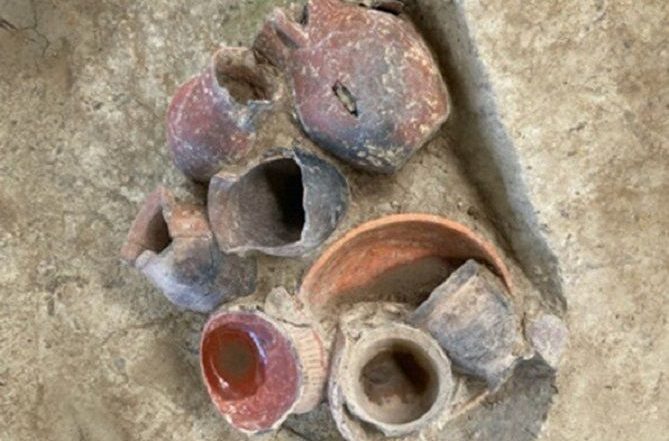
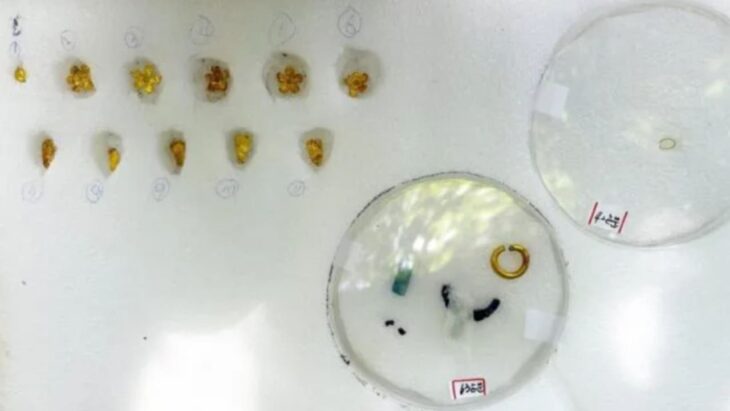
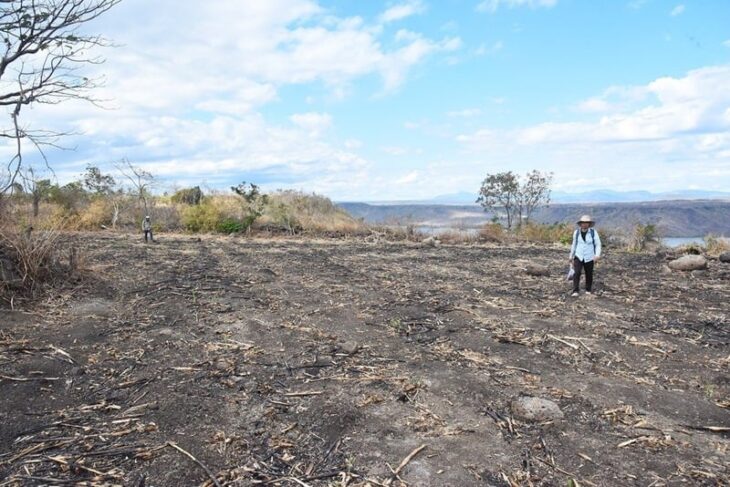
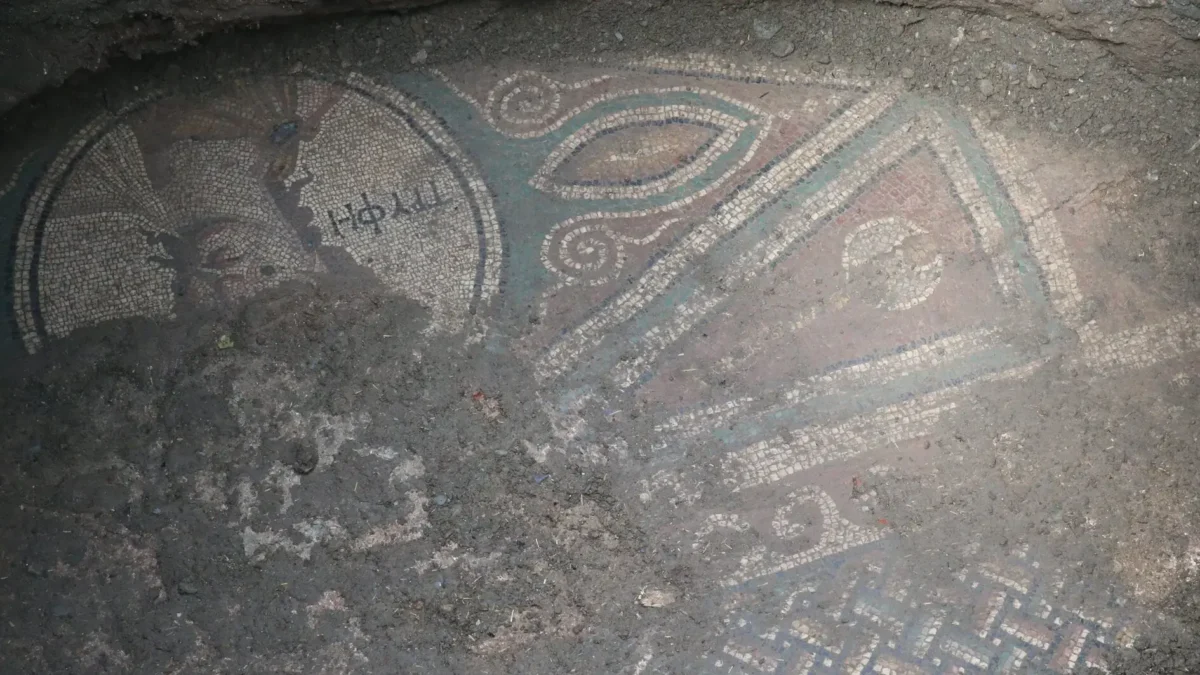A stunning mosaic has been unearthed during an illegal excavation near Zile Castle, located in the Tokat province of Türkiye, which is situated in the central part of Anatolia. Murat Tekin, the head of the Zile Castle Ancient Theater excavations and a lecturer at Tokat Gaziosmanpaşa University’s History Department, emphasizes that this find not only showcases the artistic achievements of the Roman period but also reaffirms Zile’s status as a significant center in antiquity.
The mosaic, located approximately 200 meters from the ancient theater excavation site, is believed to date back to the Roman era. Tekin notes that the word “tyrphe,” which translates to comfort and luxury, is prominently featured in the mosaic, hinting at the opulence that characterized the lifestyle of the time. “This discovery is a testament to the rich cultural tapestry of Zile, which has been an important hub since ancient times,” he stated.
Zile’s historical significance is further amplified by its connection to the Battle of Zela in 47 B.C., where Roman Emperor Julius Caesar famously declared, “Veni, vidi, vici” (I came, I saw, I conquered) after his swift victory over Pharnaces II of Pontus. This pivotal moment not only solidified Roman power in the region but also marked Zile as a key player in the annals of history.
The Tokat region, nestled in the historical heartland of Anatolia, held significant strategic value during the Roman Empire. Its geographical location positioned it as a crucial link along vital trade routes connecting the eastern and western parts of the empire. This connectivity fostered economic growth and cultural exchange, leading to the establishment of important Roman settlements and infrastructure within the region.
While historical sources provide glimpses of Roman administration and military presence, archaeological evidence has been gradually piecing together a more comprehensive picture. The fertile plains and strategic passes of Tokat likely supported agricultural activities and facilitated the movement of goods and armies.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ongoing excavations at the ancient theater, which began in 2022, have revealed layers of history that trace back to the Hittite period when the settlement was known as Anziliya. As the Romans expanded their empire, Zile, then known as Zela, became a vital center for trade and military activities, showcasing impressive architecture and cultural exchanges.
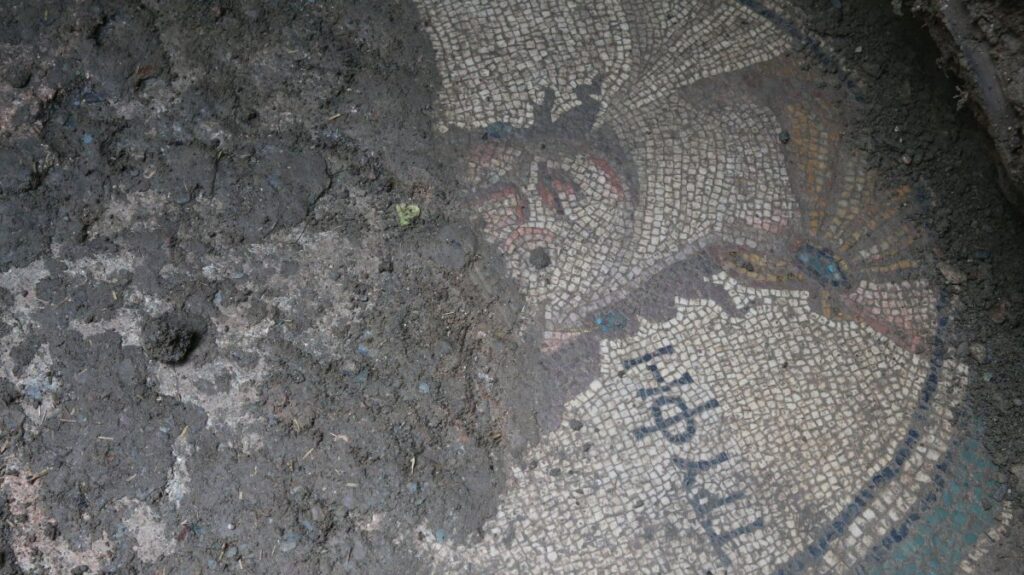

While a detailed analysis of the mosaic is yet to be conducted, initial observations suggest it dates back to the Roman period. Intriguingly, the inscription “tyrphe” found within the mosaic is believed to symbolize comfort and luxury, hinting at the opulence of the structure it once adorned. The presence of such a sophisticated piece suggests a patron with considerable means and a taste for refined aesthetics. Furthermore, the location of the mosaic near the ancient theater hints at a potentially affluent residential area or a public space designed to impress.
Tekin believes that the mosaic discovery could significantly boost tourism in Zile. “If we expand our excavation efforts in the area where the mosaic was found, it will not only enhance our understanding of the past but also attract visitors eager to explore Zile’s rich heritage,” he explained. The city is already home to various historical structures, including the ancient theater, castle, and rock tombs.
The illicit excavation that brought this remarkable mosaic to light serves as a poignant reminder of the threats facing archaeological heritage. However, the discovery itself offers a valuable opportunity to enrich our understanding of Roman influence in the region and Zile’s historical significance.
The ongoing efforts to secure and study the mosaic, coupled with continued archaeological investigations, promise to unveil more of Zile’s fascinating past, potentially transforming it into an even more prominent destination for history enthusiasts.
As the excavation team continues to analyze the mosaic and its context, there is hope that further discoveries will emerge, providing deeper insights into the lives of those who once inhabited this ancient city. The mosaic serves as a reminder of Zile’s enduring legacy and its role in the broader narrative of Roman history.
In conclusion, the recent discovery of the mosaic not only highlights Zile’s artistic and cultural significance but also reinforces the need for the preservation of its archaeological sites. The illicit nature of the excavation that unearthed this significant mosaic underscores the vulnerability of archaeological sites to looting and destruction. As interest in Zile’s history grows, so does the opportunity to celebrate and share its rich heritage with the world.
Cover Image Credit: AA