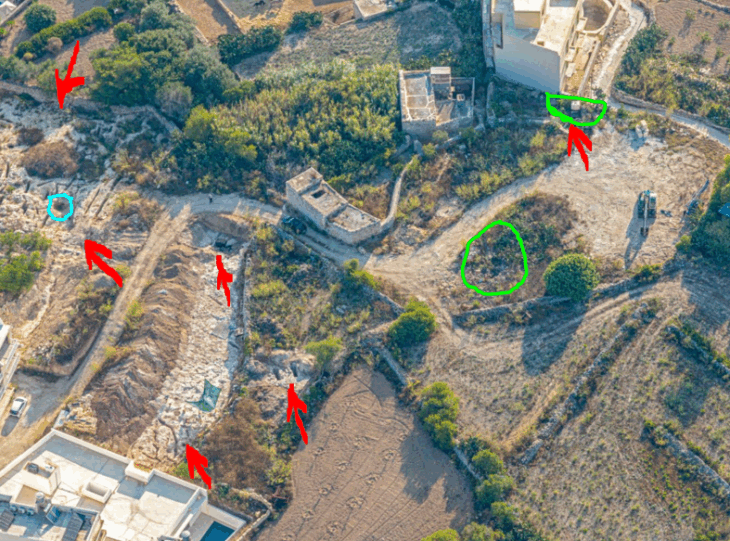
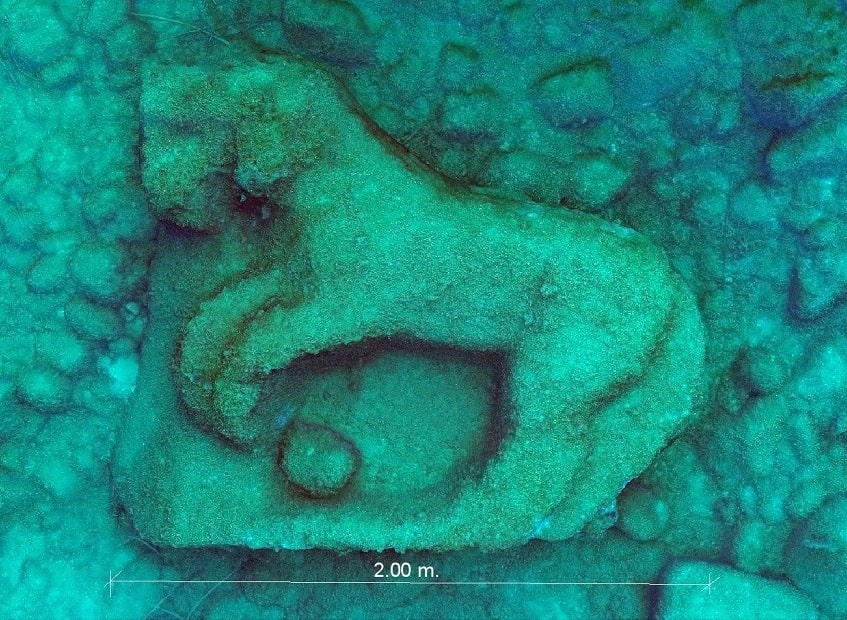
A large marble relief believed to have been part of the Temple of Olympian Zeus frieze in Agrigento, Sicily, has been recovered from the seabed off the coast of San Leone, not far from the mouth of the Akragas River.
The find recovered is most likely a marble frontal decoration belonging to the famous Temple: the fragment depicts a prancing horse, an iconic element in artistic representations of the Greek period.
Divers from the Carabinieri’s Diving Unit carried out the operations alongside representatives from the Superintendency of the Sea, the Carabinieri’s Cultural Heritage Protection Unit, and the Underwater Group of BCsicilia, a volunteer organization that promotes and protects Sicily’s cultural heritage and disseminates information.
Covered with concretions, the find, almost certainly made of Proconnesian marble, measuring 2 meters by 1.6 meters and 35 cm thick, lay about 300 meters from the coast, at a depth of 9 meters, although this piece was already generically cataloged in the area.
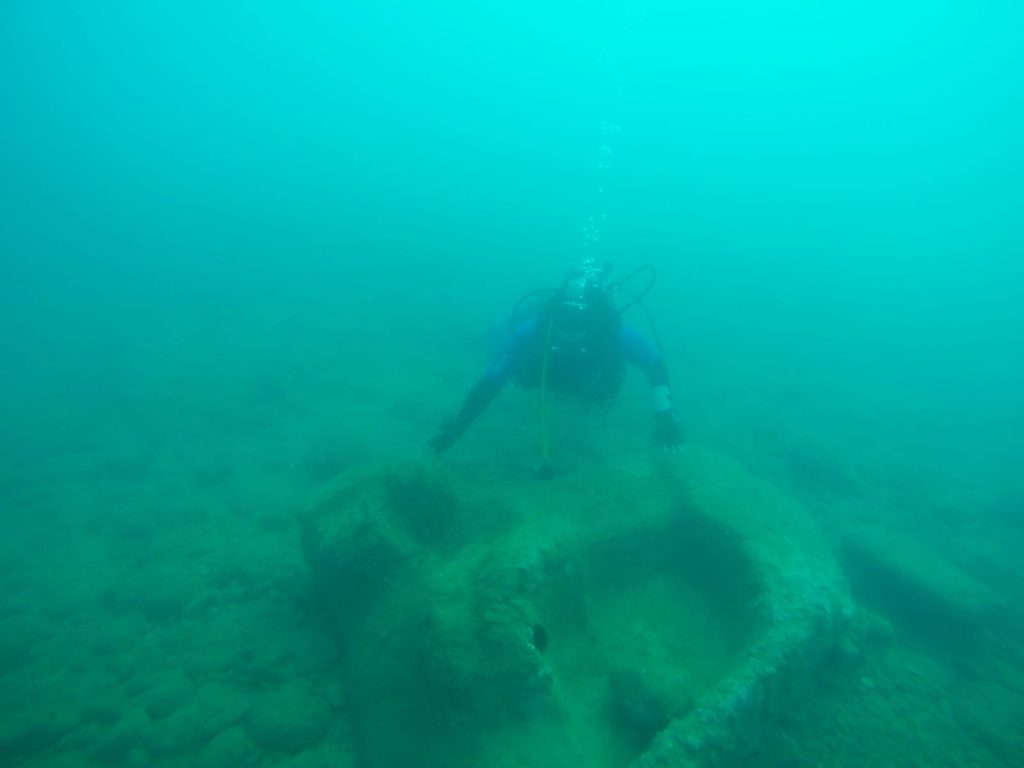

Under the direction of engineer Gaetano Lino, the BC Sicily Subgroup discovered the element’s potential in October through photogrammetric studies. They successfully rescued the fragment today after informing the authorities and overcoming meteorological challenges.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Its study will provide new insights into this grand construction from the 5th century BC.
The Temple of Zeus was erected by the tyrant Theron, ruler of the Greek colony of Acragas (now known as Agrigento) and a large part of Western Sicily. He built the temple after his victory in the Battle of Himera in 480 B.C., for its proportions, were one of largest of antiquity.
It is an essentially Doric building but it was pseudoperipteral i.e. there were no free-standing columns but demi-columns, seven by fourteen, engaged into a continuous wall. In the intercolumni (spaces between the columns) stood giant statues (7.61 meters high) called Telamons or Atlantes.
Cover Photo: 3D image of the in situ find from October 2022 processed by BCsicilia.