Tiffany Earley-Spadoni, associate professor of history at the University of Central Florida (UCF), and a researchers team have made important discoveries at Kurd Qaburstan, an urban-sized Bronze Age site in northern Mesopotamia, southwest of Erbil in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq.
Researchers have made important discoveries, the objects date to about 1800 BCE, and include clay tablets with ancient cuneiform writing, a game board, and large structural remains, which could provide a wealth of information about this Middle Bronze Age city and shed light on Mesopotamia’s hidden history.
The clay tablets are the first of their kind found in the region and are still being interpreted. Studying the clay tablets may help historians understand the ancient city’s relationship to neighboring cities in the Middle Bronze Age – a period of northern Iraq’s history that is poorly understood.
For example, by studying people’s names, word choice and writing styles, scholars may better understand literacy in the region and the city’s cultural identity, Earley-Spadoni says in her fieldwork summary.
“We hope to find even more historical records that will help us tell the story of [the city] from the perspective of its own people rather than relying only on accounts written by their enemies,” Earley-Spadoni says. “While we know a great deal about the development of writing in southern Iraq, far less is known about literacy in northern Mesopotamian cities, especially near Erbil where Kurd Qaburstan is located.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Today, Mesopotamia encompasses eastern Syria, southeastern Türkiye, and most of Iraq. Its name comes from the Greek for “between rivers” referring to the area between the Tigris River and the Euphrates.It is often regarded as the birthplace of urban civilization. These cities, preserved as towering tells, mounds formed by centuries of accumulated cultural debris, have captivated scholars for generations.

“We know quite a bit about Mesopotamian cities in the south, and that’s considered the traditional heartland of cities,” Earley-Spadoni says. “When people think about where cities first arose, they imagine cities in southern Iraq, like Uruk. We seek to fill in this gap in the scholarship by investigating a large urban site, one of the few that’s ever been investigated in northern Iraq.”
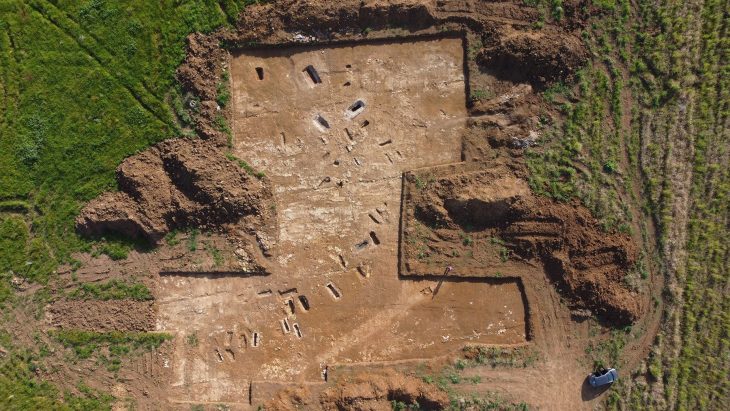
Earley-Spadoni and researchers have been working in two primary areas: the northwest residential neighborhoods and a newly discovered administrative complex identified as a lower town palace, which was theorized to exist based on findings made in 2022.
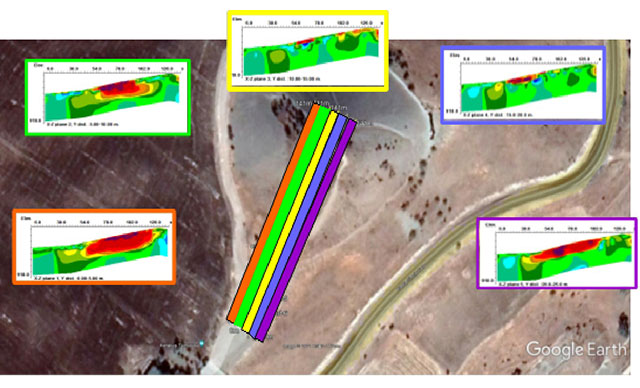
Researchers used technologies such as magnetometry, which allows researchers to peer through the ground to see architectural plans, to help excavate the site.
The research is valuable its own right and helps shed light on regional history and worldwide heritage, she says.
“The focus of the research is the organization of ancient cities, and it’s specifically the organization of Kurd Qaburstan,” Earley-Spadoni says. “You may have heard of King Hammurabi, who erected the famous law code. So, this is about that same time almost 4,000 years ago. We decided that this would be an interesting place to investigate what it was like to be an everyday person at a city during the Middle Bronze Age, which has been an understudied topic. People like to excavate palaces and temples, and very few residential areas have been excavated.”
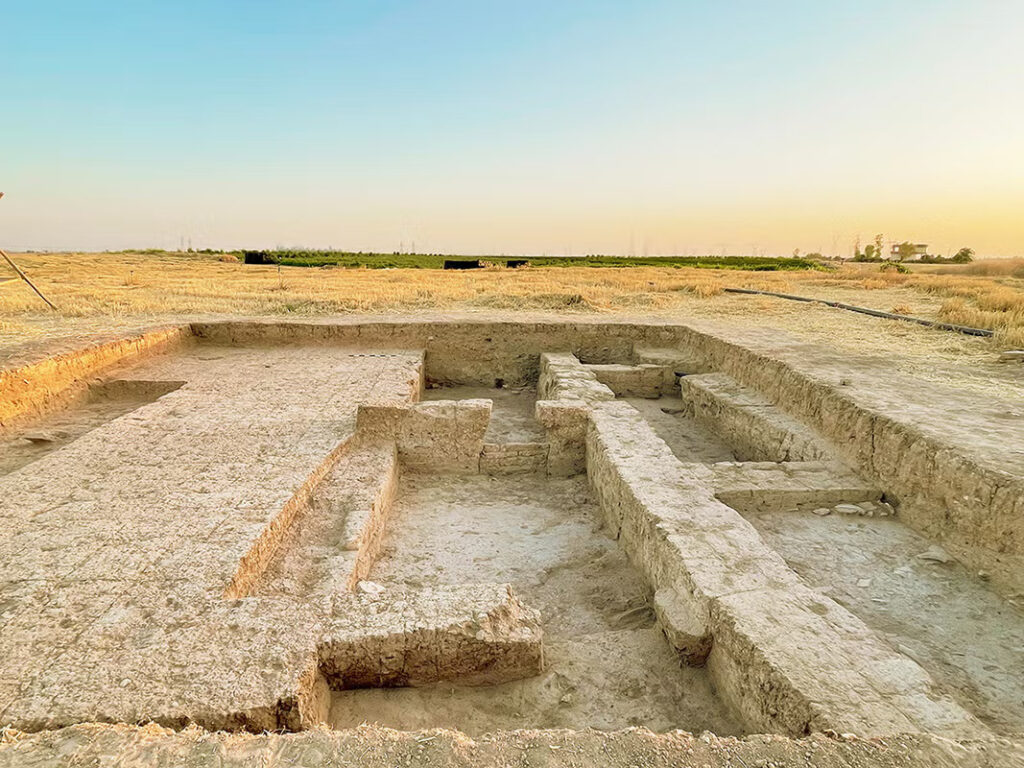

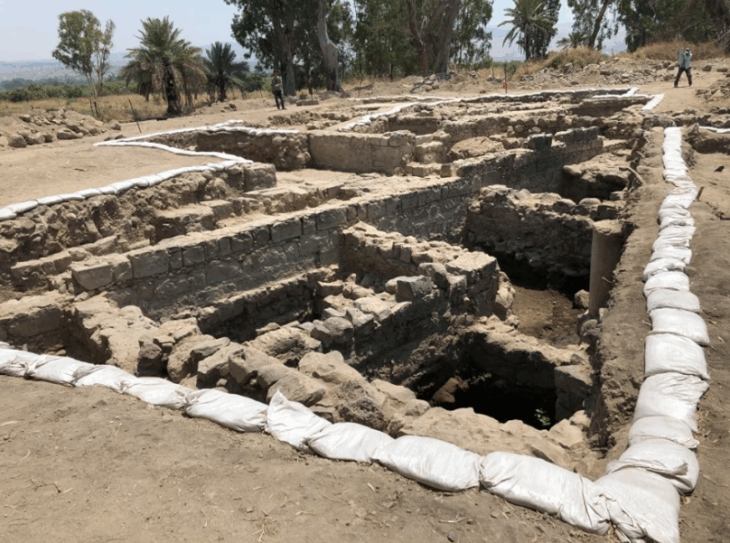
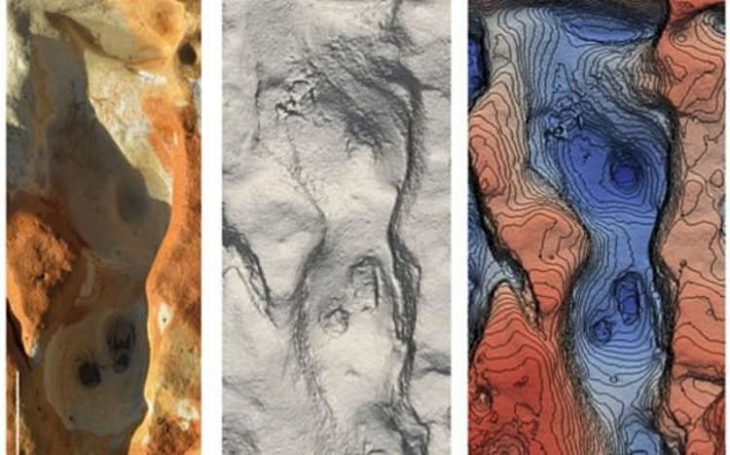
Excavations in the palace revealed monumental architecture, human remains and evidence of destruction, suggesting a significant historical event. The complex, identified through geophysical surveys, is being excavated to establish its characteristics and better understand its function.
Digging in the northwest neighbourhoods revealed exterior courtyards, clay drainpipes, cups, plates, bowls and storage jars. Fine details on the pottery, and animal remains which include both game and domesticated animals suggest that there was a greater degree of wealth among ordinary residents than previously assumed for ancient Mesopotamian cities.
It is possible that the 4,000-year-old city is the hidden city of Qabra, referenced in Old Babylonian monuments.
“Kurd Qaburstan is believed to be ancient Qabra, an important regional center mentioned in the records of other city-states,” Earley-Spadoni says. “The presence of writing, monumental architecture, and other administrative artifacts in the lower town palace further supports this identification since the site must have been an important city of its time.”
The city’s historical importance could be even greater if it is identified as Qabra, a major regional center referenced in Old Babylonian monuments like the famed Stele of Dadusha, according to Earley-Spadoni.
“The first of the three tablets was discovered in a trash-filled deposit along with building rubble and human remains,” she says. “Its context suggests dramatic events, possibly evidence of ancient warfare. We hope our work in 2025 will tell us more about this story.”
The research and excavation efforts are funded through the U.S. National Science Foundation and in partnership with the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The work occurred from May to July 2024, with previous work conducted from 2013 to 2023 by a team from Johns Hopkins University that included Earley-Spadoni.
University of Central Florida (UCF)
Cover Image Credit: A portion of the excavated Mesopotamian site of Kurd Qaburstan. Researchers uncovered many pithoi – or storage jars – that contained historical artifacts that helped to contextualize Mesopotamian history. Credit: Tiffany Earley-Spadoni