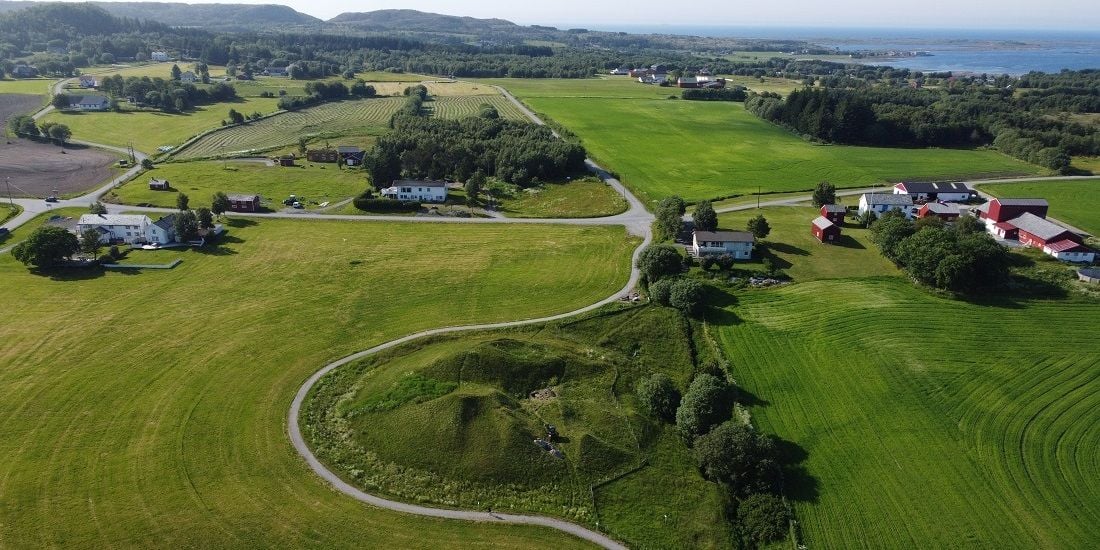
In Leka, a municipality in Norway’s Trøndelag county, archaeologists have uncovered Scandinavia’s oldest identified ship burial, dating back to around 700 AD.
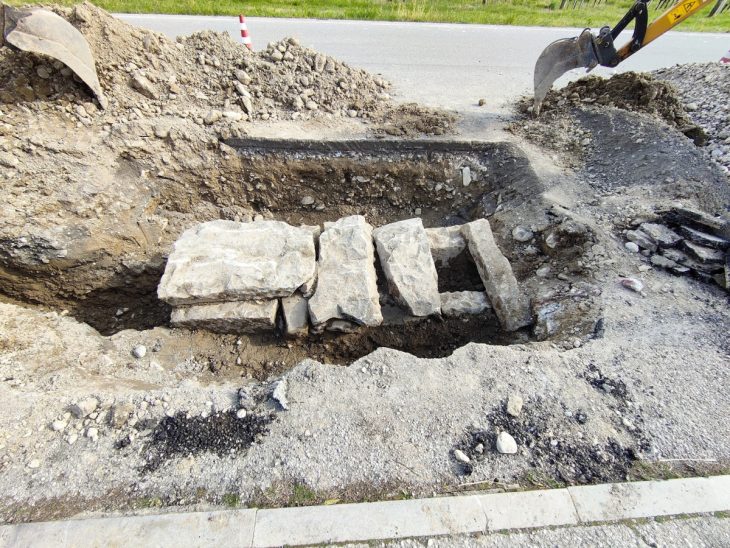
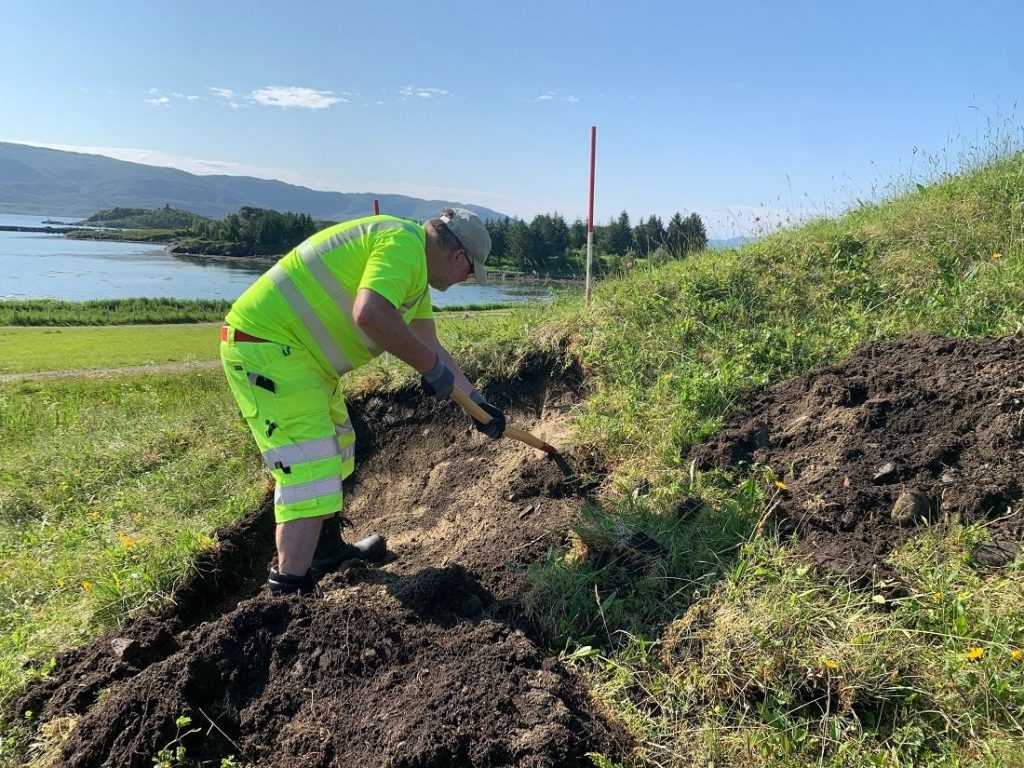
This summer, archaeologists carried out a small survey of the 60-meter mound Herlaugshaugen, a site mentioned in Snorre’s royal sagas as the final resting place of King Herlaug.
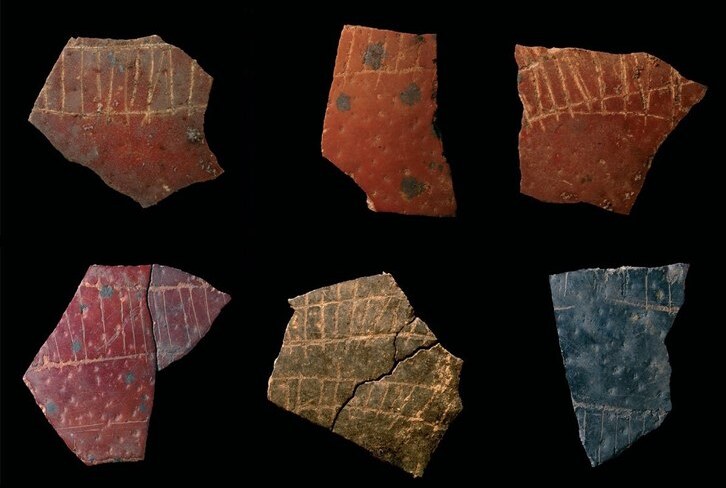
Herlaugshaugen is one of the country’s largest burial mounds. In the late 1700s, it was excavated three times. According to reports, findings included a type of wall, iron nails, a bronze kettle, animal bones, and a seated skeleton with a sword.
“Unfortunately, these findings disappeared already in the early 1920s. The skeleton was once displayed at Trondheim Cathedral School as King Herlaug, but no one knows where it ended up,” explained Geir Grønnesby, project leader from NTNU Science Museum.
The aim was to date the pile and find out if it contained a ship. They carried out the surveys on behalf of the National Archives, and in collaboration with Trøndelag County Municipality.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
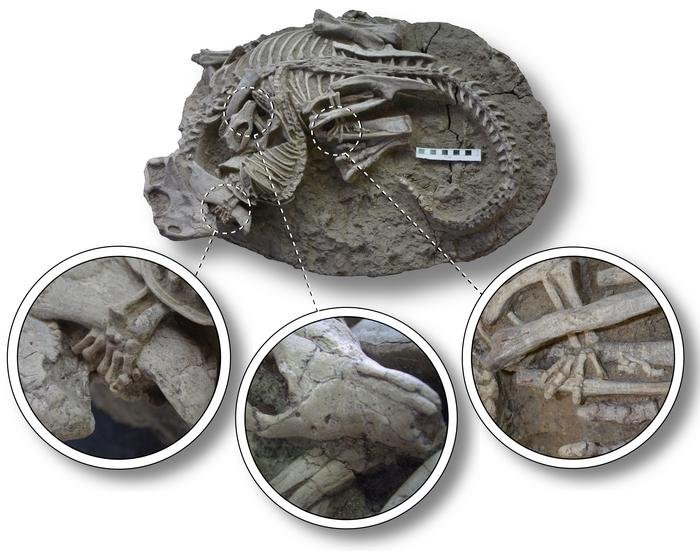
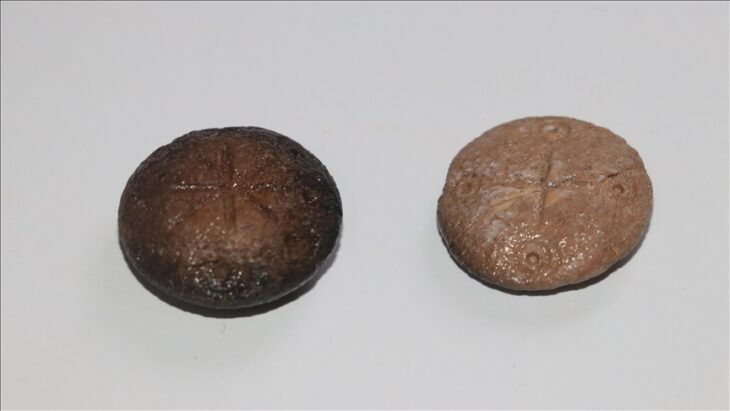
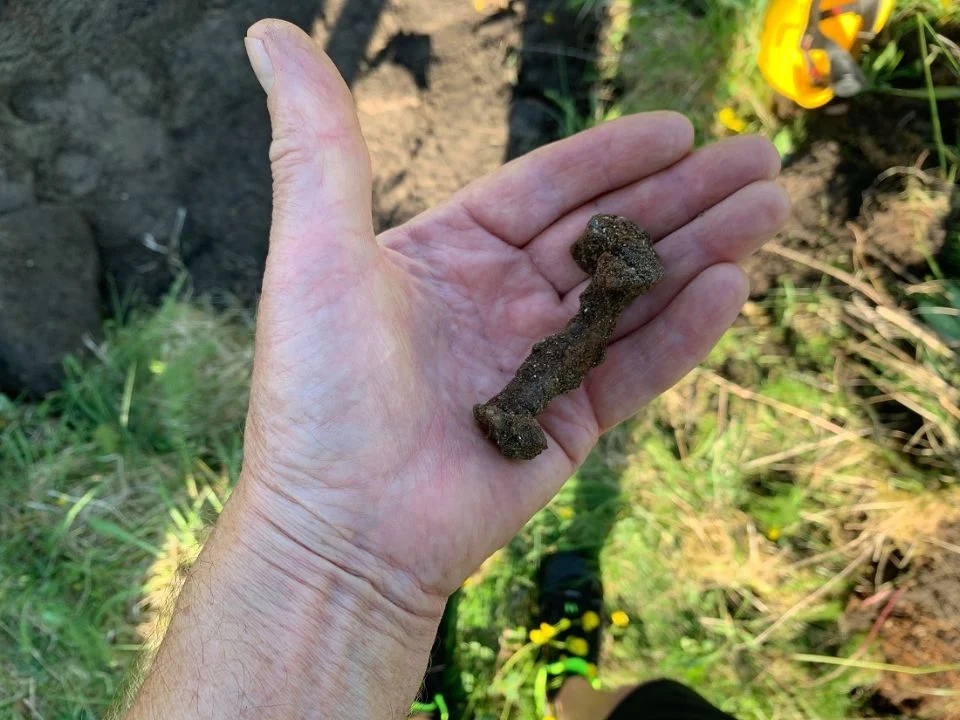
The team became extremely excited when they discovered big nails, which are a clear sign of a ship burial. The findings pushed back the origins of ship burial customs, placing the mound’s creation in the Merovingian period, roughly 700 CE.

According to Geir Grønnesby, archaeologist and project manager of research at the NTNU Science Museum, the discovery reveals the region’s advanced maritime capabilities much earlier than previously thought.
This discovery sheds light on the pre-Viking period, when ship development was critical. The ship’s size and sophistication imply a society with extensive maritime knowledge and resources. Furthermore, the Herlaugshaugen mound, one of Norway’s largest burial mounds, is regarded as a symbol of power and wealth, indicating that the region’s prosperity was likely derived from trade and maritime activities rather than agriculture alone.
The development of the ship has been central to the discussion about when and why the Viking Age began. We cannot say that the Viking Age started earlier based on this dating, but Grønnesby says that you do not build such a large ship without having a reason for it.
Grønnesby added, “The ship grave suggests that contact with the wider world was greater and earlier than previously thought: “Because when one builds somewhat large ships, it is usually because one is going to travel a distance with them.”

Connections to the Elite in Sweden & England
The Herlaug mound is dated to the Merovingian period (approx. 550 to 800 AD), which is just before the Viking Age. This is an era that is generally quite poor in terms of archaeological finds, but early in the period, the first boat burials appeared. Among these are the spectacular boat graves from Vendel and Valsgärde in Sweden, where people were buried lying on down pillows with flashy weapons and helmets.
There has been speculation about a connection between these sites and Namdalen, Norway, which has similar large mounds. Namdalen is home to roughly 10% of Norway’s large burial mounds. This link continues to Sutton Hoo in England, another important Merovingian site. Researchers are eager to delve deeper into these possible historical ties.
Cover Photo: Hanne Bryn, NTNU Science Museum