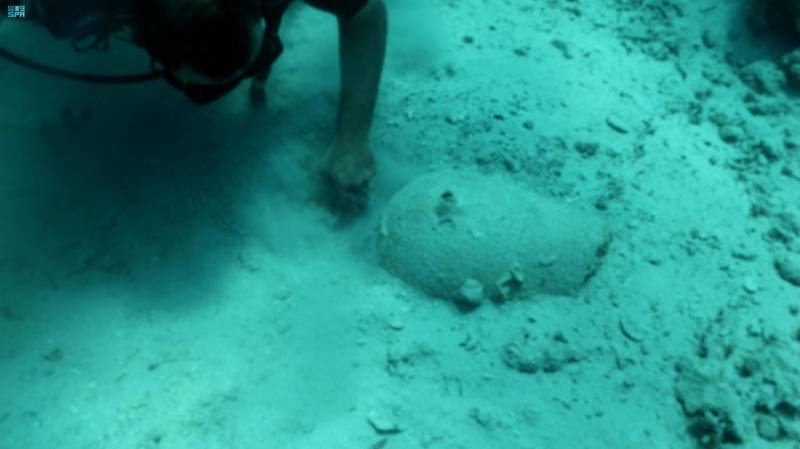
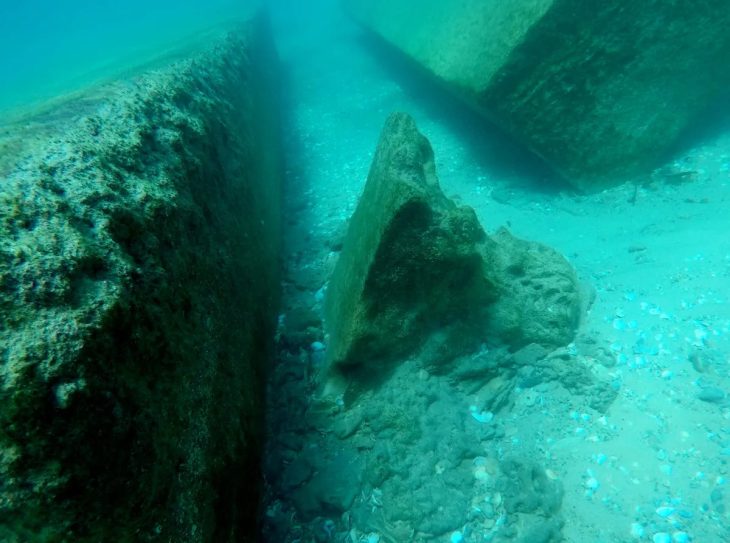
Divers from Saudi Arabia’s Heritage Authority have discovered a shipwreck in the Red Sea from the 18th century filled with hundreds of artifacts, just off the coast of Hall, in the Kingdom’s northwest.
Archaeologists believe indicate that the ship may have had a collision with coral reefs that led to the scattering of its parts and its contents being spread around.
According to a statement issued by the Saudi Heritage Commission, an archaeological mission led by five Saudi divers located the wreck of the sunken ship, and “the survey was documented by a set of three-dimensional photographs and the identification of the area containing these sunken antiquities.”

The pottery pieces, SPA reported, are from amphora manufactured in the Mediterranean basin. According to a statement by the commission, the evidence revealed that the ship’s voyage dated back to the late 18th century.
The commission is conducting surveys and excavations for submerged artifacts in the Red Sea in collaboration with foreign universities and research organizations. More than 50 sunken shipwreck sites were discovered around the Red Sea as a consequence of the survey effort, ranging in historical and archaeological importance and date.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
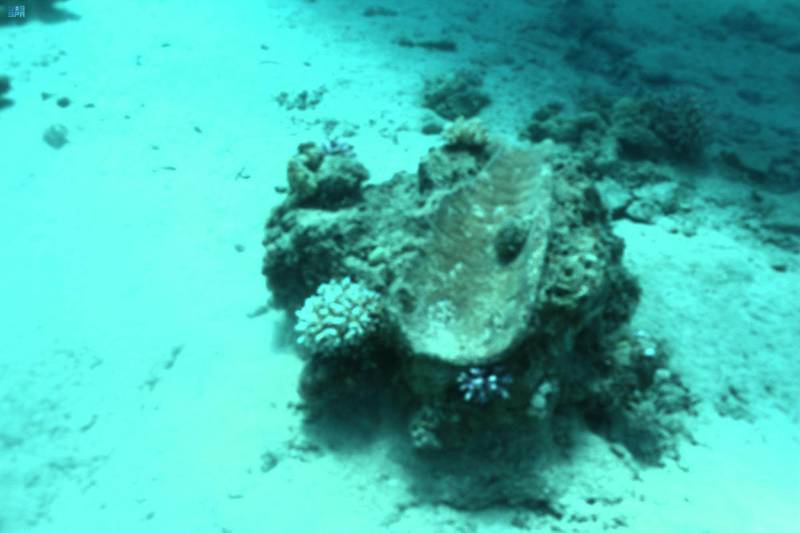

Archaeologists from the University of Napoli found the largest and most complete wooden shipwreck in the Red Sea. It contained jars, porcelain, and spices, having sunk between 1725 and 1750 in Al Wajh lagoon. The team are still curating and cataloging the finds, which will be split between the Red Sea Museum in Jeddah and the Red Sea Project.
The ruins of a Roman shipwreck in the Red Sea were discovered by a combined Saudi-German team surveying underwater historical sites on the west coast from 2012 to 2017. It is the oldest archaeological shipwreck discovered along the Saudi coast thus far. In a place between Rabigh and Shuaiba, the crew also unearthed another wreckage from the early Islamic era.