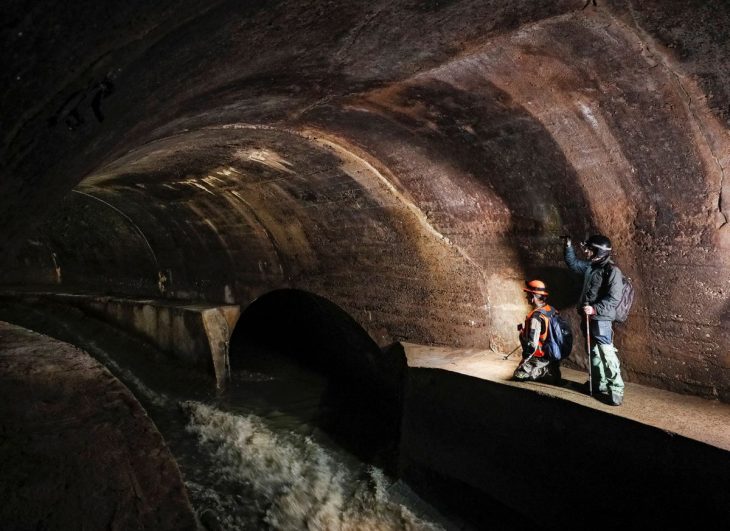
Scientists working in the Ségognole 3 cave, located in the famous sandstone massif south of Paris have identified a unique engraving that could be the oldest three-dimensional (3D) map in the world.
A recent study published in the Oxford Journal of Archaeology, reveals how hunter-gatherers over 20,000 years ago shaped and adapted the cave environment to represent water flow and potentially the surrounding landscape. Archaeologists found engravings of horses and the female human form in the cave along with the map, indicating that the site may have symbolic meaning.
The research team led by Médard Thiry and Anthony Milnes hypothesize that the set of engravings in the cave is an artificial representation of the surrounding landscape, a kind of “scale model” of the region with hydrological and geomorphological variations.
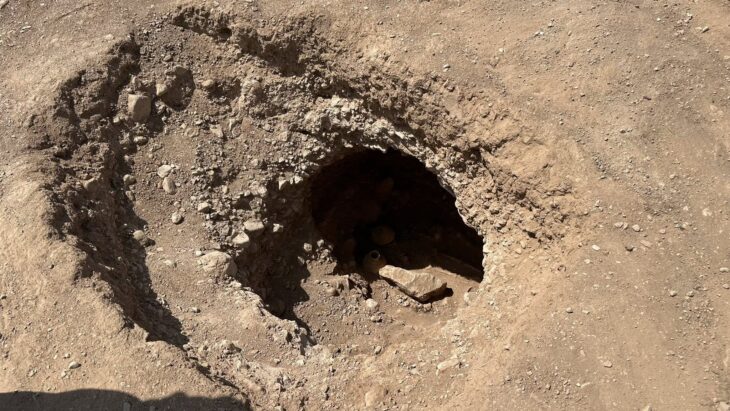
The scale model of Noisy-sur-École’s landscape is situated on the floor behind the Ségognole 3 cave. The level of detail and accuracy is astounding. The cave’s former occupants, hunter-gatherers, created an amazing miniature depiction of the area’s hydrological and geomorphological features.
Researchers explained that the floor’s surface was masterfully engraved to manipulate water flow through accurate channels, depressions, and basins. The specific indents of indents and inclinations in the stone represent the various hills in the area and how they correlate to the surrounding rivers, lakes, and deltas.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The carved motifs and their relationship with natural features in the sandstone of the shelter can be compared with major geomorphological features in the surrounding landscape,” the researchers said.
The authors claim that the engravings on the shelter may be the earliest known three-dimensional map of a region, which differs from other representations of the era that were portable and two-dimensional.
These most recent discoveries mark the end of an investigation into the engravings in the cave that began in 2020. When Thiry and Milnes discovered that all of the water that passed through the cave’s grooves ended up in a vulva-like depression, while other depressions and fractures in the cave manipulated water to flow along other paths, they realized that the patterns in the cave had a specific meaning. They clarified that rainwater entered through tiny surface fissures that were designed to catch precipitation directly from the wind’s push.
The carvings and natural cracks thus represent both the surrounding landscape and the female body.
“The natural geomorphological characteristics of the Ségognole 3 shelter thus provided appropriate disposition to imprint this fragmented representation of femininity, a theme that shows clear importance during the Upper Palaeolithic,” the researchers said in a paper about the cave.
In addition to their skill at hunting and gathering, Paleolithic hunter-gatherers also demonstrated a deep awareness of their surroundings and the capacity to abstract and use them in practical ways, as evidenced by the discovery at Ségognole 3.
https://doi.org/10.1111/ojoa.12316
Cover Image Credit: SYGREF, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons