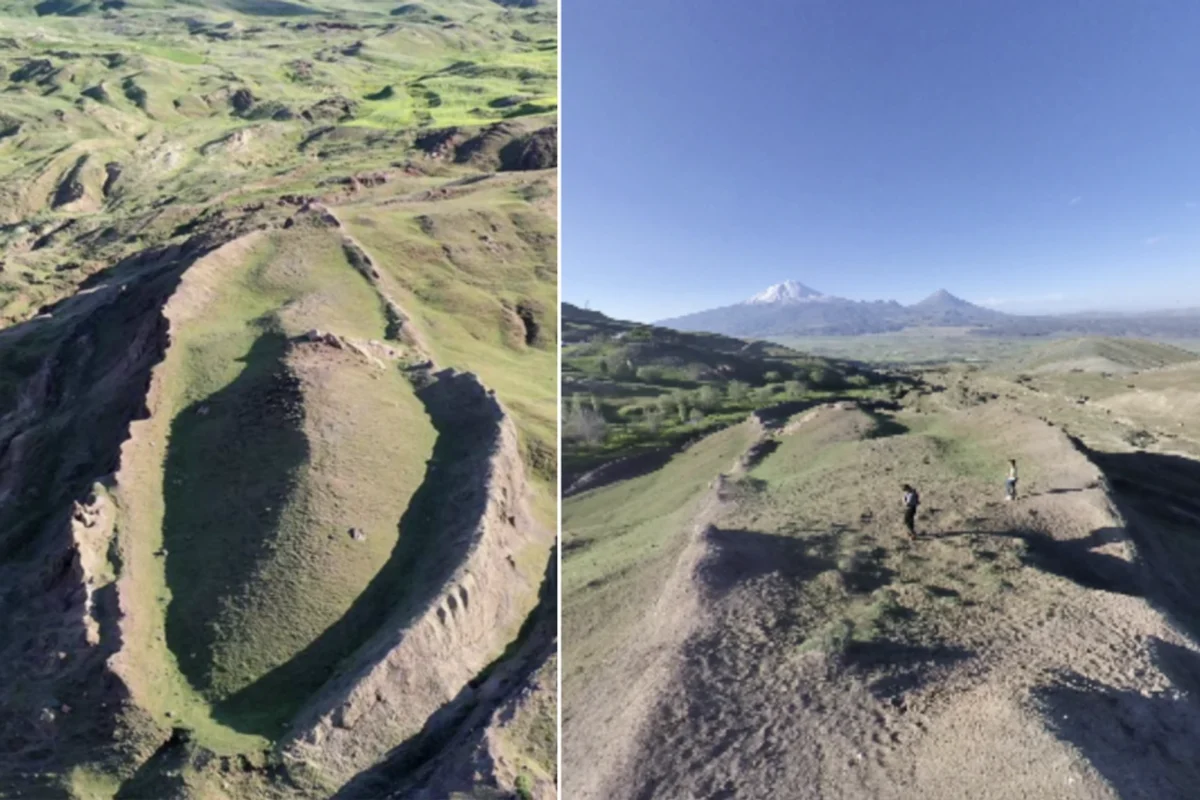
A recent discovery in Türkiye has ignited interest among experts who believe they may have found the fossilized remains of Noah’s Ark. Researchers have identified a boat-shaped mound in the Durupinar Formation, located approximately 30 kilometers south of Mount Ararat (Ağrı Dağı), which has long been linked to the biblical narrative of Noah’s Ark. This mound, believed to have been submerged during a catastrophic flood around 5,000 years ago, has attracted the attention of an international team of researchers since 2021.
The Mount Ararat and Noah’s Ark Research Team, comprising experts from Istanbul Technical University, Agri Ibrahim Cecen University, and Andrews University in the United States, has focused its efforts on studying the Durupinar formation, a geological structure measuring 164 meters in length. The dimensions of this formation closely resemble the biblical description of Noah’s Ark, which states that the Ark was “300 cubits long, 50 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high.”
In a significant phase of their research, the team collected nearly 30 samples of rock and soil from the site. Analysis conducted at Istanbul Technical University revealed traces of clay-like materials, marine deposits, and remnants of sea life, including mollusks. These materials have been dated to between 3,500 and 5,000 years old, aligning with the Chalcolithic period, which corresponds to the time of the biblical flood as described in Genesis 6:14-16.
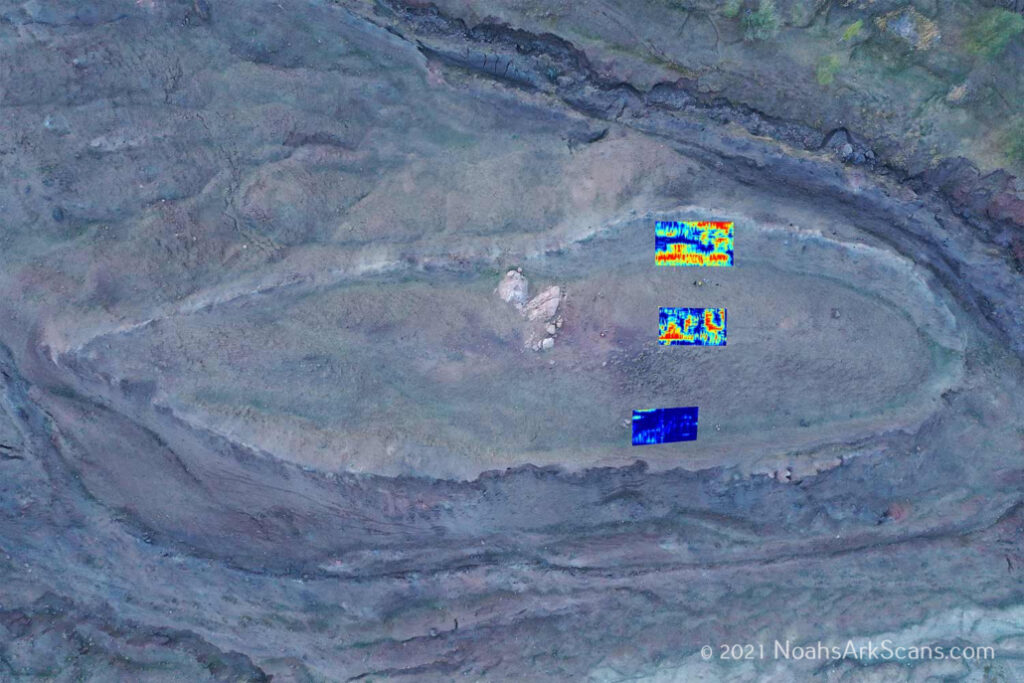

Professor Dr. Faruk Kaya, Vice Rector of Agri Ibrahim Cecen University and a lead researcher, stated, “According to the initial results, it’s believed there were human activities in this region since the Chalcolithic period.” He emphasized the importance of conducting further research in the surrounding areas, known as the Mesopotamian region.
The Durupinar formation has captivated researchers due to its ship-like shape and dimensions that echo the biblical account. Despite skepticism from many geologists who argue that the formation is a natural landmark, the researchers remain committed to uncovering more evidence to support their claims. The team first presented their findings at the 7th International Symposium on Mount Ararat and Noah’s Ark, held in eastern Türkiye in late 2023.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
While the identification of the Durupinar formation as Noah’s Ark remains controversial, the researchers believe their findings provide a legitimate basis for further exploration. They view the biblical account not merely as myth but as a narrative with potential historical significance. As they continue their work, the team hopes to shed light on one of history’s most enduring mysteries.
Cover Image Credit: Noah’s Ark Scans