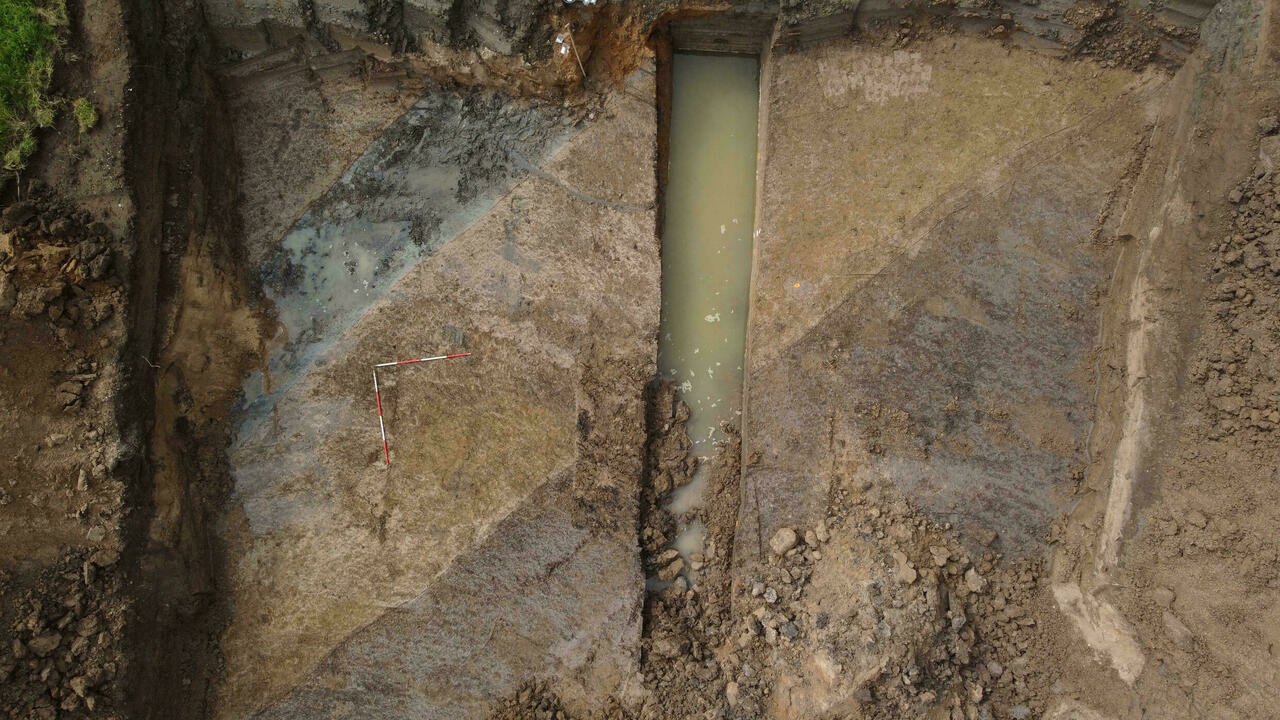
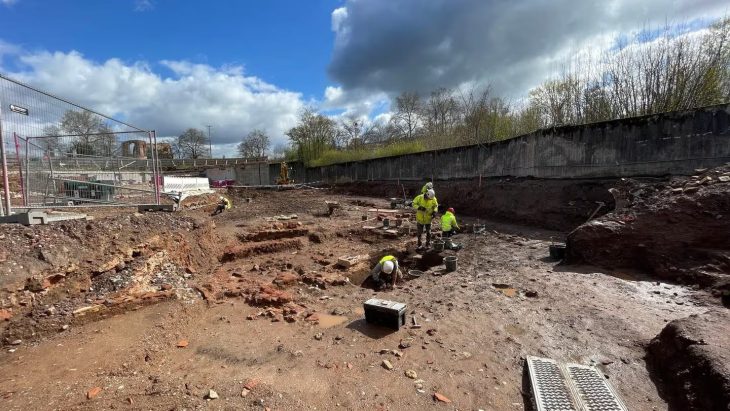
Dutch archaeologists that a canal and gravel road thought to have been built and used by the Roman military have been unearthed near the city of Nijmegen in the eastern Netherlands.
The canal and road, which is more than 10 meters (33 feet) wide, were discovered near ancient military camps that were listed this week on UNESCO’s list of World Heritage sites.
According to RAAP, the country’s largest archaeological and cultural history consulting agency, they are believed to have been built and used by the Roman army.
Archaeologist Eric Noord of RAAP told AFP the 33-foot-wide canal probably linked nearby Roman settlements and military bases to the Rhine River in order to transport troops, supplies, and building materials along the border of the Roman Empire.
Nijmegen is located on the Rhine, which was the Roman Empire’s boundary at the time, and the finding was “unique” for that part of the nation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Eric Noord, who is in charge of the project, told AFP that this Roman highway with the original gravel pavement provided a new perspective on the road network about 2000 years ago.
Nijmegen was, like many other ancient cities, a fact a set of settlements, some of which existed at the same time. The name Nijmegen is derived from Noviomagus, the name of a Roman city in the second and third centuries.
Nijmegen is located on the banks of the Waal, a tributary of the Rhine in the ‘Great Rivers’ area, and is only 10 kilometers from the German border. The city, which is of Roman antiquity (whose name originates from ‘Noviomagus,’ which means ‘new market,’ celebrated its 2000th anniversary in 2005. Nijmegen the oldest city in the Netherlands
The Great Rivers were the Roman Empire’s northern boundary, and no doubt the Romans moved here because of the magnificent strategic view of enemy land across the river. Subsequent monarchs and rulers selected Nijmegen as their place of residence for similar strategic reasons.
Photo: A Roman-era canal was discovered in Oosterhout, in the eastern Netherlands, along with a road, both from around 2,000 years ago ERIC NORDE RAAP/AFP