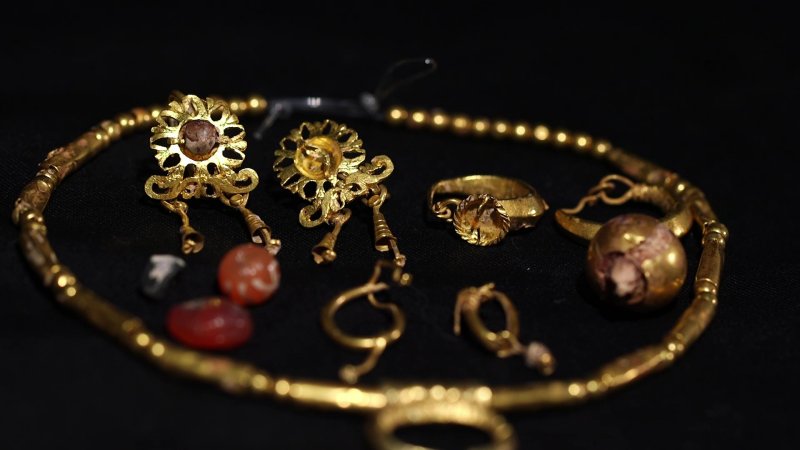
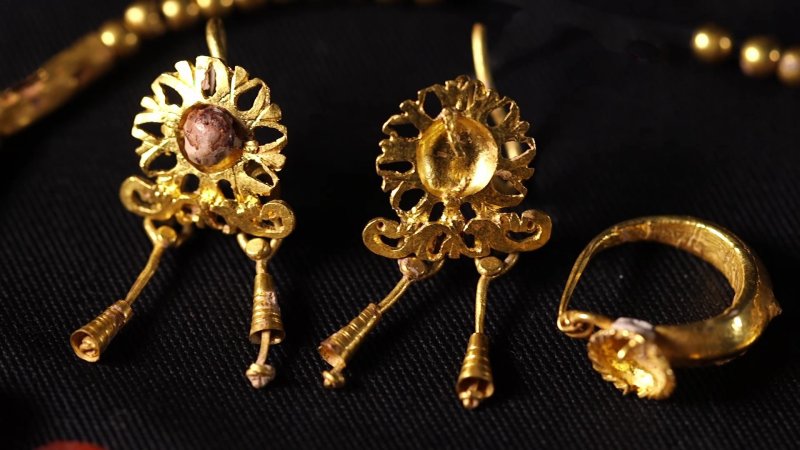
“After the destruction of the Jerusalem Temple and the exodus of the Jewish population, late Roman Jerusalem—renamed Aelia Capitolina—had a mixed population. During this period, some young girls were buried adorned with fine gold jewelry.
The jewelrys was discovered in a lead coffin on Mount Scopus during excavations led by late archaeologist Yael Adler of the Israel Department of Antiquities. The find included gold earrings, a hairpin, a gold pendant, gold beads, carnelian beads, and a glass bead, according to the IAA.
The jewels were discovered in 1971, in an excavation carried out by Yael Adler (deceased) of the Israel Department of Antiquities but the finds were not published.
The jewels were recently located as part of the Israel Antiquities Authority’s “Publication of Past Excavations Project,” which aims to publish previously incomplete excavation reports.
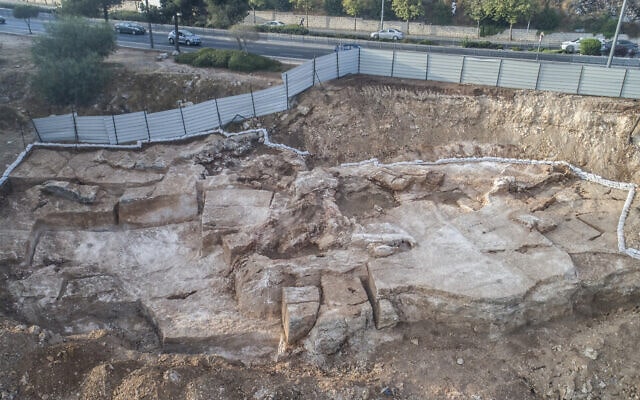
Impressive gold jewelry discovered in previous excavations in Jerusalem burial caves will be on display for the first time to the public at the 48th Archaeological Congress, organized by the Israel Antiquities Authority, the Israel Exploration Society, and the Israel Archaeological Association.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The congress will take place at the Jay and Jeanie Schottenstein National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel, now inaugurated in Jerusalem.
“The location of the original reports that gathered dust over the years in the Israel Antiquities Authority archives, and physically tracing the whereabouts of the items themselves, has shed light on long-forgotten treasures,” says Dr. Ayelet Dayan, Head of the Archaeological Research Department, who heads this project. “The beautiful jewelry that we researched is an example of such treasures.”
Researchers from the Israel Antiquities Authority, Dr. Ayelet Dayan, Dr. Ayelet Gruber, and Dr. Yuval Baruch, believe that the priceless objects bearing the symbols of Luna, the Roman moon goddess, accompanied the girls during their lifetimes and were buried with them after they passed away to continue to protect them in the afterlife.
Their investigation revealed that Prof. Vassilios Tzaferis had found two pairs of identical gold earrings in a previous excavation on the Mount of Olives for the Department of Antiquities in 1975.
The finds, according to researchers, are from a time after Jerusalem had almost entirely been destroyed following the siege of 70 CE. The pagan Roman deities Jupiter and others received special honors in Hadrian’s new city. At that time, Jews were forbidden from entering Jerusalem under penalty of death because the city was occupied by Roman legionaries.

“It seems that the girl was buried with an expensive set of gold jewelry that included earrings, a chain with a lunula pendant (named after the goddess Luna), and a hairpin,” say the researchers.
“These items of jewelry are known in the Roman world, and are characteristic of young girl burials, possibly providing evidence of the people who were buried at these sites,” the researchers said. “Late Roman Jerusalem—renamed Aelia Capitolina—had a mixed population that reached the city after the destruction of the Jerusalem Temple and the evacuation of the Jewish population. People from different parts of the Roman Empire settled in the city, bringing with them a different set of values, beliefs, and rituals. The pagan cult of the city’s new population was rich and varied, including gods and goddesses, among them the cult of the moon goddess Luna.”
According to researchers, gold jewelry was used as an amulet against the evil eye by young pagan girls nearly 1,800 years ago. The jewelry was buried with the girls to continue protecting them in the afterlife.
“The interring of the jewelry together with the young girl is touching,” said IAA Director Eli Escusido. “One can imagine that their parents or relatives parted from the girl, either adorned with the jewelry or possibly lying by her side and thinking of the protection that the jewelry provided in the world to come. This is a very human situation, and all can identify with the need to protect one’s offspring, whatever the culture or the period.”
Cover Photo: Emil Aladjem, Israel Antiquities Authority