Researchers say Neanderthals changed the ecosystem by turning forests into grasslands 125,000 years ago.
Around 125,000 years ago, these close human relatives transformed a largely forested area bordering two central European lakes into a relatively open landscape, says archaeologist Wil Roebroeks of Leiden University in the Netherlands, and his colleagues.
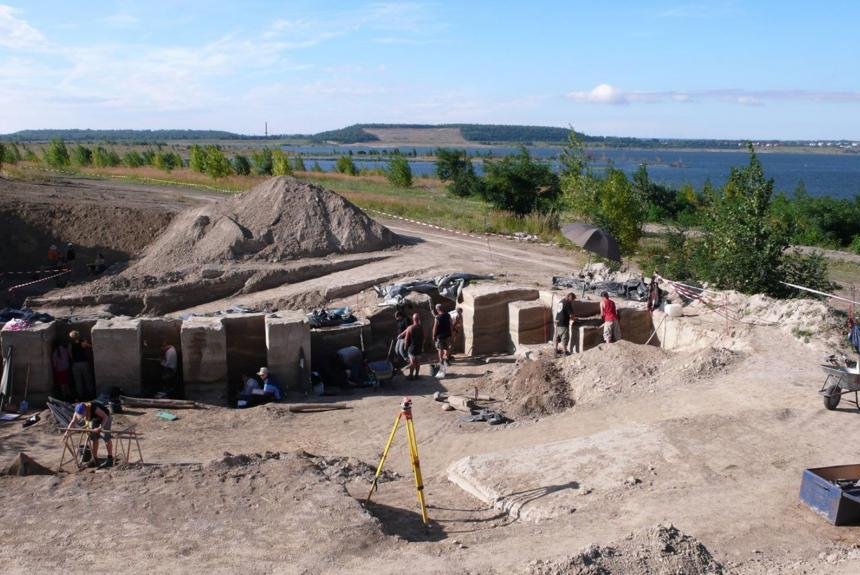
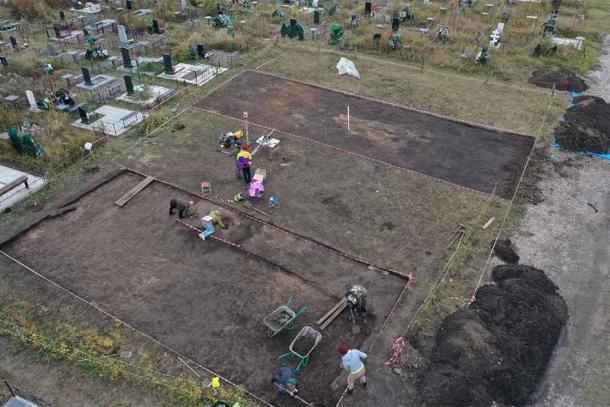
They discovered a clear imprint of Neanderthal activity in the area around the Neumark-Nord site, a dig location in the Geisel Valley in Saxony-Anhalt that dates back about 125,000 years, according to a study published Wednesday in Science Advances.
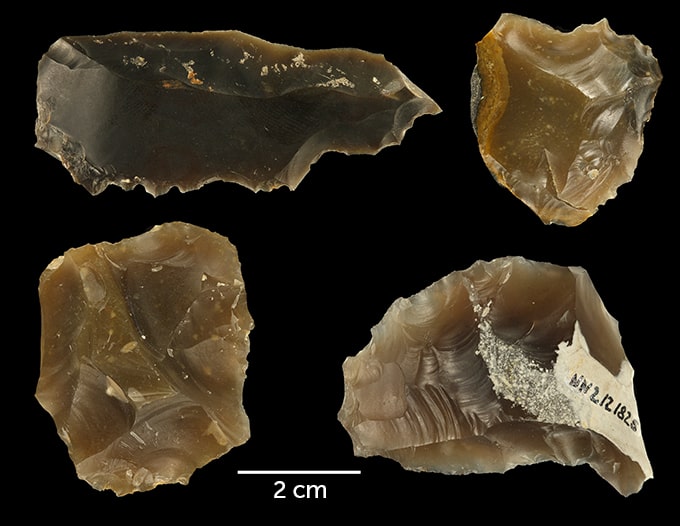
According to their results, activities including hunting, animal processing, toolmaking, and fire use may explain why the region’s woods were removed during this era compared to vegetation surrounding other neighboring lakes.
‘The question is, of course, whether it became open because of the arrival of hominins, or whether hominins came because it was open? However, we have found sufficient evidence to conclude that hunter-gatherers kept the area open for at least 2,000 years.’ Comparative research conducted by Leiden palaeobotanist Professor Corrie Bakels has shown that at similar lakes in the area, where the same animals roamed, but where there are no traces of Neanderthals, the dense forest vegetation remained largely intact.

The researchers compared the data with two other nearby locations that are also located in the eastern region of the Harz Mountains in Germany, they said.
While pollen composition and levels at these other locations imply a closed, wooded environment, pollen measurements from Neumark-Nord show more open vegetation, a pattern that contradicts the rest of the region, according to the researchers.
The findings, when combined with charcoal data and earlier evidence of the existence of Neanderthals in the area, implying that early human hunter-gatherers left a lasting impression on the region’s ecology, according to the researchers.
Until recently, it was widely assumed that people began to influence their environment around 10,000 years ago, when they began to cultivate agriculture, for example, by chopping down forests to make fields. Many archaeologists believe it began much earlier, on a lesser scale, and Neumark-Nord is the first evidence of such intervention, according to Roebroeks.
According to Roebroeks, the new study findings are crucial not just for archaeology but also for fields such as ecological restoration. ‘ It also contributes to our understanding of early hunter-gatherer behavior. They weren’t just “primal hippies” roaming the countryside gathering fruit and hunting animals. They helped shape their landscape.
W. Roebroeks et al. Landscape modification by Last Interglacial Neanderthals. Science Advances. Published online December 15, 2021. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abj5567.
Cover Photo: WIL ROEBROEKS/LEIDEN UNIVERSITY