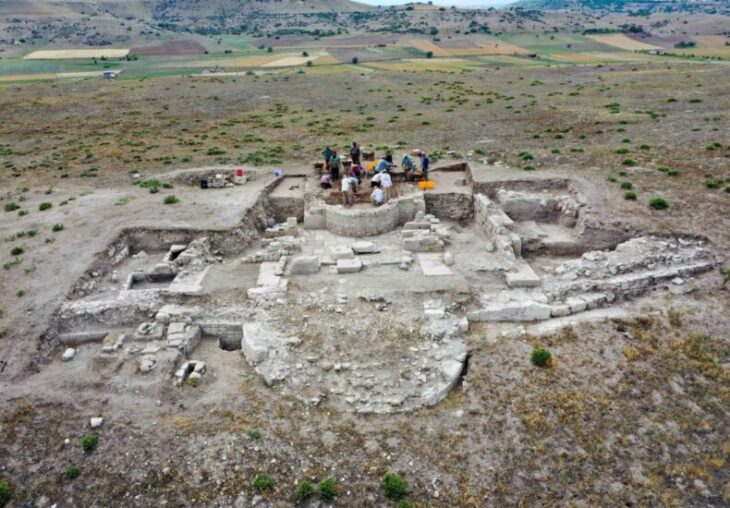
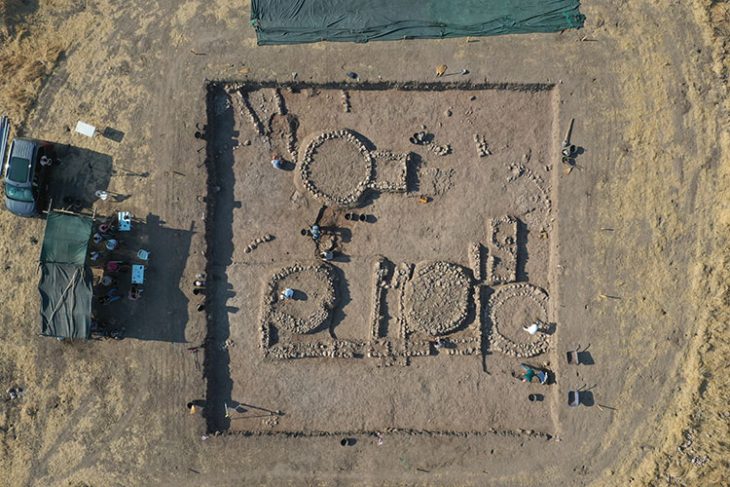Students from Goethe University Frankfurt, in collaboration with the Hesse archeology department at the Darmstadt branch of the State Monument Protection Agency, uncovered 46 graves from various ethnic groups near Nauheim, a town southwest of Frankfurt in the central-western German state of Hessen.
They uncovered 46 graves from the time when Roman legions were stationed on the Rhine during a six-week training excavation. The grave goods indicate the deceased were immigrants with Gallic funerary customs who settled in the area in the middle of the 1st century A.D.
The team expected to find Roman remains because a Roman military camp was known to have been built in the Nauheim area. The graves of early settlers came as a surprise.
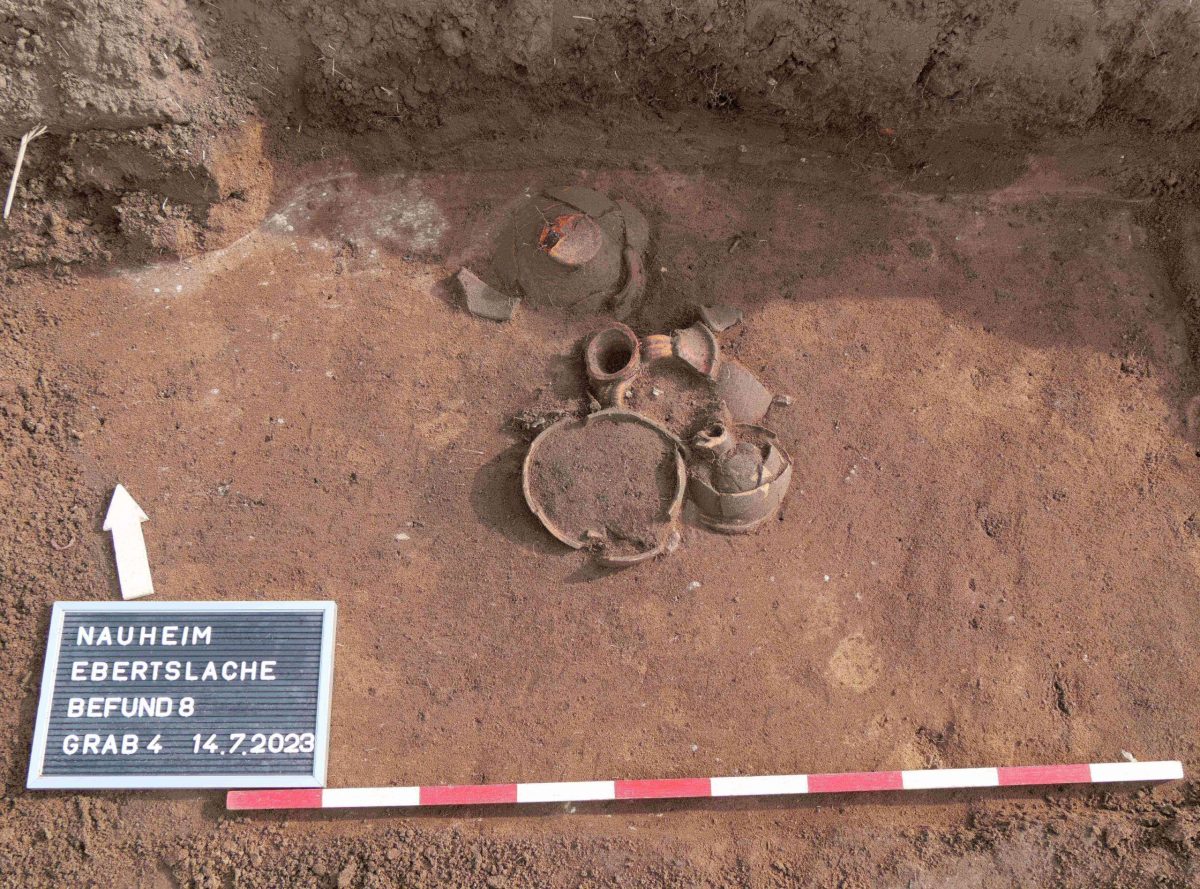
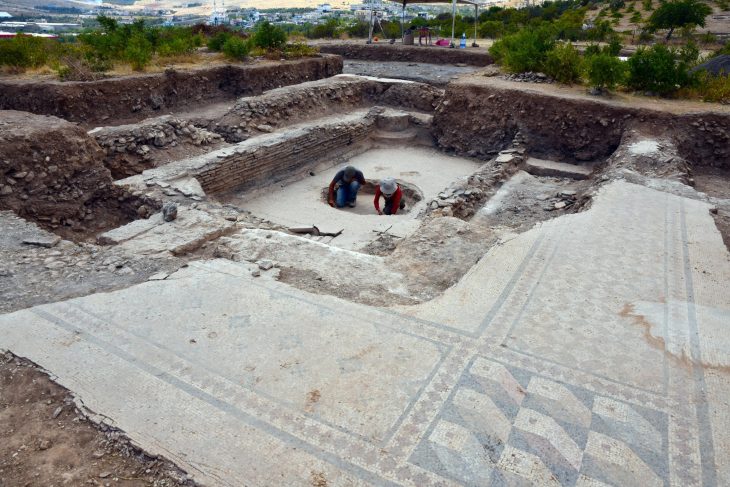
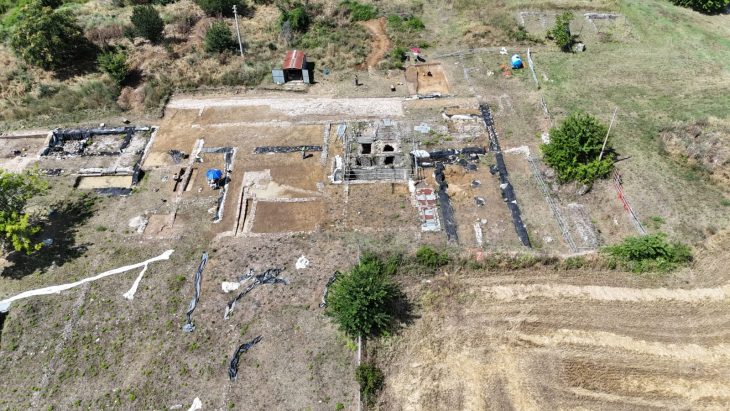
The burial ground, which eight students in two teams brought to light on a good 2,000 square meters, dates from the middle of the 1st century AD to the beginning of the 3rd century. They unearthed a total of 46 graves, 44 of them cremation burials, only two of them inhumations.
Anthropologists will now examine the bone remains from the corpse fire as well as the skeletons and determine the age at death, gender, and diseases.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Nauheim graves show who settled on the borders of the Hessian Ried almost 2,000 years ago: immigrant ethnic groups in small-scale groups. Grave goods indicate Germanic military farmers who were deliberately attracted by the Romans from the north, took over the security service in the province on the border of the Roman Empire, and then settled down.
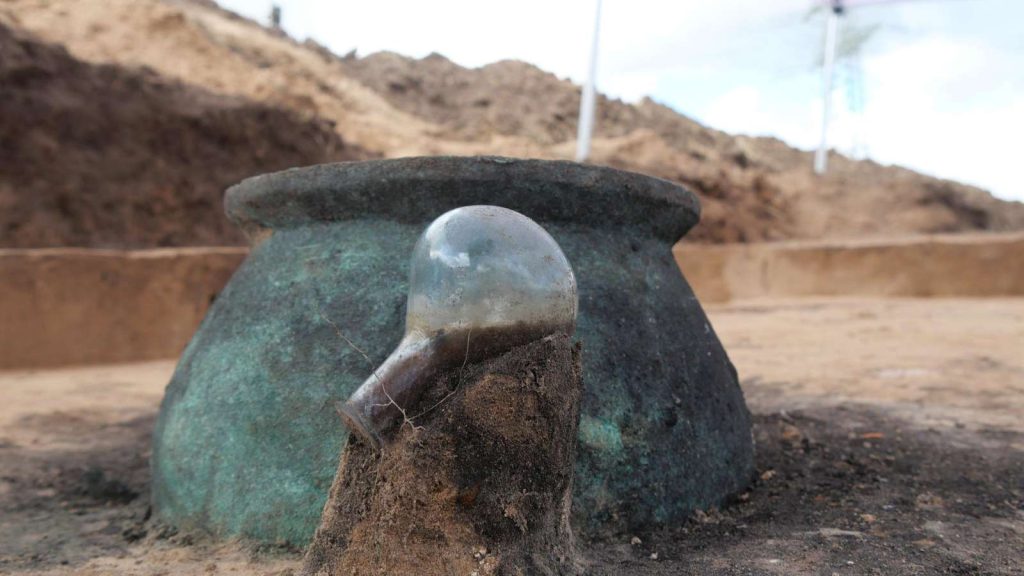

In the burial area, a 30-centimeter high vessel, in particular, indicated that the dead of newly arrived settlers found their final resting place here: a bronze bucket that probably served as a burial urn.
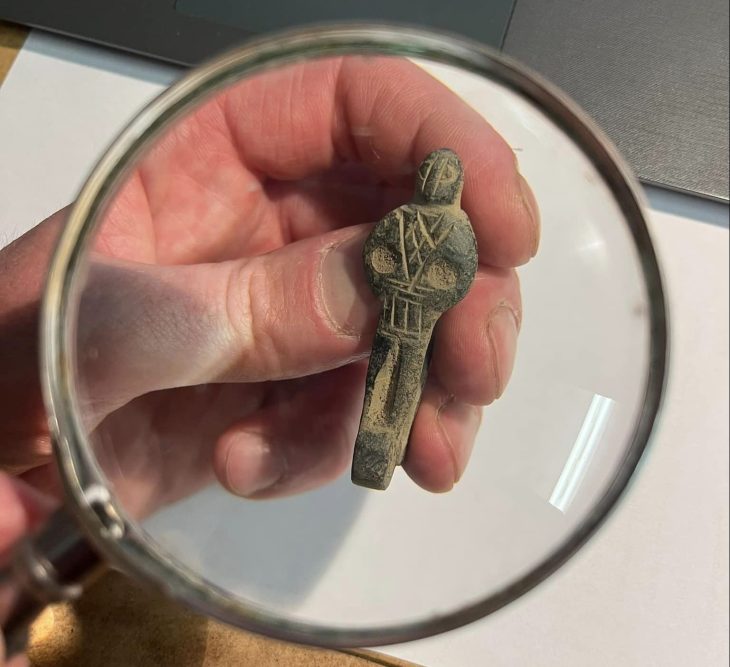
An early Nauheimer “in the bucket”. Burying a person in a bronze bucket and providing tools such as scissors or knives is atypical for Roman burials. This is also the first time that evidence of the grave enclosures mentioned has been found in southern Hesse, while the custom was widespread on the left of the Rhine in the east of Gaul in the late Iron Age (1st century BC) and the 1st century AD. For scientists, such unusual burials are clear signs that immigrants were buried here, bringing not only their culture but also their burial rites with them.
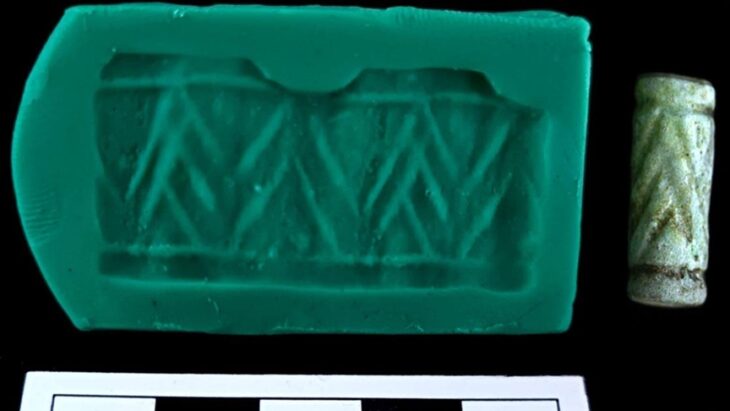
The bucket must have been imported here and probably cost a dinar or two,” said Professor Markus Scholz, head of the Archeology and History of the Roman Provinces course at Goethe University. In general, the grave goods – such as a complete urn made of green glass – were of high quality, which indicates a certain level of wealth of those buried.
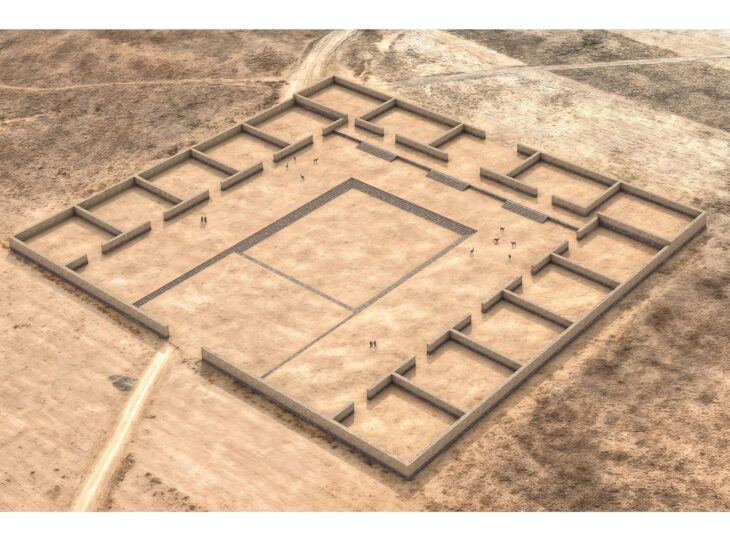
There are also six rectangular ditch systems that can be viewed as the enclosure of special burials and, according to current knowledge, all belong to the burial ground’s founding phase. In some cases, there are additions such as a complete glass urn, which attest to the wealth of those buried.